Understanding bowel blockage is crucial for timely intervention. If not treated, this condition can result in serious complications. Bowel obstruction occurs when there is a blockage preventing the normal flow of food, liquids, or gas through the intestines. This blockage can result from various factors, such as tumors, adhesions, or muscle disorders.
Recognizing the symptoms promptly and understanding the causes are essential for effective treatment. In the following sections, we will delve into the specifics of bowel blockages, their symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventative measures.
What is Bowel Blockage?
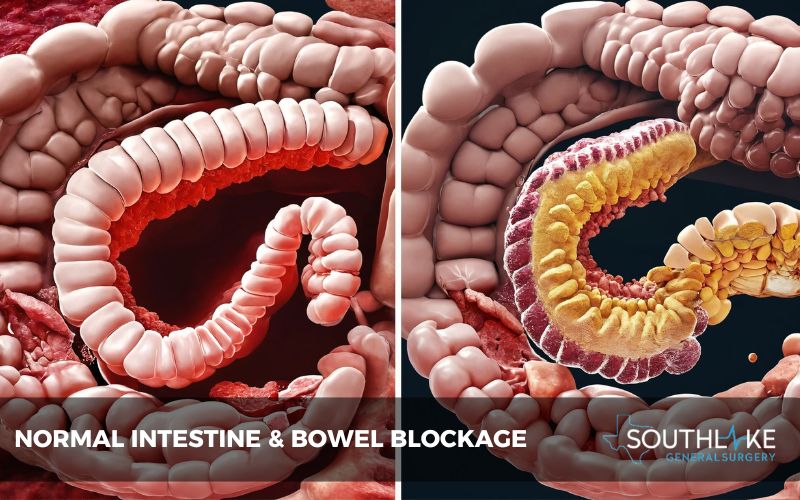
Bowel blockage, known as bowel obstruction, occurs when the intestines are partially or fully blocked. This can result from various causes, like tumors, adhesions, or muscle disorders. It is essential to comprehend these obstructions for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Defining Bowel Obstruction
Bowel obstruction refers to a partial or complete blockage in the intestines, hindering the normal flow of fluids and waste material. This condition can lead to severe complications if not promptly addressed. Bowel obstructions are often classified based on the underlying cause, whether it be a physical obstruction or a functional issue within the gastrointestinal tract.
Understanding the specific type of obstruction is crucial in determining the most effective course of treatment. Various factors, such as adhesions, tumors, or muscle disorders, can contribute to the development of bowel obstructions. Prompt diagnosis and intervention are essential to managing this condition effectively.
Types of Bowel Blockages
Intestinal obstructions can manifest in various forms, each with distinct characteristics. Mechanical obstructions result from physical barriers like tumors, adhesions, or hernias that block the bowel.
On the other hand, functional obstructions arise from issues with the natural contractions of the intestines, possibly due to nerve or muscle malfunctions.
Understanding these differences is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment approach for each type of bowel blockage. A proper diagnosis is essential to identify the specific type of obstruction and guide healthcare providers in devising an effective treatment plan.
Identifying Symptoms of Bowel Blockage

Recognizing the signs of a bowel blockage is crucial in seeking timely medical attention to prevent complications. Some common symptoms include:
- Severe abdominal pain and cramping
- Bloating and distension
- Inability to pass gas or stool
- Nausea and vomiting
- Constipation or diarrhea, alternating
- Lack of appetite and weight loss
Being aware of these symptoms can help individuals identify a potential bowel obstruction early on, prompting them to consult healthcare professionals for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
Early Warning Signs
- Cramping, bloating, and constipation are early indicators of a possible bowel blockage.
- Persistent abdominal pain, along with vomiting and the inability to pass gas, may signal a more serious issue requiring prompt medical attention.
- These symptoms, if left unchecked, can lead to complications necessitating surgical intervention to resolve the small bowel obstruction.
- Recognizing these warning signs and seeking timely medical evaluation is crucial to preventing further complications and ensuring appropriate treatment.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical attention promptly if you experience persistent abdominal pain, bloating, or vomiting. Sudden and severe symptoms such as intense cramping, inability to pass gas, or fecal vomiting indicate a possible small bowel obstruction necessitating immediate evaluation. Delaying treatment could lead to severe complications requiring surgical intervention.
