Gallbladder disease can harm your overall health. It’s crucial to understand it for quick diagnosis and treatment. The gallbladder may be small, but it serves a significant purpose in the body. It functions as a reservoir for bile and plays a crucial role in the digestion of fats.
If you’re experiencing abdominal pain or nausea, it’s a good idea to seek help early for any potential gallbladder issues. Treatments should be specific for each case because the disease can appear differently, like gallstones or inflammation.
By knowing about gallbladder disease, you can better care for your health and explore ways to reduce its effects.
Key Highlights
- The gallbladder is a small yet significant organ that contributes to your digestive system’s function. It stores and releases bile. Bile is important for digesting fats.
- Gallbladder diseases often occur because of gallstones. Gallstones may lead to pain in the abdominal region and digestion issues.
- If you feel severe abdominal pain, feel nauseous, vomit, or see jaundice, you should get medical help right away.
- To find out what is wrong, doctors usually look at pictures from ultrasounds or CT scans and may also do blood tests.
- Treatment can include lifestyle changes, medicines, or surgery to remove the gallbladder. This surgery is known as cholecystectomy.
The Gallbladder’s Role and Function

The gallbladder is a small organ located at the lowest part of the liver. It holds bile, which is necessary for digesting fats. Bile helps the body absorb fats. The liver makes bile constantly. The gallbladder stores it and releases it when necessary.
When we eat fatty foods, bile moves into our intestines. If the gallbladder does not function well, digesting fats can be tough. This may lead to digestive problems and result in not getting enough nutrients.
Understanding Bile’s Importance
Bile is a thick yellow-green substance that plays a crucial role in the digestive process of our food. It acts like soap to break down fats in the small intestine. The liver generates bile, which then moves through the bile ducts. Bile changes fats into small droplets. This makes it easier for us to absorb the fats.
- This mechanism helps the body in utilizing fats and absorbing vitamins that dissolve in fats.
- Issues with bile flow, such as gallstones or liver disease, can lead to serious digestion problems.
- When there is not enough bile, signs include diarrhea, fatty stools, and missing vitamins.
Understanding how bile ducts move bile is important. This helps us see how the liver and bile ducts work together in the digestive system. Liver disease can change this process.
How the Gallbladder Works with Your Digestive System
The gallbladder may be small in size, yet it plays a significant role in the digestive process. When you consume fatty foods, it triggers a response to activate its functions. It compresses and releases the bile it has accumulated.
- Bile plays a crucial role in breaking down lipids in the small intestine, aiding in their emulsification.
- It acts like a chef, cutting large fat pieces into smaller ones.
- This helps the small intestine handle fats more easily.
This teamwork helps the body break down and take in fats properly. It provides us with the energy and essential nutrients required for our well-being. Knowing how this works shows us how important the gallbladder is for a healthy digestive system.
Types of Gallbladder Diseases
Gallbladder diseases can affect the digestive system’s function. You can face issues like gallstones, inflammation, or even rare cancers.
These problems often happen because of bile imbalances or blockages in the ducts. It’s vital to know these condition’s types, causes, and symptoms. This knowledge aids in early detection, treatment, and better management.
Gallstones (Cholelithiasis) Explained
Gallstones, also known as cholelithiasis, are solid formations that develop within the gallbladder. They happen when bile’s components are not balanced. These stones can be of different sizes. They may block the bile ducts and cause severe pain. Common symptoms include:
- Experiencing discomfort in the abdominal region, particularly on the right side.
- Back pain, between your shoulder blades.
Doctors can detect gallstones using imaging tests. This includes CT scans or gallbladder radionuclide scans.
Treatment may involve medication or surgery, such as laparoscopic gallbladder removal. It is important to know how gallstones function and how to handle them when treating gallbladder disease.
Chronic Cholecystitis and Its Impact
Chronic cholecystitis happens when the gallbladder is inflamed for a long time. This usually comes after several cases of acute cholecystitis, or if gallstones keep causing pain. When you eat, the gallbladder contracts.
Over time, this can make the walls of the gallbladder thick and form scars. This could lead to problems, like a perforated gallbladder. If the gallbladder does not store and releases bile properly, it can upset digestion.
