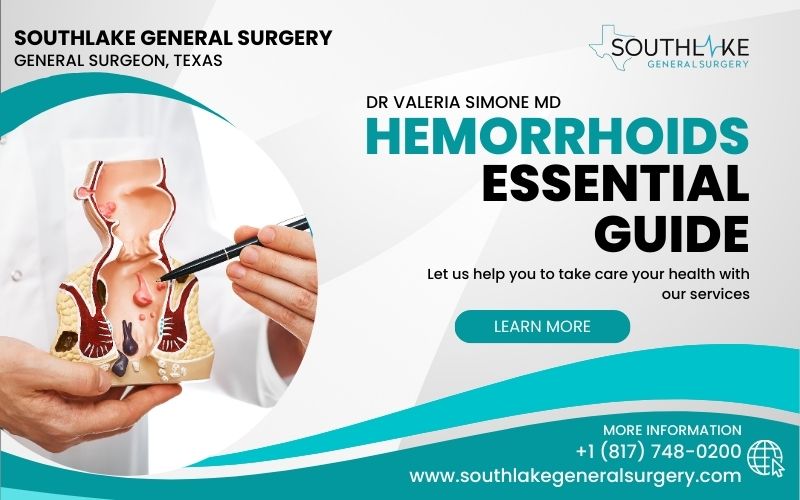
Have you ever experienced the discomfort, pain, or embarrassment of hemorrhoids? If so, you’re not alone. Millions of people suffer from this common condition, but many are hesitant to discuss it or seek help.
In this blog post, we’ll shed light on hemorrhoids what is, exploring their causes, symptoms, treatments, and prevention strategies. You’ll learn how to recognize the signs, manage the discomfort, and take proactive steps to avoid future flare-ups, enabling you to take charge of your health and well-being.
Key Takeaways
- Hemorrhoids are swollen and inflamed veins in the anal and rectal region that can cause pain, itching, discomfort, and bleeding.
- Risk factors include pregnancy, being overweight or obese, chronic constipation, etc. Early diagnosis is essential for successful treatment & prevention strategies such as lifestyle modifications & over-the-counter medications should be discussed with a doctor.
- Prevention includes maintaining a balanced diet high in fiber along with adequate hydration levels and exercising regularly to improve circulation & reduce pressure on veins around the anus.
Understanding Hemorrhoids
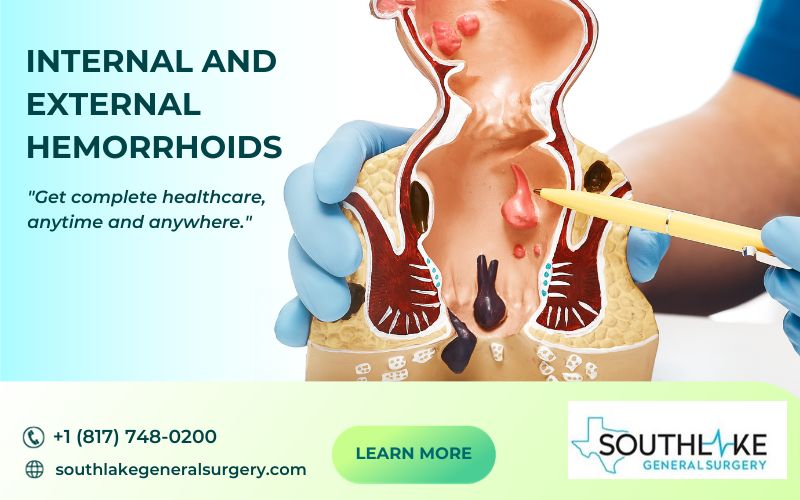
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen blood vessels in the lower rectum and around the anus. They can be classified into two main types: internal and external hemorrhoids called piles. While these swollen veins can cause varying degrees of discomfort like anal itching and pain, they are generally not life-threatening.
However, distinguishing between the two types and recognizing their symptoms is key to effective treatment and prevention.
