Hernia surgery is the most common treatment for hernias and is often the only remedy. Surgery involves repositioning the herniated tissue and reinforcing the weakened area with sutures or surgical mesh.
Whereas, hernias are a common medical condition in which a part of an organ protrudes through the muscle or tissue wall that normally contains it.
Hernias can occur in various parts of the body, but they are most commonly found in the abdomen and groin area. While some hernias may not cause any symptoms or discomfort, others can be painful and require medical intervention.
The goal of hernia surgery is to repair the hernia and prevent it from recurring. In most cases, hernia surgery is performed using open surgery or minimally invasive laparoscopic procedures, depending on the size and location of the hernia.
In this blog, we will provide answers to frequently asked questions about hernia surgery. We will cover the types of hernias, symptoms, surgical options, recovery process, potential complications, and more. By understanding the basics of hernia surgery, you can make informed decisions about your healthcare and ensure a smooth recovery process.
Key Highlights
- Hernia surgery is the most common treatment for hernias and is often the only remedy.
- There are different types of hernias, including inguinal, ventral, and hiatal hernias, each with its own symptoms and surgical approaches.
- Surgery is usually recommended when lifestyle changes or other non-surgical treatments are not effective in repairing the hernia.
- Hernia surgery can be performed using open surgery or minimally invasive laparoscopic procedures, depending on the size and location of the hernia.
- The surgery involves repositioning the herniated tissue and reinforcing the weakened area with sutures or surgical mesh.
- Recovery from hernia surgery varies depending on the type of surgery and the individual, but most people can return to normal activities within a few weeks.
Types of Hernias and Their Symptoms
Various types of hernias occur in specific areas of the body. Among the most frequent types are inguinal hernias, ventral hernias, and hiatal hernias. Hernias in the groin area are more frequently seen in men.
Hernias in the abdominal wall commonly develop at the location of a prior surgical procedure. Hiatal hernias occur when part of the stomach or other organs protrude into the chest cavity. Symptoms of hernias can vary but often include:
- pain
- discomfort
- a visible bulge at the site of the hernia
What are the different types of hernias that require surgery?
Hernia surgery typically addresses:
- inguinal hernias (in the groin)
- umbilical hernias (around the belly button)
- femoral hernias (upper thigh)
- incisional hernias (resulting from previous surgery).
Surgery becomes necessary when hernias cause pain, grow larger, or pose a risk of complications.
Identifying Common Hernias: Inguinal, Ventral, and More
Inguinal hernias are the most common type of hernia and occur in the groin area. They are more common in men, affecting 25 percent of them in their lifetimes compared to 2 percent of women.
Ventral hernias occur in the abdominal wall and can be umbilical hernias (belly button) or incisional hernias that develop at the site of a previous surgery.
Hiatal hernias occur when part of the stomach or other organs protrude into the chest cavity. Another less common type of hernia is a femoral hernia, which occurs in the upper thigh area.
It is important to identify the type of hernia accurately to determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
- Inguinal hernias, which appear in the groin area, disproportionately affect males.
- Abdominal wall ventral hernias typically develop at the location of prior surgical procedures.
- Hiatal hernias occur when part of the stomach or other organs protrude into the chest cavity.
- Femoral hernias occur in the upper thigh area and are less common than inguinal hernias.
Recognizing the Symptoms: When to Seek Medical Advice

The size and location of a hernia can affect the symptoms that a patient may experience. But here are some of the most prevalent hernia symptoms:
- Pain or discomfort in the affected area, such as the groin, abdomen, or chest.
- A visible bulge or lump at the site of the hernia.
- An uncomfortable feeling of weight or pressure on the afflicted area.
- Discomfort or pain that worsens with physical activity, coughing, or sneezing.
It is important to seek medical advice if you experience any of these symptoms or suspect that you may have a hernia. Untreated hernias can lead to complications, such as bowel obstruction or strangulation, which require immediate medical attention.
Your healthcare provider can evaluate your symptoms, perform a physical examination, and recommend appropriate treatment options, including hernia surgery if necessary.
