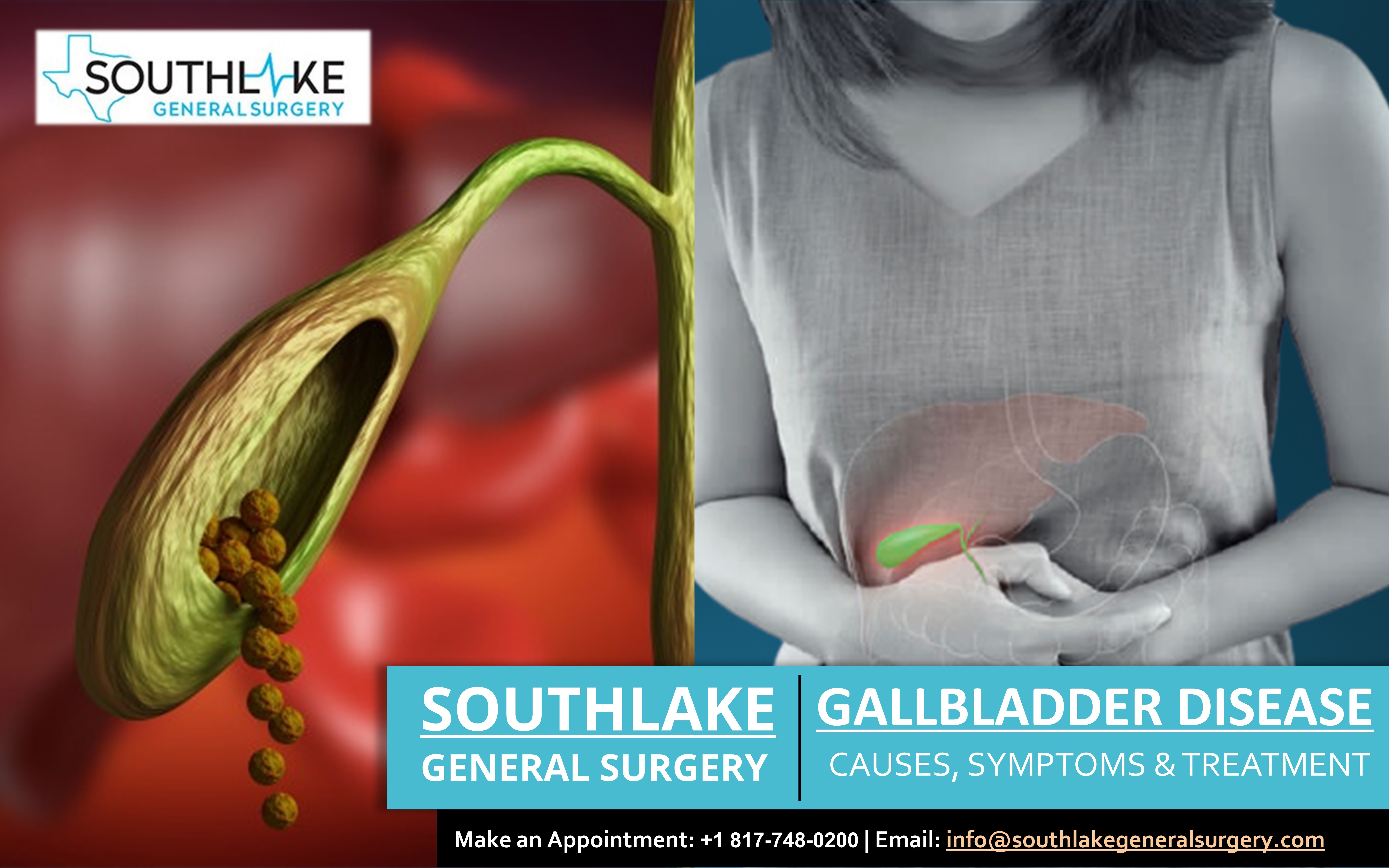
Gallbladder disease is a sickness caused by many kinds of conditions that can influence the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located under the liver that helps store bile developed by the liver and passes the bile to the small intestines to process the fats. Let’s explore more about the gallbladder.