Defining Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are anal and rectal veins which become swollen and inflamed. They contribute to pain and discomfort in the area. These swollen veins can cause a range of irritating symptoms, such as itching, pain, and bleeding.
Hemorrhoids are often compared to varicose veins, as both conditions involve enlarged veins. However, unlike varicose veins that typically form on the legs, hemorrhoids develop in the anal and rectal regions.
The two types of hemorrhoids are internal and external hemorrhoid. Internal hemorrhoids form inside the rectum and typically don’t cause pain, but can lead to bleeding.
External hemorrhoids, on the other hand, form outside the rectum and are often painful and itchy. Identifying the type of hemorrhoid you have is important, as it will guide the treatment approach.
Internal Hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids are veins that have become swollen. They are located inside the rectum. An internal hemorrhoid generally doesn’t cause discomfort but can lead to rectal bleeding. This bleeding may manifest as bright red blood on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl after a bowel movement.
In more severe cases, internal hemorrhoids may prolapse, extending beyond the anus and causing further complications. Healthcare professionals use a grading system ranging from 1 to 4 to classify the degree of prolapse of internal hemorrhoids.
Correct diagnosis and treatment are necessary to relieve symptoms and avoid complications like strangulated hemorrhoids, where the blood supply to the swollen veins is disrupted, resulting in intense pain.
External Hemorrhoids
An external hemorrhoid, unlike its internal counterparts, forms in the anus and lower rectum and can cause pain, itching, and discomfort. These external hemorrhoids are covered by sensitive skin and may appear as small lumps just outside the anus.
In some cases, blood clots can form within external hemorrhoids, affecting the blood supply to the affected area and causing sudden, severe pain.
Treatment options for external hemorrhoids range from home remedies or home treatments such as warm baths, to medical interventions, including topical therapies or surgery. Prevention strategies, including adopting a healthy diet, maintaining hydration, and regular physical activity, are key to reducing the risk of external hemorrhoids.
Risk Factors and Causes
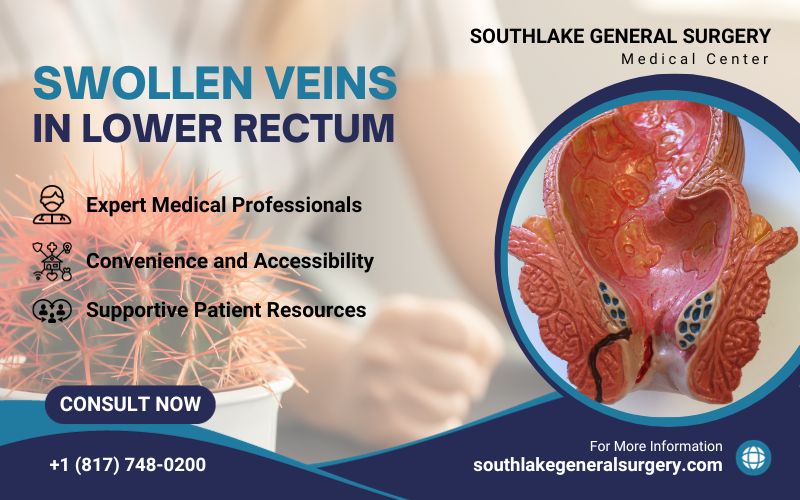
Hemorrhoids result from a combination of factors that cause swollen blood vessels in the lower part of the anus and rectum. Common causes include chronic constipation, straining during bowel movements, and prolonged sitting on the toilet.
Risk factors associated with the development of hemorrhoids include pregnancy, being overweight, and straining during bowel movements. Understanding these risk factors and causes can guide you in taking steps to prevent hemorrhoid development and manage symptoms more effectively.
Pressure on Veins
Increased pressure on veins around the anus can lead to the development of hemorrhoids. This pressure can result from various factors, such as prolonged sitting or standing, lack of physical activity, or chronic venous insufficiency.
During bowel movements, hemorrhoids are pushed against the sphincter muscle, and patients with hemorrhoids tend to have a higher resting anal canal tone.