Preparing for Your Hernia Surgery Consultation
Before your hernia surgery consultation, it is important to be prepared and informed about the procedure. During the consultation, your healthcare provider will discuss the details of the surgery, including the type of hernia repair, the use of general anesthesia, and the expected recovery process.
They may also perform a physical examination to evaluate the size and location of the hernia. This information will help determine the most appropriate surgical approach and ensure the best possible outcome.
Essential Questions to Ask Your Surgeon

When meeting with your surgeon for a hernia surgery consultation, it is important to ask the right questions to fully understand the procedure and its potential risks and benefits. Some essential questions to ask your surgeon may include:
- What kind of hernia am I dealing with, and how may it be treated?
- What is the recommended surgical approach, and why?
- Will surgical mesh be used in the repair, and what are the benefits and risks?
- What is the expected recovery process, and how long will it take?
Additionally, you may want to inquire about the qualifications and experience of the surgical team, as well as any specific instructions or preparations for the surgery and recovery period.
Asking these questions will help you make informed decisions about your hernia surgery and ensure that you have a clear understanding of what to expect.
Understanding the Risks and Benefits of Hernia Surgery
Like any surgical procedure, hernia surgery carries certain risks and benefits. It is important to understand these factors to make an informed decision about your treatment. The benefits of hernia surgery include:
- Repairing the hernia and preventing potential complications.
- Relieving symptoms such as pain, discomfort, and a visible bulge.
- Improving quality of life and allowing for a return to normal activities.
However, there are also risks associated with hernia surgery, including:
- Infection at the surgical site.
- Bleeding or bruising.
- Complications related to anesthesia.
- Recurrence of the hernia.
Your healthcare provider will discuss these risks and benefits with you during your consultation and help you weigh the potential outcomes. It is important to have realistic expectations and understand that every individual’s experience with hernia surgery may vary.
Hernia Surgery Explained
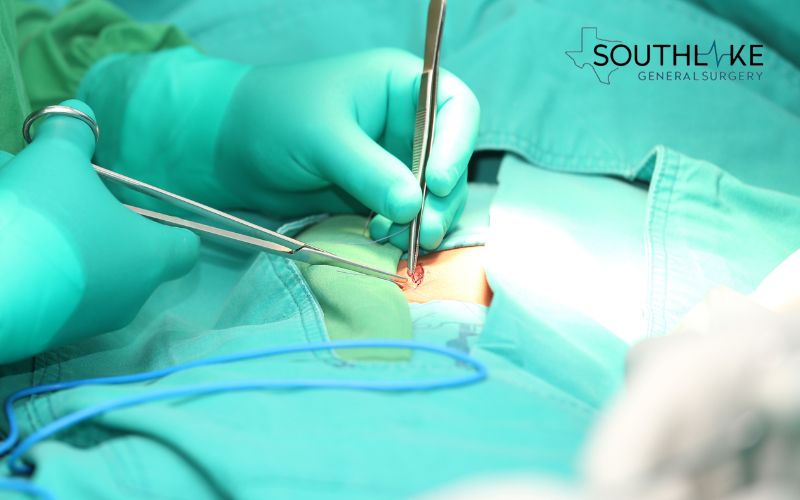
Hernia surgery, also known as herniorrhaphy, is a surgical procedure used to repair a hernia. It involves repositioning the herniated tissue and reinforcing the weakened area with sutures or surgical mesh.
Hernia surgery can be performed using open surgery or minimally invasive laparoscopic procedures. General anesthesia is typically used to ensure the patient’s comfort during the procedure.
The Different Surgical Options Available
There are different surgical options available for hernia repair, depending on the type and size of the hernia. The two main approaches are open hernia surgery and laparoscopic hernia repair surgery.
- In open hernia surgery, the surgeon makes a small incision in the skin around the affected area and fixes the hernia that way.
- Laparoscopic repair is a minimally invasive procedure that involves making several small incisions on the lower abdomen and using a laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera) and surgical instruments to repair the hernia. This laparoscopic surgery approach offers the advantages of smaller incisions, less postoperative pain, and faster recovery. Local anesthesia is often used for laparoscopic hernia repair.
What Can I Expect on My Surgical Day?
