Gallbladder function plays a vital role in digestive health, storing bile from the liver to facilitate fat digestion and nutrient absorption, highlighting its importance in overall gastrointestinal well-being.
Our digestive system would be incomplete without the gallbladder, a small yet vital organ that assists in breaking down and absorbing fats from the foods we eat. This guide will explain how the gallbladder function, cover common problems it may have, and suggest ways to keep it healthy.
Key Highlights
- The gallbladder is a small organ that plays an important role in the process of digestion. The liver is responsible for producing bile, which is then stored and eventually discharged.
- Bile plays a crucial role in the digestion of fats within the small intestine. This makes it easier for our bodies to absorb and use fats.
- A common issue with the gallbladder is gallstones. They can cause pain, swelling, or other problems that might need help from a healthcare provider.
- Staying at a healthy weight is one of the best things you can do for your gallbladder. A balanced diet with lots of fiber and low in saturated fats is helpful. Also, staying active is important.
- If you feel severe or ongoing abdominal pain, especially after eating, you should see a healthcare provider. They can check for any gallbladder problems.
Understanding the Gallbladder’s Role
When it comes to digestion, the gallbladder is essential. Bile storage and thickening are the principal roles of this organ. The liver secretes bile, a color ranging from greenish yellow, into the bloodstream.
Bile contains bile salts, cholesterol, and various other components that play a crucial role in helping us digest and absorb fats. You can find the gallbladder on your right side in the abdomen.
When we eat, especially fatty foods, hormones tell the gallbladder to squeeze. This results in the bile being propelled into the small intestine.
The gallbladder is a storage space. It keeps bile until we need it for digestion. This storing and releasing of the bile helps our digestion. It makes sure that bile is ready whenever we need it.
The Importance of Bile in Digestion
Bile is very important for breaking down and absorbing fats in our digestive tract. If we don’t have bile, our body cannot break down fats into smaller pieces. This can cause problems when trying to absorb essential fatty acids and fat-soluble vitamins.
- Eating fatty foods causes your gallbladder to contract and release bile, which is an important part of digestion.
- When this bile combines with the fats, it breaks them down into tiny droplets.
- This method improves the efficiency of digestive enzymes by increasing the lipids’ surface area.
Emulsifying fats is key for us. It assists our bodies in absorbing fats, vitamins, and various other nutrients. Bile plays a big role in breaking down fats. To maintain good health, this procedure is necessary.
How the Gallbladder Interacts with the Liver and Intestines
The gallbladder, liver, and intestines are linked by tubes called the biliary tree. They work together in this way:
- The liver makes bile. The gallbladder stores this bile after it travels through the hepatic ducts.
- When food enters the small intestine, the body releases a hormone called cholecystokinin (CCK). The gallbladder responds to this hormone by secreting the bile.
- Bile is transferred from the gallbladder to the common bile duct when the sac contracts. After that, the bile makes its way to the duodenum.
- Bile mixes with food in the duodenum, playing an important role in digestion. This helps break down fats so the body can digest and absorb them better.
Anatomy and Structure of the Gallbladder
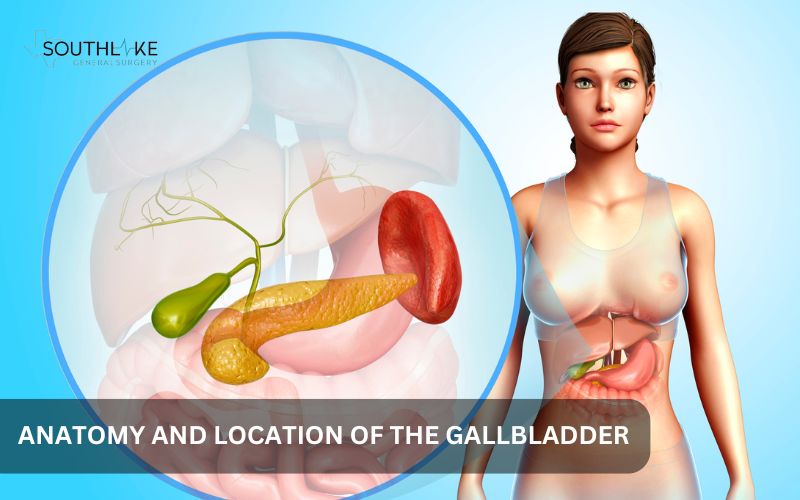
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ. It is positioned beneath the liver on the right side of the abdominal area. There are two main gastrointestinal systems that are connected to the gallbladder: the small intestine and the liver. It does this through several tubes that make up the biliary system.