A common sign of chronic cholecystitis is a “gallbladder attack.” This attack can feel like sharp pain in the upper right abdomen. The pain might also radiate to the right shoulder. Many people say it feels like a golf ball is pressing on the area.
Eating fatty meals can sometimes cause these attacks. They can affect many parts of the body and make daily activities hard. It is important to know these symptoms and get medical help quickly.
Chronic inflammation can cause issues beyond just stomach problems. When the gallbladder stays inflamed for a long time, it may become infected. In some situations, it can even burst, which can impact the pancreatic duct. This can also raise the risk of cancer.
To manage chronic cholecystitis properly and reduce these risks, it is important to get a quick diagnosis and the right treatment.
Acalculous Gallbladder Disease Overview
Acalculous gallbladder disease represents a rare condition that impacts the gallbladder. It happens when the gallbladder becomes inflamed or doesn’t function properly, but there are no gallstones present. We don’t completely know what causes this condition. However, various elements could play a role in this, including:
- Not enough blood reaching the gallbladder
- Infections
- Problems with gallbladder movement
People with acalculous gallbladder disease can feel symptoms like those of gallstones, even if they do not have gallstones. They often feel severe pain in the upper right abdomen after they eat. This pain can be intense enough to necessitate a visit to the hospital’s emergency room.
Other common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, fever, and blood pressure changes. Due to the resemblance of these symptoms, diagnosing this disease can be quite challenging.
Doctors need to be careful and may have to use imaging tests and lab work together to figure out what is wrong.
Treatment for acalculous gallbladder disease is similar to other gallbladder issues. Healthcare professionals might suggest modifications to your nutritional intake for assistance.
They may also suggest ways to manage pain. In severe cases or if there are complications, doctors often advise gallbladder removal surgery.
Recognizing Symptoms of Gallbladder Issues

Gallbladder problems can show different signs that mean something is wrong. The most common symptom of gallbladder disease can change based on the issue.
A key sign is pain in the upper right abdomen. This pain may also spread to the shoulder or upper back, especially after eating fatty foods.
Other signs are digestive issues like nausea, vomiting, bloating, and changes in bowel habits. It is important to recognize these symptoms quickly to get medical help on time.
Identifying Biliary Colic and Its Causes
Biliary colic refers to pain associated with gallbladder complications. It can feel like intense cramps or a deep ache. You usually feel this pain in the upper right side of your abdomen, right below your ribs. Biliary colic is unique because it can hit suddenly and strongly, especially after eating a fatty meal.
- A common cause of biliary colic is a gallstone that gets stuck in the cystic duct for a short time.
- The gallbladder and the common bile duct are connected by this duct.
- When this duct is blocked, bile cannot flow as it should.
- The gallbladder then squeezes tightly to try to move the blockage, causing sharp pain and spasm.
These painful episodes often disappear in a few hours once the blockage is cleared. However, you should pay attention if you still feel biliary colic. It might be an early sign of gallbladder disease. This could need more tests and proper treatment.
Signs of Acute vs. Chronic Cholecystitis
Knowing the difference between acute and chronic cholecystitis is important for getting the right medical help. Here are the main points that explain how these two types of conditions are not the same:
Acute cholecystitis:
- The cystic duct can become obstructed due to the presence of a gallstone.
- This can cause sudden and intense pain in the upper right abdomen.
- The feeling of pain is intense and resembles a piercing sensation. It gets worse when you move or take deep breaths.
- At times, discomfort may radiate to your right shoulder blade or back area.
- You might also feel fever, nausea, vomiting, and tenderness in the upper right abdomen.
Chronic cholecystitis:
- It forms slowly over time.
- You feel mild pain and discomfort in the upper belly multiple times.
- A dull, aching pain often happens after eating, especially with fatty foods.
- Fever and throwing up can happen, but they are less common than in acute cholecystitis.
- This shows long-term inflammation of the gallbladder, usually caused by several acute episodes or irritation from gallstones.
It is very important to know the difference between these two types of cholecystitis. Chronic cholecystitis usually needs surgery. This surgery helps stop more serious problems and makes a person feel better in their daily life.
Understanding Choledocholithiasis Symptoms
Choledocholithiasis occurs when gallstones get stuck in the bile duct. This is a serious kind of gallbladder disease. The blockage stops bile from flowing properly from the liver and gallbladder to the small intestine. This condition can cause several symptoms that need quick medical help.