Most gallbladder disease happens due to inflammation. Inflammation of the gallbladder walls refers to cholecystitis. This irritation mainly happens because of obstruction of the bile duct due to gallstones leading to bile buildup. This condition further leads to necrosis or gangrene.
Types of gallbladder disease
There are many types of gallbladder disease, which are as follows:
Gallstones
Gallstones are hardened digestive fluids that block the passageways of the gallbladder and bile ducts. It can range from as small as a sand grain to as large as a golf ball. Gallstones develop when the gallbladder doesn’t empty properly. Let’s explore more about the Gallstones.
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis is the most widely recognized sort of gallbladder disease. It introduces itself as either an acute or chronic aggravation of the gallbladder.
Acute cholecystitis
Gallstones are the primary cause of acute cholecystitis. However, it might likewise be the consequence of tumors or other ailments. Let’s explore more about Acute cholecystitis.
Chronic cholecystitis
Cholecystitis is an unexpected inflammation of the gallbladder. If an individual experiences this continuous overtime for about a few months along with repeated attacks or intermittent problems with the functionality of the gallbladder, this refers to chronic cholecystitis.
After numerous outbreaks of acute cholecystitis, your gallbladder can recoil and lose its functionality to store and deliver bile. The patient may experience vomiting, nausea, and abdominal pain. Laparoscopic gallbladder removal surgery is recommended for the treatment of chronic cholecystitis. Let’s explore more about chronic cholecystitis.
Choledocholithiasis
Gallstones may get stuck in the bile ducts or in the neck of the gallbladder. Once the gallbladder is connected in this form, bile can’t discharge, and it will further restrict bile discharge from the liver to the small intestines. This may prompt the gallbladder to get aggravated or swollen. Let’s understand more about Choledocholithiasis.
Biliary dyskinesia
Biliary dyskinesia is a condition of the gallbladder when its function is lower than normal. This condition generally occurs when an individual has continuous gallbladder aggravation.
Symptoms of biliary dyskinesia can include nausea, heartburn, and upper abdominal pain after meals. Having a fatty meal may trigger the symptoms in an individual. In this condition, an individual generally doesn’t have gallstones in the gallbladder.
For the diagnosis of biliary dyskinesia, your doctor may prescribe a HIDA scan to measure the function of the gallbladder. Biliary dyskinesia is generally diagnosed when the gallbladder is about 40 percent or less.
Sclerosing cholangitis
Continuous irritation and damage to the bile duct can prompt scarring. This medical condition is known as sclerosing cholangitis. But it’s obscure what precisely this sickness is.
Almost a large portion of people with Sclerosing cholangitis don’t have symptoms. If an individual encounters symptoms, they may include:
- jaundice
- itching
- upper abdominal pain
- fever
An estimated 70–80 percent of the individuals with this condition experience ulcerative colitis. In this condition, the risk of liver cancer increases, which can be treated through a liver transplant.
Abscess of the gallbladder
When the gallbladder gets aggravated with pus, this condition is known as an abscess of the gallbladder. Symptoms may include abdominal pain in the upper section, fever, and chills. Learn more about abscess of the gallbladder.
Acalculous gallbladder disease
A gallbladder inflammation that happens without the existence of gallstones refers to acalculous gallbladder disease. It’s a considerable chronic illness or serious medical health condition. The symptoms of acalculous gallbladder disease are almost the same as those of acute cholecystitis with gallstones. Let’s explore more about Acalculous Gallbladder Disease.
Gangrene of the gallbladder
If your gallbladder creates insufficient blood circulation, it can develop gangrene. This is a severe complication for an individual with acute cholecystitis. Learn more about the Gallbladder gangrene.
Gallbladder cancer
Gallbladder cancer is a rare disease. However, there are various types of gallbladder cancer. These can be difficult to diagnose in the early stages and hard to treat. Let’s understand more about gallbladder cancer.