The gallbladder is small, but it is very important for digestion. Knowing where it is and what it looks like helps us understand what it does. This understanding shows us how diseases can affect the biliary system.
Detailed Look at Gallbladder Location
In the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, just beneath the liver, you’ll find the gallbladder. It is near the abdominal wall. Because of this position, you can easily feel it if the gallbladder is swollen or irritated.
- The gallbladder does not connect directly to the liver. It connects to the liver with a tube known as the cystic duct.
- The common hepatic duct is another tube that connects to the cystic duct. This duct transports the bile generated by the liver. The term used to describe this system of tubes is the common bile duct.
- The common bile duct plays an important role in transporting bile to the duodenum, a section of the small intestine.
When you have gallbladder pain, you can feel it most in the upper right part of your belly. At times, this pain can also spread to the back or shoulder.
Variations in Gallbladder Anatomy
The gallbladder usually looks like a pear. But its size and shape can be different for each person. Some might even have more than one gallbladder. Most of the time, these changes do not cause any symptoms. We often discover them by accident when doing X-rays or surgeries.
Transferring bile from the gallbladder to the liver is facilitated by the cystic duct. This duct can be of different lengths and connect to the common bile duct in several ways. Some people have a special shape of the gallbladder, known as a Phrygian cap.
As an organ, the gallbladder aids in the digestive process. It has a thin layer of connective tissue and hollow ducts that reach the first section of your small intestine. Some people may have a septated gallbladder, which means it has a wall that divides it into two parts.
Most of these differences are safe. They have no impact on the functionality of the gallbladder. However, in rare cases, they can make surgery harder. Some gallbladder problems could be worsened by this as well.
Common Gallbladder Conditions and Symptoms

The gallbladder can have many issues. These can be gallstones or more serious problems, like gallbladder cancer. The key is to spot these problems before they escalate.
Doing so allows for prompt treatment and better results. If you notice the signs quickly, you can get the care you need sooner. This can reduce complications and improve your health outcomes.
Identifying Gallstones: Causes and Effects
Gallstones are small hard pieces that can form in your gallbladder. A lot of people have this problem. Gallstones happen when bile, which helps with digestion, has too much cholesterol or bilirubin or even both.
Some risk factors can cause gallstones.
- Being overweight
- Fast weight loss
- Diets high in fat
- Family history of gallstones
- Certain health problems like diabetes
Many people with gallstones do not feel pain. However, some may feel pain if the stones block the biliary tract. The symptoms can include:
- Severe, abrupt pain in the abdominal region
- Pain that moves to the back or shoulder
- Feeling nauseous and vomiting
- Uneasy stomach
- The skin and eyes turn yellow when you have jaundice
Cholecystitis: Symptoms and Treatment Options
Cholecystitis involves painful inflammation of the gallbladder. This usually happens because a gallstone blocks the cystic duct. Through the cystic duct, the gallbladder is linked to the common bile duct. When this duct is blocked, the bile can start to build up.
The signs of cholecystitis can feel a lot like a gallbladder attack. However, cholecystitis is usually more serious and it lasts longer. Some symptoms may include:
- There is severe pain in the upper right abdomen that worsens with deep breaths.
- A fever is present.
- There may be nausea and vomiting.
- A loss of appetite is common.
- The skin might turn yellow, which is called jaundice.
- Medications to reduce pain and inflammation
- A special diet that is low in fat
- Cholecystectomy, the surgical removal of the gallbladder, may be necessary in some cases
- Fluids and rest to help heal the body
- Antibiotics to help with infection
- Pain medicine
- IV fluids
Diagnostic Approaches for Gallbladder Health

Diagnosing gallbladder problems includes a few steps. First, doctors examine the body and note the symptoms. Next, they use imaging tests to help. An ultrasound is usually the first two tests performed. It is a safe method to see the gallbladder and find any problems.