- When stones become lodged in the common bile duct, they can induce significant discomfort in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen.
- This pain could radiate to the back or the right shoulder.
- It can feel like a gallbladder attack and may come with other signs. These signs include fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, and jaundice.
- Jaundice results in a yellowish appearance of the skin and the sclera (whites of the eyes).
- Bilirubin, a pigment present in bile, can accumulate in the blood when there is a blockage, leading to this condition.
Cholecystitis is when the gallbladder becomes swollen. This problem often occurs with a condition called choledocholithiasis. This condition makes it harder to tell what is wrong.
It is key to knowing the signs of choledocholithiasis. If you get help quickly, you can lower the risk of serious problems. These problems can be infections, pancreatitis, and liver damage.
Risk Factors for Developing Gallbladder Disease
Some things can increase the chance of getting gallbladder disease. Factors include age, genetic predisposition, and the probability of developing gallbladder cancer.
Lifestyle choices matter a lot. You can change them to lower the risk. By understanding these factors, people can make healthier choices and avoid this painful problem. If we concentrate on the risk factors we can control, we can keep our gallbladder healthy.
Gender and Age Considerations
When talking about gallbladder disease, age and gender are important factors. Women have a higher chance of gallstone disease compared to men. The exact reasons for this difference are not fully known. It could be related to hormonal changes, especially estrogen.
Estrogen can affect cholesterol in bile. This change may increase the risk of getting gallstones and common bile duct stones. This risk is greater during pregnancy or when using hormone therapy.
Age matters when we look at risk. Our bodies change as we grow older. This includes the amount of bile our body produces and how well our gallbladder works. These changes can cause gallstones. Gallstones are the main reason for gallbladder disease.
Both men and women feel the changes that come with aging, but women over 40 have a higher risk. This shows that hormones and age play key roles. Understanding these differences can help in finding gallbladder disease earlier. Early detection can lead to quicker treatment.
Lifestyle and Diet Influences

The phrase “you are what you eat” carries importance for the well-being of your gallbladder. What you choose to eat can affect your chances of getting gallbladder disease.
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial. A well-rounded diet is essential for maintaining optimal health. Some eating habits can help prevent gallbladder issues, while others can increase the risk.
Maintaining a healthy weight is very important. You can achieve this by eating good food and exercising regularly. If a person is overweight, their chance of getting gallstones increases. This happens because extra weight changes the way bile works in the gallbladder.
However, losing weight too quickly can also increase this risk. When you lose weight fast, your body puts more cholesterol into the bile.
To support your gallbladder, focus on this type of diet:
- Foods High in Fiber: These consist of produce, plant-based foods, and unrefined cereals.
- Good Fats: This has avocados, almonds, and olive oil as its components.
Fewer Processed Foods: It is better to avoid sugary drinks, refined grains, and unhealthy fats.
Genetic Predisposition and Other Risks
Lifestyle choices can have a big effect on gallbladder health in the United States. But genetics is also important for red blood cells.
If you have a family history of gallstones, especially in close relatives, your chance of developing them might be higher. This is because the traits passed down in your family can change how bile is produced or how well the gallbladder works.
- Diabetes can change how the body manages cholesterol. This might increase cholesterol levels in bile.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and blood problems like sickle cell anemia can increase the risk of gallbladder issues.
- Conditions such as primary sclerosing cholangitis can block bile flow. This may lead to complications and various issues.
By learning about these genetic and health risks, you can receive early assistance. You can also keep an eye on your gallbladder health.