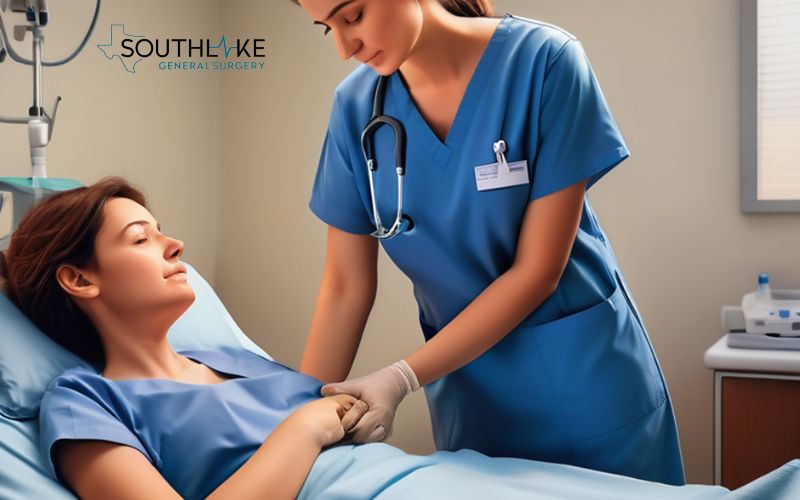
On the day of your hernia surgery, you will typically be scheduled to arrive at the hospital or surgical center a few hours before the procedure. This allows time for preoperative preparations, including checking your vital signs, starting an intravenous (IV) line, and administering any necessary medications.
You will also have the opportunity to speak with your surgeon and anesthesia team to address any last-minute questions or concerns.
During the surgery, you will be under general anesthesia, which means you will be unconscious and unable to feel any pain or discomfort. Your surgeon will use surgical instruments, including a laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera) if you are having a laparoscopic procedure, to repair the hernia. The specific details of the surgery will depend on the type and location of your hernia.
Following is a detailed summary of what to expect on the day of your hernia surgery.
- Preoperative Preparations
- Arrival at the medical facility or surgery center
- Vital signs and preoperative assessments
- Starting an intravenous (IV) line
- Administering necessary medications
- Meeting with your surgeon and anesthesia team for final discussions
Post-Surgery Care and Recovery After Hernia Surgery

After hernia surgery, it is important to follow post-surgery care instructions to ensure a smooth recovery. The specific recovery process will depend on the type of surgery and the individual, but here are some general guidelines:
- Take any prescribed pain medications as directed to manage postoperative discomfort.
- Avoid heavy lifting or strenuous activity for a certain period of time, as advised by your surgeon.
- To avoid infection, make sure to keep the surgical incisions dry and clean. If your surgeon has instructed you to change your dressing, do it exactly as directed.
- Follow a balanced diet and stay hydrated to support the healing process.
- To keep checks on how you’re doing while you recover, be sure to attend all your doctor’s appointments.
Immediate Post-Operative Care Tips
Immediate post-operative care is crucial to ensure proper healing and minimize the risk of complications. Here are some tips to follow during the initial recovery period:
- Take any prescribed pain medications as directed to manage postoperative discomfort.
- Avoid strenuous activities that could strain the surgical area and disrupt the healing process.
- After surgery, make sure the wounds are dry and clean. As directed by your surgeon, replace your dressing as prescribed.
- Be mindful of any signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or drainage from the incision site.
- If surgical mesh was used during the repair, follow your surgeon’s instructions for caring for the mesh and preventing complications.
- Make sure you don’t miss any follow-up appointments with your surgeon so you can track your healing and voice any concerns.
Long-Term Recovery: Timeline and Tips
The long-term recovery from hernia surgery can vary depending on the individual and the type of surgery performed. Here is a general timeline and some tips for a smooth recovery:
- In the first few weeks following surgery, you may need to limit physical activity and avoid heavy lifting to allow the surgical area to heal.
- Over the next few months, gradually increase your activity level and resume normal daily activities, as advised by your surgeon.
- It is important to strengthen the abdominal muscles to support the repair and prevent future hernias. Your surgeon or a physical therapist may recommend specific exercises or activities.