If you suspect a bowel blockage operation is needed, do not hesitate to contact a healthcare provider for a timely assessment and proper management. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial in preventing further complications or the need for complex surgical treatment.
Common Causes Behind Bowel Blockage
Several factors can contribute to bowel blockages. Common causes include adhesions from previous surgeries, hernias, inflammatory bowel disease, tumors, and strictures. Adhesions, bands of tissue that form after surgery, can obstruct the intestines.
Hernias, especially if they become incarcerated, may lead to blockages. Inflammatory bowel disease like Crohn’s can cause narrowing and blockages. Tumors can physically obstruct the bowel passage, while strictures are narrowed areas hindering normal bowel flow.
Obstructive Causes: Tumors and Adhesions
Obstructive Causes: Tumors and Adhesions: When small bowel obstruction occurs, it’s essential to consider underlying causes such as tumors or adhesions. Tumors can be benign or malignant growths that block the bowel passage, while adhesions are fibrous bands that form between tissues, often due to previous surgeries or inflammatory conditions.
Surgeons may need to remove the obstruction caused by tumors or release adhesions to restore proper bowel function. Identifying and addressing these causes promptly can lead to better outcomes for patients.
Functional Causes: Muscle or Nerve Disorders
Functional causes of bowel blockage often stem from underlying muscle or nerve disorders affecting the gastrointestinal tract. These issues can disrupt the normal movement of the bowels, leading to a potential small bowel obstruction. Conditions such as intestinal pseudo-obstruction or Hirschsprung’s disease can contribute to these complications.
Surgical treatment may be necessary in severe cases that do not respond to other interventions. Understanding the role of muscle and nerve function in bowel obstruction is crucial for tailored management strategies.
Diagnosing Bowel Blockage
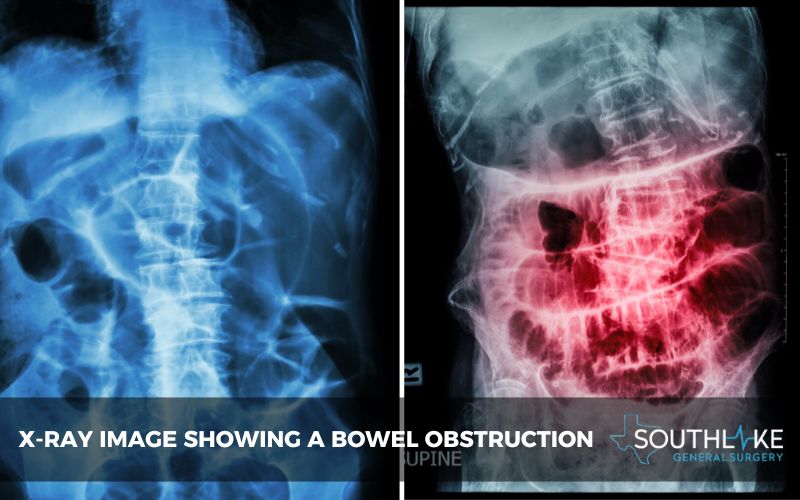
Bowel blockages can be diagnosed through various methods, including physical exams, imaging tests such as X-rays or CT scans, and endoscopic procedures like colonoscopies. Doctors may also utilize blood tests to assess for signs of infection or other abnormalities.
In some cases, a healthcare provider might recommend a trial of non-invasive treatments to see if symptoms improve, helping to confirm the diagnosis before considering surgical intervention.
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the most effective treatment approach tailored to each patient’s specific condition and needs.
Medical History and Physical Examination
A medical history and a thorough physical examination are crucial in diagnosing bowel blockages. Understanding a patient’s past medical issues, previous surgeries, and medications helps in assessing the risk factors for small bowel obstructions.
During the physical exam, signs such as abdominal tenderness, bloating, and abnormal bowel sounds can indicate a bowel obstruction. A detailed history and examination aid in determining the need for surgical treatment and ensuring the most appropriate care plan is implemented.
