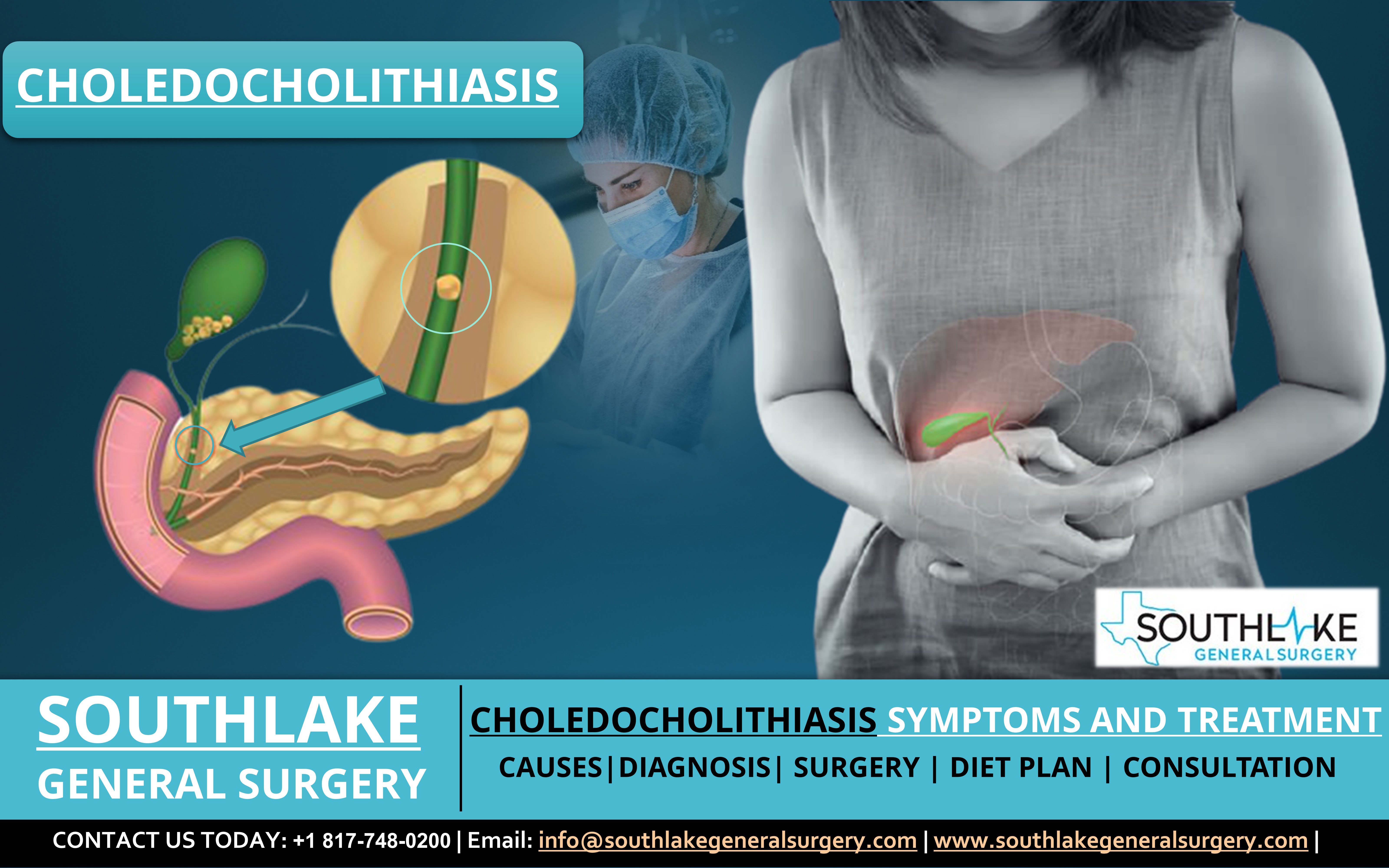
The presence of gallstones in the bile common bile duct (also known as bile duct stones or gallstones in the bile duct) in medical terms is called Choledocholithiasis. The bile duct is the small tube that conveys bile from the gallbladder to the small intestine.
The gallbladder is a small pear-shaped organ underneath the liver in the upper right half of the abdomen. The gallstones mainly stay in the gallbladder or pass through the common bile duct unhampered.
Approximately 15 percent of the people in North America will have gallstones in the bile duct or choledocholithiasis.
Symptoms of Choledocholithiasis or Gallstones in the bile duct
An individual may not experience symptoms of gallstones in the bile for a couple of months or a year. But if the bile duct gets blocked due to stone, an individual may have the following:
- Abdominal pain in the center upper abdomen or right upper abdomen.