Gallbladder polyps
Gallbladder polyps are wounds or developments that happen inside the gallbladder. It’s typically benign with no symptoms. However, it is often recommended to go for gallbladder removal surgery for polyps bigger than 1 cm. It will have a higher chance of being cancerous.
Diagnosis of gallbladder disease
To diagnose gallbladder disease your doctor may prescribe the following tests:
- Detailed medical history.
- Physical exam
- Chest and abdominal X-ray
- Ultrasound and HIDA scan
- Other tests: CT scan, MRI scan, Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), and Blood Tests.
Treatment of gallbladder disease
Treatment of the gallbladder disease at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, as explained by the board-certified, experienced general surgeon Dr. Valeria Simone MD.
Changes in lifestyle and eating habits.
Certain medical conditions increase the risk of the development of gallstones, and changes in lifestyle and eating habits may help individuals deal with gallbladder disease without any symptoms. Individuals who are overweight and have diabetes increase their chances of having gallstones. Maintaining a healthy weight and controlling diabetes may help individuals reduce the risk.
However, drastic changes in weight or weight loss can lead to gallstone development. Speak to your physician about a healthy diet and exercise to maintain good health.
Medicines for gallbladder disease treatment
In its initial state, gallbladder disease is treated with pain medicines. At times, pain is serious, and your doctor prescribes the medication.
Over-the-counter medicines such as Aleve and Advil might not be taken as frequently since there is a higher risk of nausea and vomiting. In the circumstances of dehydration, the patient may experience kidney problems.
Please consult with your physician if you’re experiencing problems with pain management and its symptoms at home.
Gallbladder Surgery
Gallbladder Surgery, or cholecystectomy, will be prescribed to remove the gallbladder in case you’ve encountered various intervals of aggravation. Laparoscopic gallbladder surgery is the most recommended procedure for the treatment of gallbladder disease. Gallbladder surgery can be performed using any of the two methods:
Open Surgery: In this procedure, the general surgeon makes one large incision on the abdomen to remove the gallbladder.
Laparoscopic surgery, which is also known as minimally invasive surgery, is a procedure in which the doctor makes 3–4 small incisions in the abdomen to remove the gallbladder. The patient can get discharged from the hospital the same day after the gallbladder surgery and recovery time is also reduced, resulting in less blood loss and less scarring.
Individuals who have had gallbladder surgery may experience after-surgery impacts such as diarrhea that might last for a few weeks. However, in a few instances, it may last for about a year. If the patient experiences continuous diarrhea for about two weeks or more, contact your doctor.
What are the complications of Gallbladder Disease?
The gallbladder may form a strange way, or fistula, between the gallbladder and the digestive system to help manage the liver’s bile. This is generally the difficulty of ongoing chronic inflammation identified with gallstones.
There are various other complications, which can include:
- inflammation
- surgical scarring
- intestine obstruction
- malignant conversion-in this case, a change in cell goes through to turn into a cancerous tumor.
- an opening in the gallbladder known as perforation.
- Peritonitis, a bacterial infection of the abdomen
How to prevent gallbladder disease?
Many reasons contribute to gallbladder diseases, like sex and age, which can’t be altered. An individual’s eating regime may contribute to the formation of gallstones. To prevent gallstones, it is recommended to eat fiber-rich meals and eat healthy fats (Whole grains such as brown rice and whole wheat bread and healthy fats like fish and olive oil.)
Avoid meals such as sweet desserts and refined grains that include white rice, pasta, and bread, which are related to a greater risk of gallbladder disease.
If the gallbladder disease is identified and treated at an early stage, it is more uncertain whether critical complications will happen. It is always recommended to consult with your PCP in case you encounter any signs or symptoms of gallbladder disease.
Appointment
For more information on gallbladder disease – causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, surgery, and doctor consultation. Please contact our healthcare expert at +1 (817) 748-0200. You can also make an online appointment.
Follow us on Facebook