Imaging Tests Used in Diagnosis
To diagnose a bowel blockage, healthcare providers may rely on imaging tests. Computed tomography (CT) scans are commonly used to visualize the intestines and identify any obstructions. This non-invasive procedure provides detailed images to pinpoint the location and severity of the blockage.
Another imaging test is an abdominal ultrasound, which uses sound waves to produce images of the abdominal organs. These tests play a crucial role in confirming the presence of a small bowel obstruction before deciding on the appropriate surgical treatment. Consulting a specialist for accurate diagnosis and treatment is imperative.
Treatment Options for Bowel Blockage
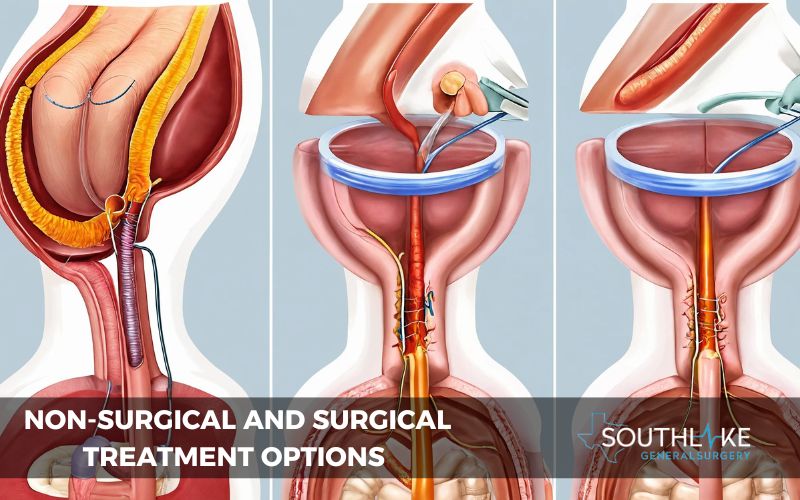
Surgical treatment is often necessary for resolving a small bowel obstruction. The type of surgery required depends on the underlying cause of the blockage.
In some cases, a minimally invasive procedure may be sufficient to alleviate the obstruction, while more severe cases may require open surgery. A surgical intervention aims to remove the blockage and restore normal bowel function.
It is essential to follow post-operative care instructions diligently to ensure a successful recovery and minimize the risk of future obstructions. Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider are crucial to monitoring your condition and preventing recurrence.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments for small bowel obstruction involve various strategies to alleviate symptoms without resorting to surgical intervention. Medical options such as bowel rest, intravenous fluids, and nasogastric decompression are commonly employed to manage mild cases effectively.
Additionally, the administration of medications to reduce inflammation and relieve pain can help in the treatment process. Close monitoring by healthcare providers is essential to assess the effectiveness of these non-surgical approaches and determine if further interventions are necessary, ensuring a comprehensive and personalized care plan for patients.
Surgery for Small Bowel Obstruction
Surgery for small bowel obstruction is a significant step towards addressing persistent blockages that do not respond well to non-surgical treatments. These surgical interventions are aimed at alleviating the obstruction and restoring normal bowel function.
Procedures such as bowel resection, adhesiolysis, and bowel diversion surgery may be performed depending on the severity and underlying cause of the blockage. These surgical treatments aim to restore normal bowel function and prevent recurrent episodes of small bowel obstruction.
Types of Bowel Obstruction Surgery
- Bowel resection: A surgical procedure to remove the affected part of the intestine, commonly performed in cases of tumor blockages or severe inflammation.
- Adhesiolysis: Surgery to break down adhesions or scar tissue causing the bowel obstruction, facilitating proper bowel movement.
- Bowel diversion surgery: Involves creating a stoma to redirect the flow of intestinal contents past the blockage area, allowing for natural healing of the affected segment.
- Exploratory laparotomy: A diagnostic surgical procedure to identify the cause and extent of bowel blockage, guiding further treatment decisions.
Your healthcare provider will determine the most suitable surgical approach based on your specific condition and overall health status. It’s important to have open communication with your medical team and ask any questions or concerns you may have regarding the operation.
Remember, a successful recovery often depends on following post-operative instructions diligently and attending follow-up appointments for ongoing monitoring and support.