Diagnostic Approaches for Gallbladder Disease
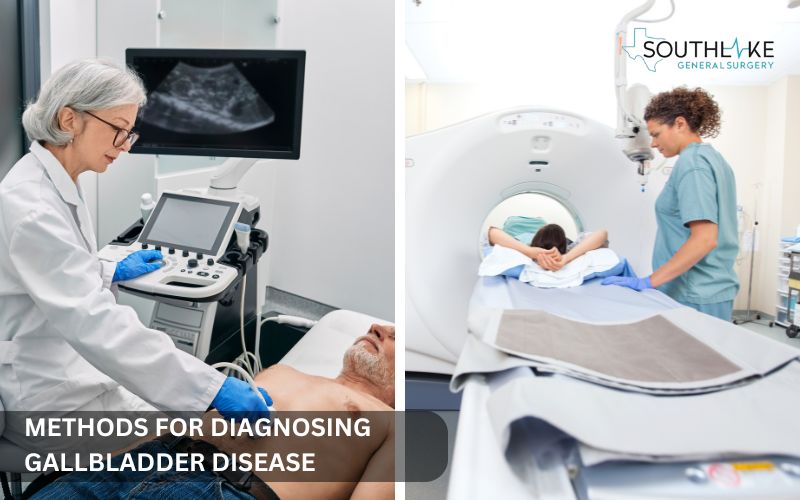
Diagnosing gallbladder disease begins by looking at the patient’s medical history and symptoms. This step is important for picking the right tests.
Imaging tests are crucial for spotting problems and checking how well the gallbladder functions. Blood tests are used to assess liver health and check for inflammation. The details from these tests help doctors choose the best treatment.
Utilizing Imaging Techniques for Diagnosis
Multiple approaches can be utilized for this, which include:
- Ultrasounds: This test uses sound waves to create live pictures of the gallbladder and nearby areas. It helps find gallstones and check for inflammation of the gallbladder. It can also show if there are blockages in the bile ducts.
- CT scan: Provides detailed images. It helps find issues like abscesses, pancreatitis, or tumors.
- HIDA scan: Assess the efficiency of the gallbladder in its functions of bile storage and release.
Imaging tests are important. They help discover where there is gallbladder disease and how serious it is. This information is good for making choices about treatment.
The Role of Laboratory Tests
Imaging techniques help us see problems with the gallbladder. Laboratory analyses provide crucial insights into the body’s responses.
Blood tests are key in diagnosing these issues. They share vital details about liver function, signs of infection, and overall health.
- Tests for liver function evaluate the concentrations of particular enzymes and proteins synthesized by the liver.
- If these levels are higher than usual, it could mean there is inflammation, damage, or a blockage in the liver or bile ducts.
- This information helps us understand how serious gallbladder disease is.
- Blood tests can provide insights into the presence of infection.
- This is very important when gallstones block the bile duct.
- A rise in white blood cell counts is a common sign of infection. This needs quick medical care to avoid issues like sepsis.
- By using information from imaging and blood tests, doctors can fully assess the situation and create effective treatment plans for people with gallbladder disease.
Treatment Options for Gallbladder Disease
Treating gallbladder disease depends on the problem and how serious it is. Some people may only need to change their habits and keep an eye on their condition. Some individuals may require medication or possibly surgical procedures.
Knowing the different types of treatments can help patients choose wisely. These options range from simple solutions to more serious ones. By learning about them, patients can make smart choices with help from their doctors.
Non-Surgical Management Strategies
In situations where gallbladder disease is found early or shows mild symptoms, non-surgical treatments can be the best choice.
These methods focus on managing symptoms, preventing issues, and helping the gallbladder stay healthy. For example, changing your diet can help reduce symptoms a lot, especially for those who have gallstones.
- Avoid high-fat foods. This can stop gallbladder contractions and reduce pain.
- Eat a balanced diet. It includes fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. This helps with good digestion and eases discomfort.
- Doctors may prescribe medication. This can dissolve small cholesterol gallstones or help manage pain.
For bile duct stones, doctors can use a procedure known as ERCP. They use an endoscope along with special tools. This helps remove blockages and get bile flow back to normal.
If a person has high-risk gallbladder polyps, the doctor may suggest surgery to reduce the risk of cancer.
Surgical Interventions: Cholecystectomy Explained
When simple treatments do not help or gallbladder issues get worse, surgery might be needed. This surgery is called cholecystectomy. The procedure involves the removal of the gallbladder and is widely regarded as a common and safe choice.
The doctors make small incisions. They use a thin tube camera and special tools to take out the gallbladder. This method has several advantages. It causes less pain, helps you heal faster, and leaves small scars.
- Laparoscopic surgery is a less invasive option. It makes small incisions and uses a laparoscope with special tools to remove things. Most people can go home the same day or stay just overnight. Recovery takes less time as well.