- Be mindful of any signs of recurrence or complications, such as the return of pain or a visible bulge in the surgical area. See your surgeon immediately if concerns arise.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, to support the long-term success of the hernia repair and overall well-being.
Potential Complications and How to Avoid Them
While hernia surgery is generally safe and effective, there are potential complications that can occur. Some potential complications include infection at the surgical site, recurrence of the hernia, and complications related to the use of surgical mesh.
To minimize the risk of complications, it is important to follow your surgeon’s post-operative care instructions, keep the surgical incisions clean and dry, and attend any scheduled follow-up appointments.
If you experience any signs of infection or recurrence, such as increased redness, swelling, pain, or a visible bulge, contact your surgeon for further evaluation and treatment.
Common Post-Surgery Complications
While complications after hernia surgery are relatively rare, some potential complications can occur. These may include:
- Infection at the surgical site: This can be minimized by keeping the incision clean and dry and following any dressing change instructions provided by your surgeon.
- Acid reflux: Some individuals may experience acid reflux after hiatal hernia repair surgery. This can be managed with lifestyle modifications and medications as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Impaired blood supply: In rare cases, the blood supply to the repaired area may be compromised, leading to tissue damage or necrosis. This requires immediate medical attention to restore blood flow.
- Recurrence of the hernia: Although hernia surgery is designed to repair the hernia and prevent recurrence, there is a small risk of the hernia coming back. This can be minimized by following post-operative care instructions and avoiding activities that could strain the repaired area.
Preventative Measures and Solutions
To minimize the risk of complications and prevent future hernias, it is important to take preventative measures and follow your surgeon’s recommendations. Some preventative measures and solutions may include:
- Avoiding activities that put a strain on the abdominal muscles, such as heavy lifting or repetitive bending.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, to support overall abdominal health.
- Following your surgeon’s instructions for caring for any surgical mesh used during the repair.
- Keeping regular follow-up appointments with your care team to monitor your recovery progress and address any concerns.
- Listening to your body and seeking medical advice if you experience any new symptoms or concerns.
- By taking these preventative measures and staying proactive in your care, you can minimize the risk of complications and improve your overall quality of life after hernia surgery.
Returning to Daily Activities

Returning to your daily activities after hernia surgery is an important part of the recovery process. The timeline for returning to daily activities may vary depending on the individual and the type of surgery performed.
In general, it is important to listen to your body and gradually increase your activity level as you heal. Your surgeon or a physical therapist may provide specific guidelines for resuming physical activity and strengthening the abdominal muscles.
By following these guidelines and taking a gradual approach, you can safely return to your normal daily activities and maintain a healthy lifestyle after hernia surgery.
Guidelines for Resuming Work and Exercise
Returning to work and exercise after hernia surgery should be done gradually and in consultation with your surgeon. Here are a few overarching principles to adhere to:
- Resuming work: If you have a physically demanding job that involves heavy lifting or strenuous activity, you may need to take more time off work to ensure proper healing. For less physically demanding jobs, you may be able to return to work within a week or two, depending on your recovery progress.
- Resuming exercise: Start with light exercises, such as walking or gentle stretching, and gradually increase your activity level over time. Avoid strenuous activities or exercises that put a strain on the abdominal wall until your surgeon gives you the go-ahead.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to any pain or discomfort during work or exercise and adjust your activities accordingly. If you experience any new or worsening symptoms, consult your surgeon or healthcare provider for further guidance.
What to Avoid to Prevent Recurrence
To prevent the recurrence of a hernia after surgery, it is important to avoid certain activities and behaviors that can put strain on the repaired area. Here are some things to avoid:
- Strenuous activity: Avoid heavy lifting or intense physical activity that can put excessive strain on the abdominal muscles and weaken the repair.
- Abdominal pressure: Avoid activities that increase intra-abdominal pressure, such as straining during bowel movements or chronic coughing.
- Obesity: Maintaining a healthy weight and lifestyle can help prevent the development of new hernias or the recurrence of a repaired hernia.
- Smoking: Smoking has the potential to obstruct the healing process and heighten the possibility of problems. Before and after hernia surgery, it is advisable to stop smoking to enhance results and minimize the probability of a recurrence.