Partial Bowel Obstruction Surgery
Partial bowel obstruction surgery may be recommended in cases of lower bowel obstruction where the blockage is not complete. Surgical treatment for small bowel obstruction aims to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
In situations of partial bowel obstruction, surgery focuses on relieving the partial blockage to restore normal bowel function. This may involve procedures such as adhesiolysis or bowel resection, tailored to address the specific underlying cause and severity of the obstruction.
Surgery for partial bowel obstruction is crucial in preventing a complete blockage and its associated risks, allowing for timely intervention and effective management of the condition.
Partial bowel obstruction surgery typically involves fewer extensive procedures compared to full bowel obstruction surgeries. In cases of partial blockage, measures such as bowel rest, intravenous fluids, and monitoring may be initially attempted to allow the bowel to recover on its own.
However, if symptoms persist or worsen, surgical intervention may be necessary to prevent complete blockage and potential complications.
Recovery After Treatment

After undergoing a bowel blockage operation, the recovery process is crucial. Patients typically stay in the hospital for observation post-surgery to ensure no complications arise. Depending on the severity of the blockage and the type of surgical treatment, the recovery timeline varies.
It’s important to follow the surgeon’s instructions diligently to promote healing. Rest and gradually reintroducing food are essential steps. It is crucial to follow post-operative care guidelines for a successful healing process.
Post-Surgical Care
- Following a bowel blockage operation, post-surgical care plays a crucial role in aiding recovery and preventing complications.
- Patients typically receive close monitoring to ensure proper healing and to address any potential issues promptly.
- This involves monitoring for signs of infection or inflammation and managing pain effectively.
- Additionally, patients may require dietary modifications to support their healing process and promote optimal gastrointestinal function.
- Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to track progress, address concerns, and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
Long-Term Management
Long-term management of small bowel obstruction often involves surgical treatment for persistent or recurring cases. Regular follow-up checks are crucial to monitor the condition post-operation and ensure proper healing. Patients need to adhere to dietary recommendations to prevent future episodes and maintain digestive health.
Southlake General Surgery emphasizes the significance of consistent medical supervision and lifestyle modifications to manage bowel blockages effectively in the long run. Overall, a comprehensive approach involving medical guidance and patient compliance is key to the successful long-term management of bowel obstructions.
Preventing Future Episodes

- Maintaining digestive health is crucial to preventing future episodes of small bowel obstruction.
- Dietary modifications play a significant role in managing this condition.
- Embracing a high-fiber diet can aid in regular bowel movements, reducing the risk of blockages.
- Furthermore, ensuring adequate hydration supports the smooth passage of stool through the intestines.
- Regular follow-up checks with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor any underlying issues that could lead to a recurrence.
- By prioritizing these preventive measures, individuals can minimize the chances of requiring surgical treatment for bowel blockages in the future.
Dietary Recommendations
Maintaining a diet high in fiber can help prevent small bowel obstructions. Thus, prioritize consuming fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to ensure a healthy digestive system. Additionally, staying hydrated is crucial; aim for eight glasses of water daily.
Avoid foods that are difficult to digest or known to cause blockages, such as processed foods high in fat. Be mindful of your eating habits and chew food thoroughly to aid digestion.
Regular Follow-Up Checks
Regular follow-up checks are crucial after a bowel blockage operation. These appointments help monitor the recovery progress, detect any complications early on, and ensure the effectiveness of the surgical treatment.
Scheduled visits allow healthcare providers to assess the patient’s condition, address any concerns, and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
These follow-up checks play a vital role in promoting optimal healing and reducing the risk of recurrence, providing patients with ongoing support and guidance throughout their recovery journey.
A Note From Southlake General Surgery
At Southlake General Surgery, we specialize in treating small bowel obstructions with advanced surgical techniques. Our team of experts is committed to delivering customized care to every patient. With a focus on minimally invasive procedures, we aim to ensure quicker recovery times and better outcomes for our patients.
Trust us to deliver exceptional surgical treatment for bowel blockages, prioritizing your health and well-being above all else. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the first step towards a smoother recovery.