- Loss of hunger, fever, queasiness, and heaving
- Jaundice (change in skin and eye colour to yellow)
- Change in stool colour to clay
An individual may experience irregular or intermittent abdominal pain due to gallstones in the bile duct. This can be mild on occasion and later severe pain. If you experience severe pain, immediately contact emergency medical treatment. In the event of severe pain, people may get confused with a cardiac arrest.
If a gallstone gets stuck in the bile duct, it can infect the bile. The bacteria from the infection can further quickly spread and may shift into the liver. This medical condition is a serious for any individual and it can be dangerous for life. There are other complications that may occur like pancreatitis and biliary cirrhosis.
Causes of Choledocholithiasis
A gallstone can be of two types: Cholesterol gallstones and pigment gallstones.
Cholesterol Gallstones
Cholesterol gallstones are the most common sort of gallstones that mainly appear yellow in colour. Researchers consider cholesterol stones occur due to bile that contains:
- excess amount of bilirubin
- less bile salts
- excess amount of cholesterol
This condition usually occurs when the gallbladder doesn’t void properly.
Pigment Gallstones
There is no medical reason available for pigment stones yet. Although it happens to individuals who have:
- Infection in biliary tract
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Excess production of bilirubin by the liver due to genetic disorder
Who all are at the risk of bile duct stone?
Individuals with a medical history of gallbladder disease or gallstones are more prone to risk for bile duct stones. Also, individuals who had gallbladder removal surgery in the past may develop bile duct stones.
An individual may develop the risk of gallstones in the following conditions:
- low-fiber diet
- meals with high calories and fat
- being overweight
- lack of physical exercise
- frequent weight loss or persistent fasting
- pregnancy
Risks of Choledocholithiasis
The following are the irreversible risk factors that include:
- gallstones problems are more common in women
- old age people are mainly at higher risk for gallstones
- ancestral history of gallstone in the family
How to diagnose choledocholithiasis?
If an individual has symptoms of gallstones, the doctor will prescribe for a physical examination to diagnose gallstones in the bile duct and that may include:
- Abdominal CT scan for cross-sectional X-rays.
- Endoscopic ultrasound is the procedure to examine the digestive tract through a flexible endoscopic tube placed through the mouth.
- Transabdominal ultrasound (TUS) is a methodology that captures pictures with high-frequency sound waves to take a look at the gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, and liver.
- Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is an MRI of the pancreatic duct, gallbladder, and bile duct.
- Percutaneous Transhepatic Cholangiogram (PTCA) is a type of X-ray for bile ducts
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiography (ERCP) is used to locate tumors, and stones constricting in the bile ducts.
To diagnose choledocholithiasis the doctor may prescribe the following blood test to inspect the signs of infection, examine the liver functionality along with the pancreas.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC), Pancreatic Enzymes, Liver Function Tests (LFT), and Bilirubin
Treatment of Choledocholithiasis
Treatment of choledocholithiasis at Southlake General Surgery is performed by the experienced general surgeon Dr. Valeria Simone MD. In this procedure, the doctor unblocks the gallstones obstruction in the bile duct. It includes:
- Biliary stenting, removal of gallstones, or fragmenting stones (lithotripsy)
- Gallbladder removal surgery (Cholecystectomy)
- Sphincterotomy at Southlake general surgery is a surgical procedure to remove gallstones from the common bile duct or make them pass.
Biliary Endoscopic Sphincterotomy (BES) is the most opted treatment for gallstones in the bile duct. In this procedure, the surgeon inserts a balloon and basket type of equipment into the bile duct to remove the gallstones.
In case, gallstones don’t move all alone or can’t be extracted BES procedure, the surgeon may opt for lithotripsy to capture the stone or make them pass.
According to Dr. Valeria Simone MD, individuals with medical conditions such as gallbladder disease or gallstone in the bile duct may choose to have gallbladder removal surgery at Southlake General Surgery, Texas. During the surgical procedure, our doctor will also examine the bile duct for leftover gallstones.
If an individual doesn’t want to remove the gallstones and has a medical history of gallstones problem our doctor may recommend biliary stents to open the blockage. This procedure helps prevent gallstones infection and gallstones in the bile duct (choledocholithiasis) in the future.
How to prevent gallstones in the bile duct?
Gallstones in the bile duct can be a recurring problem for any individual even after the gallbladder removal surgery. A few changes in diet and daily routine can help prevent the recurrence of gallstones in the future.
For more information on gallstones in the bile duct (choledocholithiasis) – causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, diet plan, and consultation. Please contact our healthcare expert today at +1 (817) 748-0200. To make an online appointment. Click Here
Follow us on Facebook