Reducing pressure on veins requires regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy body weight, and avoiding prolonged sitting or standing. Such measures not only prevent hemorrhoids but also ease existing symptoms.
Chronic Constipation
Chronic constipation is a long-term condition characterized by:
- infrequent, difficult, or incomplete bowel movements
- alterations in diet
- lack of physical activity
- underlying medical conditions
Chronic constipation can lead to hemorrhoids due to straining during bowel movements. It’s vital to tackle the root causes of chronic constipation to prevent hemorrhoids. This might involve identifying and addressing the primary cause, alongside making pertinent lifestyle changes like increasing fiber intake and regular physical activity.
Pregnancy and Aging
Pregnancy and aging are also significant factors contributing to the development of hemorrhoids. During pregnancy, the expanding uterus places pressure on the veins, leading to increased blood flow to the pelvic area and an increased risk of hemorrhoids due to hormonal changes and increased intra-abdominal pressure.
On the other hand, the weakening of the connective tissues that support and hold hemorrhoids in place can be attributed to age. Being aware of these factors is important for implementing preventive measures during pregnancy and as you age.
Adopting a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and engaging in regular physical activity can help minimize the risk of hemorrhoids in these situations.
Symptoms and Diagnosis

Recognition of symptoms and diagnosis of hemorrhoids are vital for appropriate treatment and management. Symptoms can vary depending on the type of hemorrhoid and may include:
- Rectal pain
- Itching
- Bleeding
- Potential prolapse
A medical history and physical exam can help get hemorrhoids diagnosed, with external hemorrhoids usually apparent, especially if a blood clot has formed. You should consult with a doctor if hemorrhoids do not respond to treatment after a week or if recurring hemorrhoids are present.
Medical attention should be sought if serious anal discomfort, heavy rectal bleeding, or a fever is present. Seek help immediately to avoid any further complications.
Recognizing Symptoms
Itching, mild pain throughout, and bleeding could be symptoms of hemorrhoids. These symptoms should not be ignored.
Internal hemorrhoids are generally painless but can cause rectal bleeding, while external hemorrhoids can cause itching and pain in the anal region. The severity of symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the hemorrhoids.
In some cases, the symptoms of hemorrhoids may be mild and can be managed with at-home remedies. In other cases, the symptoms may be more severe and may require medical treatment.
Recognizing the symptoms associated with hemorrhoids is key to obtaining suitable treatment and managing the condition effectively. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, consult your doctor for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Diagnosing Hemorrhoids
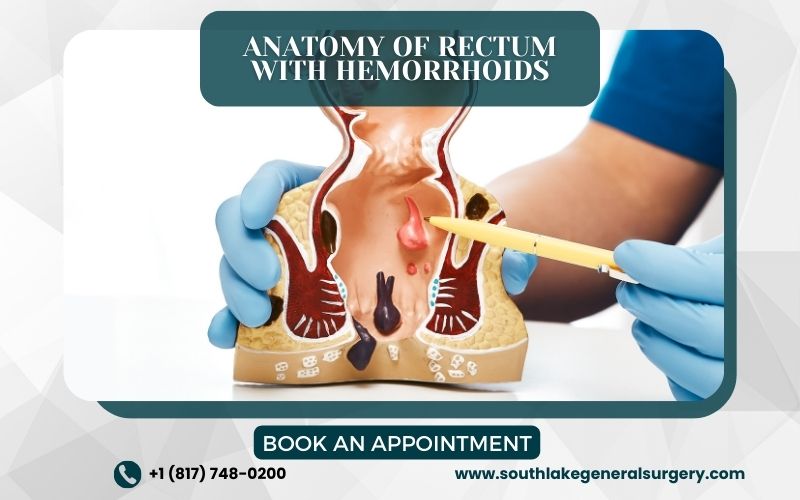
Diagnosing hemorrhoids involves a physical examination of the anus and rectum, which may include a digital rectal exam or visual inspection of the area around your anus to assess for the presence of swollen veins.
A digital rectal exam involves manually examining the anus using a gloved, lubricated finger to assess for the presence of blood, sensitivity, and lumps.