Conclusion
In conclusion, timely recognition and treatment of bowel blockages are crucial for preventing complications. Understanding the symptoms and causes can aid in prompt medical intervention, often involving surgical treatment for severe cases like small bowel obstruction.
It’s essential to prioritize regular follow-up checks and adhere to dietary recommendations to minimize the risk of recurrence. Remember, early detection and management play a significant role in ensuring the best possible outcomes for individuals with bowel blockages. Stay informed, prioritize your health, and consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Make An Appointment
To address any concerns related to bowel blockages or potential symptoms, you can contact our healthcare expert today at +1 (817) 748-0200, we at Southlake General Surgery recommend scheduling an appointment promptly.
Our experienced team specializes in small bowel obstruction and offers advanced surgical treatments tailored to individual needs. Taking proactive steps by consulting with our experts can ensure timely intervention and personalized care.
To prioritize your health and well-being, reach out to us to make an appointment for a comprehensive assessment and an appropriate management plan. Your journey towards recovery begins with a simple step: booking a consultation with our dedicated professionals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Diet Influence Bowel Blockage Risk?
Consuming a high-fiber diet can help prevent bowel blockages by promoting regular bowel movements and reducing the risk of constipation. Avoiding foods low in fiber and staying hydrated are key factors in maintaining a healthy digestive system.
Do people recover from bowel obstruction?
Yes, people can recover from bowel obstruction with prompt medical intervention. Treatment may involve surgery, medication, or a combination, depending on the underlying cause. Early detection and appropriate management play crucial roles in a successful recovery.
When Is Bowel Obstruction Surgery Needed?
Surgery for bowel obstruction is typically needed when other treatments fail to relieve the blockage or if there are signs of severe complications like tissue damage or infection.
What should I anticipate if I have a bowel obstruction?
Symptoms of bowel obstruction may include severe abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, vomiting, and an inability to pass gas. Immediate medical attention is crucial to preventing serious complications. Treatment options range from dietary changes to surgery, depending on the severity of the blockage.
What is the recovery process like after a bowel blockage operation?
Recovery after a bowel blockage operation involves hospitalization, IV fluids, and monitoring. The gradual reintroduction of food is crucial to prevent complications. Follow-up appointments ensure appropriate healing and tackle any issues that may arise.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
References:
- Peacock, O., Bassett, M. G., Kuryba, A., Walker, K., Davies, E. J., Anderson, I. D., & Vohra, R. (2018, March 30). Thirty-day mortality in patients undergoing laparotomy for small bowel obstruction. British Journal of Surgery. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.10812
- Aryaie, A., Lalezari, S., Sergent, W. K., Puckett, Y., Juergens, C., Ratermann, C., & Ogg, C. (2018, January 19). Decreased opioid consumption and enhance recovery with the addition of IV Acetaminophen in colorectal patients: a prospective, multi-institutional, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study (DOCIVA study). Surgical Endoscopy. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-018-6062-y
- Jeppesen, M. H., Tolstrup, M., Kehlet Watt, S., & Gögenur, I. (2016). Risk factors affecting morbidity and mortality following emergency laparotomy for small bowel obstruction: A retrospective cohort study. International Journal of Surgery, 28, 63-68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2016.02.059
- Ford MM. Crohn’s Disease Obstructions. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2021;34(4):227-232. https://doi:10.1055/s-0041-1729926
- Aryaie, A., Lalezari, S., Sergent, W. K., Puckett, Y., Juergens, C., Ratermann, C., & Ogg, C. (2018, January 19). Decreased opioid consumption and enhance recovery with the addition of IV Acetaminophen in colorectal patients: a prospective, multi-institutional, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study (DOCIVA study). Surgical Endoscopy. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-018-6062-y
- Ford MM. Crohn’s Disease Obstructions. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2021;34(4):227-232. https://doi:10.1055/s-0041-1729926
- Sleiman J, El Ouali S, Qazi T, et al. Prevention and Treatment of Stricturing Crohn’s Disease – Perspectives and Challenges. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;15(4):401-411. https://doi:10.1080/17474124.2021.1854732
- Giglia MD, Stein SL. Overlooked Long-Term Complications of Colorectal Surgery. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2019;32(3):204-211. https://doi:10.1055/s-0038-1677027