- Open surgery represents a conventional approach to surgical procedures. It needs a larger incision and is used for more complicated problems or if laparoscopic surgery does not work. This usually means a longer hospital stay and more time to heal.
Open surgery is essential for handling more intricate scenarios. These can be serious swelling, infections, or anatomical problems.
When choosing between laparoscopic surgery and open surgery, several factors are important. They consist of the person’s overall health, the complexity of the gallbladder issue, and the skills of the surgeon.
Conclusion
Understanding gallbladder disease is very important. It helps you get the right diagnosis and treatment. You should know the signs and risky factors. A family history of gallbladder issues and rapid weight loss are key examples.
Many problems can affect your gallbladder, such as gallstones and chronic cholecystitis. Each problem needs a different type of treatment.
There are choices for treatment. These can be non-surgical or include laparoscopic gallbladder removal. It is important to act early to manage these issues. If you feel abdominal pain, especially in the upper right abdomen, see a healthcare professional.
This can help prevent serious problems like gallbladder cancer. Stay informed and eat whole grains. Don’t hesitate to ask for medical advice if you are worried about your gallbladder’s health.
Make an Appointment
To set up a meeting with Dr. Valeria Simone, MD, call +1 (817) 748-0200. She is an experienced general surgeon at Southlake General Surgery in Texas, USA. Dr. Simone focuses on gallbladder issues.
This includes treatments like laparoscopic gallbladder removal. If you have problems like abdominal pain or weight loss, please call for a full evaluation. You will receive a personalized care plan. Start caring for your gallbladder health by booking your appointment today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the early signs of gallbladder problems?
Abdominal pain is a frequent problem. It often happens in the upper right abdomen. This pain can get worse after you eat fatty foods. At times, it might also feel like it is spreading to the right shoulder. If you feel this kind of pain, you could have a gallbladder attack or dealing with chronic cholecystitis. Moreover, if you have chronic diarrhea, it might mean your body is not digesting fats well. This could be due to problems with your gallbladder.
Can gallbladder disease be managed without surgery?
Yes, it is possible to address chronic gallbladder disease in certain cases without the need for surgical intervention. A healthier lifestyle can really help. This includes eating a diet that is lower in fat. There are also medicines available that can help dissolve stones or ease pain. However, if your symptoms do not improve or start to get worse, surgery may be needed.
Do Doctors often misdiagnose Gallbladder disease?
Doctors may occasionally misdiagnose gallbladder disease because symptoms can mimic other conditions. It’s crucial to undergo diagnostic tests like ultrasound, CT scans, or blood tests for an accurate diagnosis. Seeking a second opinion if symptoms persist is always advisable to ensure proper treatment.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
References:
- Descoteaux-Friday, G. J., & Shrimanker, I. (2023, August 7). Chronic diarrhea. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544337/
- Menon, G., & Babiker, H. M. (2024, August 17). Gallbladder carcinoma. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK442002/
- Jones, M. W., Genova, R., & O’Rourke, M. C. (2023, May 22). Acute cholecystitis. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459171/
- Tanaja, J., Lopez, R. A., & Meer, J. M. (2024, August 17). Cholelithiasis (Archived). StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470440/
- Jones, M. W., Gnanapandithan, K., Panneerselvam, D., & Ferguson, T. (2023, August 8). Chronic cholecystitis. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470236/
- Coucke, E. M., Akbar, H., Kahloon, A., & Lopez, P. P. (2022, November 26). Biliary obstruction. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539698/
- Ji, Y., Huang, W., Guo, J., & Hu, B. (2024). Endoscopic management of benign gallbladder diseases. The Turkish Journal of Gastroenterology, 35(9), 681–689. https://doi.org/10.5152/tjg.2024.24149
- Morimoto, M., Matsuo, T., & Mori, N. (2021). Management of porcelain gallbladder, its risk factors, and complications: a review. Diagnostics, 11(6), 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11061073
- Wanjara, S., & Kashyap, S. (2023, January 23). Bile duct stricture. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559217/
- Shin, Y., Choi, D., Lee, K. G., Choi, H. S., & Park, Y. (2017). Association between dietary intake and postlaparoscopic cholecystectomic symptoms in patients with gallbladder disease. The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine, 33(4), 829–836. https://doi.org/10.3904/kjim.2016.223