In certain cases, additional tests may be conducted to detect the presence of blood in the stool or to assess the muscle tone of the anus. These tests can help confirm the diagnosis of hemorrhoids and determine the appropriate treatment options.
At-Home Remedies and Treatments

Many individuals prefer to treat hemorrhoids at home using lifestyle changes and over-the-counter medications before considering more invasive medical procedures or surgical options. At-home remedies can be effective in alleviating mild to moderate symptoms and can help you manage the discomfort and extreme pain associated with hemorrhoids.
Through simple lifestyle modifications and the use of over-the-counter treatments, you can manage your symptoms and enhance your overall quality of life.
Lifestyle Changes
One of the most effective ways to treat hemorrhoids at home is by making lifestyle changes, such as increasing fiber intake and avoiding prolonged sitting. Consuming high-fiber foods, like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help soften stools and reduce the pressure on hemorrhoids.
Staying hydrated can also help keep stools soft and prevent constipation, a common cause of hemorrhoids. Additionally, avoiding extended periods of sitting can help reduce pressure on the veins in the rectal area, thus alleviating most hemorrhoid symptoms.
Over-the-Counter Medications
Over-the-counter medications, such as creams, ointments, and suppositories, can provide relief from hemorrhoid symptoms.
These products often contain ingredients like hydrocortisone, witch hazel, or lidocaine, which can help reduce inflammation, pain, and itching. It’s important to follow the instructions on the product label and consult your doctor if your hemorrhoid symptoms do not improve after a week of treatment.
While over-the-counter medications can provide short-term relief, it’s imperative to tackle the root causes of hemorrhoids and implement necessary lifestyle changes to prevent recurrence and ensure lasting relief.
Medical Procedures and Surgical Options

In some cases, at-home remedies and treatments may not be enough to alleviate the symptoms of hemorrhoids. When this occurs, medical procedures and surgical options may be necessary. These treatments can provide more permanent relief and can be particularly helpful in cases of severe or recurrent hemorrhoids.
It’s important to discuss your symptoms and treatment options with your doctor, who can help guide the best course of action based on your personal needs.
Nonsurgical Procedures
Nonsurgical procedures, and alternative treatments such as rubber band ligation and sclerotherapy, can be effective in treating hemorrhoids. Rubber band ligation involves placing a rubber band around the base of a hemorrhoid, cutting off its blood supply and causing it to shrink and eventually fall off.
Sclerotherapy involves injecting a chemical solution into the hemorrhoid tissue or scar tissue, causing it to shrink and eventually disappear. Both procedures can be performed in a doctor’s office and typically involve minimal discomfort and downtime.
Surgical Treatments (Hemorrhoids Surgery)
Surgical treatments, like hemorrhoidectomy, are reserved for severe cases of prolapsed hemorrhoids or cases where nonsurgical treatments have been unsuccessful. A hemorrhoidectomy involves the complete removal of external hemorrhoids or prolapsed internal hemorrhoids and is typically performed under anesthesia.
While this procedure has a high success rate, it can be associated with significant pain and a longer recovery time compared to nonsurgical treatments. You should discuss the risks and benefits of surgical treatments with your doctor to ascertain if they are the suitable option for you.
Hemorrhoids Surgery in Texas
If you’re seeking relief from persistent or severe hemorrhoids, there are options for hemorrhoids surgery in Texas. These surgical procedures are designed to provide long-term relief from the discomfort and complications associated with this condition.
With expert surgeons and advanced medical facilities, Southlake General Surgery offers top-notch care for patients dealing with this common but troublesome condition.
Remember, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to understand the best treatment options for your specific situation.
Prevention Strategies

Preventing hemorrhoids is often easier than treating them. Here are some tips to reduce your risk of developing hemorrhoids and keep your digestive system functioning optimally:
- Adopt a healthy diet
- Stay hydrated
- Exercise regularly
- Maintain proper posture
By following these guidelines, you can take steps to prevent hemorrhoids.