- By following these guidelines and making positive lifestyle changes, you can reduce the risk of hernia recurrence and maintain a healthy, hernia-free life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding hernia surgery is crucial for anyone considering or undergoing the procedure. From recognizing symptoms to post-operative care, being well-informed can lead to better outcomes. Consult with your surgeon, ask essential questions, and know the risks and benefits involved.
Follow post-surgery care instructions diligently for a smooth recovery. Remember, early intervention and proper guidance are key in managing potential complications.
If you have more questions or need personalized advice, don’t hesitate to get in touch with our experts. No matter what, you can count on our unwavering support to prioritize your health and wellbeing.
Schedule an Appointment
If you have been experiencing symptoms of a hernia and are considering surgery, it is important to schedule an appointment with a specialist at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Our team of experts can provide you with the information and guidance you need to make an informed decision about your treatment options. Don’t hesitate to reach out and schedule a consultation today at +1 (817) 748-0200.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Hernia Surgery Be Performed Laparoscopically?
Yes, hernia surgery can be performed using a laparoscopic approach. This minimally invasive technique involves making small incisions and using a camera and specialized surgical instruments to repair the hernia. Laparoscopic hernia surgery offers benefits such as smaller incisions, less postoperative pain, and a faster recovery process compared to open surgery.
What is the typical duration of hospital stay following hernia surgery?
The length of hospital stay after hernia surgery depends on various factors, including the type of surgery performed and the individual’s overall health. In many cases, hernia surgery is performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing patients to go home the same day. However, more complex hernia repairs may require a short hospital stay of one to two days.
Is Hernia Surgery Covered by Insurance?
In the United States, hernia surgery is typically covered by health insurance, but coverage can vary depending on the specific insurance plan and the type of surgery required. It is important to check with your insurance provider to understand the coverage details and any potential out-of-pocket costs associated with hernia surgery. Your surgeon’s office can also help guide you through the insurance process and provide information on the estimated costs of the procedure.
What is the postoperative recovery period after hernia surgery?
The recovery process after hernia surgery can vary depending on the individual and the type of surgery performed. It typically involves a period of rest and limited physical activity followed by a gradual return to normal activities. Your surgeon will provide specific instructions regarding post-operative care, including wound care, pain management, and activity restrictions. The overall timeline for recovery can range from a few days to several weeks, depending on the individual’s healing process and the extent of the surgery.
What are some common misconceptions about hernia surgery?
There are several common misconceptions about hernia surgery. Some of these include:
- Surgical mesh is always required: While mesh is often used, some hernias can be repaired without it.
- Traditional open surgery is always necessary: Laparoscopic repair is a minimally invasive option for many hernias.
- Laparoscopic repair is always better: The choice of surgery depends on various factors, and open surgery may be more appropriate in certain cases. It is important to discuss with your surgeon to determine the best approach for your specific hernia.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
References:
- Website, N. (2023, December 4). Hernia. nhs.uk. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/hernia/
- Hernias: Overview. (2020, January 30). InformedHealth.org – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK395554/
- Lassandro F, Iasiello F, Pizza NL, Valente T, Stefano ML, Grassi R, Muto R. Abdominal hernias: Radiological features. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2011 Jun 16;3(6):110-7. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v3.i6.110. PMID: 21860678; PMCID: PMC3158902.
- Armijo PR, Pokala B, Flores L, Hosein S, Oleynikov D. Current state of robotic use in inguinal hernia repair: a survey of minimally invasive hernia surgeons. Updates Surg. 2020 Mar;72(1):179-184. doi: 10.1007/s13304-020-00709-6. Epub 2020 Mar 5. PMID: 32141046.
- Haladu N, Alabi A, Brazzelli M, Imamura M, Ahmed I, Ramsay G, Scott NW. Open versus laparoscopic repair of inguinal hernia: an overview of systematic reviews of randomised controlled trials. Surg Endosc. 2022 Jul;36(7):4685-4700. doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09161-6. Epub 2022 Mar 14. PMID: 35286471; PMCID: PMC9160137.
- Hernias: Overview. (2020, January 30). InformedHealth.org – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK395554/