Comprehending the risk factors and causes of hemorrhoids enables you to take proactive steps in your health management to prevent this prevalent condition.
Diet and Hydration
Consuming a high-fiber diet and staying hydrated can help prevent hemorrhoids by softening stools and reducing the need to strain during bowel movements. Some tips for preventing hemorrhoids include:
- Eating fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to provide the necessary fiber for regular bowel movements
- Drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated
- Avoiding excessive straining during bowel movements
- Establish a routine of regular physical activities to boost your digestive system’s efficiency and promote optimal health
By following these tips, you can minimize the risk of developing hemorrhoids and maintain good digestive health.
Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can also help keep stools soft and prevent constipation, further reducing the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
Exercise and Posture
Engaging in regular exercise, such as walking, jogging, or swimming, can help improve circulation, strengthen the muscles supporting the veins in the rectum and around your anus, and reduce the likelihood of constipation.
In addition to exercise, maintaining proper posture can alleviate pressure on the veins in the rectal region, helping to reduce the risk of hemorrhoids. To maintain proper posture, ensure your feet are flat on the floor, maintain an upright posture, and limit extended sitting or standing.
Summary
Hemorrhoids, a prevalent health issue, impact countless individuals across the globe. Understanding the causes, symptoms, treatments, and prevention strategies can help you take charge of your health and alleviate the discomfort associated with this condition.
Whether you choose at-home remedies, medical procedures, or surgical options, it’s essential to address the underlying causes and make the necessary lifestyle changes to prevent recurrence and achieve long-term relief.
By adopting a healthy diet, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, and maintaining proper posture, you can reduce your risk of developing hemorrhoids and enjoy a happier, healthier life.
Appointment
If you’re suffering from persistent or severe hemorrhoids, it’s important to seek professional medical advice. At Southlake General Surgery, our team of experienced healthcare professionals is ready to assist you.
We offer comprehensive consultations and a range of treatment options tailored to your specific needs. Don’t let the discomfort of hemorrhoids interfere with your quality of life.
Isn’t it time you put a stop to the discomfort of hemorrhoids? Let’s tackle this together!
Schedule an appointment with us today and take a giant leap towards relief and recovery. Your journey to a more comfortable life starts now! For Quick Appointments you can contact our healthcare expert today at +1 (817) 748-0200.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main cause of hemorrhoids?
The main cause of hemorrhoids is increased pressure in the lower rectum due to straining during bowel movements, sitting for long periods of time, having chronic diarrhea or constipation, and other factors such as pregnancy, being overweight, and having a family history.
Do hemorrhoids go away?
Hemorrhoids can go away on their own but sometimes require medical attention. Small hemorrhoids usually clear up within a few days, while larger hemorrhoids may take longer to resolve and may cause pain and discomfort. Chronic or recurrent cases may also interfere with daily activities.
Are hemorrhoids serious?
Hemorrhoids may cause unpleasant symptoms and be a recurrent and painful intrusion, but they are rarely dangerous. While they can sometimes develop anemia or blood clots, these are rare cases. Most hemorrhoids can go away on their own with simple lifestyle changes, and more severe cases can be managed by treatments.
What do hemorrhoids look like?
Hemorrhoids can appear as soft lumps in bunches of skin around your anus or the anus or as a hard, red lump protruding from scar tissue on the outside of the anal area.
What makes hemorrhoids go away?
To make hemorrhoids go away, the key is to let them heal without straining and adding more fiber to the diet to soften stools. Also, try applying a hemorrhoid cream or suppository containing hydrocortisone, use witch hazel pads, take a warm bath or sitz bath, and soak regularly in warm water for 10-15 minutes.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
References
- National Library of Medicine. Definition & Facts of Hemorrhoids https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/hemorrhoids/definition-facts
- Harvard Health Publishing. Hemorrhoids and what to do about them. https://www.health.harvard.edu/diseases-and-conditions/hemorrhoids_and_what_to_do_about_them
- National Library of Medicine. Lifestyle and Risk Factors in Hemorrhoidal Disease. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8416428/