If doctors want clearer images, they may use specific methods like magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). These methods are important for selecting the right treatment. They also help make sure that patients get good care.
Ultrasound: A Non-Invasive Diagnostic Tool
Ultrasound is a simple and safe test. It helps doctors check how well the gallbladder is working. This test creates images of the gallbladder, bile ducts, and nearby areas. There is no need for surgery, even laparoscopic surgery.
Ultrasound uses sound waves to detect problems. It can reveal issues like gallstones, swelling, or changes that are not normal. This helps with the diagnosis of gallstones. Doctors might also ask for blood tests to gather more information about gallbladder issues.
This type of imaging helps doctors, like Dr. Valeria Simone, MD, find and keep track of problems with the gallbladder. This is important for creating good treatment plans at Southlake General Surgery in Texas, USA.
Advanced Imaging Techniques
Ultrasound is good at finding most gallbladder problems. However, sometimes you might need better imaging methods.
- Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is another kind of MRI. It provides clear images of the biliary tree, including the bile ducts in the liver, the gallbladder, and the pancreas. Because it does not involve radiation, this test is completely safe for the human body.
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a minor surgery. A thin, flexible tube with a camera is used along with X-rays. This helps to see and fix issues in the biliary and pancreatic ducts.
These advanced imaging methods provide clear details about the biliary system. They assist doctors in finding and diagnosing both serious and mild gallbladder problems.
Strategies for Maintaining Gallbladder Health

Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is key for good gallbladder health. Eating healthy foods and exercising regularly can help prevent gallstones.
Choosing foods that support digestion is also important. Understanding how your diet and weight influence your gallbladder health helps you make better choices. This can reduce your chances of having gallbladder problems later.
Diet and Lifestyle Adjustments
Having a healthy lifestyle is important for your gallbladder. A good diet is crucial to prevent gallstones. Eating well also helps your gallbladder work correctly.
Here are a few suggestions regarding your diet:
- Add high-fiber foods: Eat more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These help keep your digestion regular and can prevent gallstones.
- Choose healthy fats: Use unsaturated fats from olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds. Try to lower your intake of saturated and trans fats.
- Stay hydrated: Make sure to drink lots of water every day. This supports digestion and bile flow.
Making changes in your daily life can help reduce the risk of gallbladder problems. Staying active and keeping a healthy weight can really do wonders for you.
Understanding the Impact of Weight and Diet
Maintaining a healthy weight is very important for good gallbladder health. If you are overweight, particularly with extra weight around your belly, your chances of getting gallstones are higher. If you lose weight too quickly, it might lead to gallstones.
This can happen through quick diets or weight loss surgery. Quick weight loss changes the bile in your body. These changes can lead to problems. In severe cases, you might need to have the removal of the gallbladder to fix these issues.
- What you eat can affect how well bile works and your gallbladder health.
- A diet that has a lot of saturated fats and cholesterol can raise cholesterol levels in bile. This can lead to gallstones.
- Eating a balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats helps you stay at a good weight. It also promotes healthy bile flow, lowering the chances of gallbladder problems.
Conclusion
The gallbladder is important for good health. It stores bile, which helps with digestion. If there are problems with the gallbladder, your health can be seriously affected.
Therefore, getting the right diagnosis and treatment on time is very important. To keep your gallbladder healthy, eat a balanced diet and make smart choices in your lifestyle.
If you notice any symptoms of gallbladder problems, you should see a healthcare provider as soon as possible. Don’t forget that the gallbladder is a critical part of the digestive system.
It’s important not to ignore any issues. Take care of your health and speak to a doctor about any concerns about your gallbladder health.
Make an Appointment
If you need help with your gallbladder health, you can meet Dr. Valeria Simone, MD an experienced general surgeon at Southlake General Surgery in Texas, USA. To make an appointment, just call +1 (817) 748-0200.
Dr. Simone knows a lot about gallbladder problems. She can give you detailed check-ups and plans for treatment that work for you. You can trust her skills to help you have good gallbladder function and feel better.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Gallbladder Problems Be Prevented?
Sometimes, you just can’t avoid gallbladder issues. But you can lower your risk factors by staying healthy. It’s all about eating a balanced diet, staying active, and maintaining a healthy weight.
How Do You Know It’s Time to Visit the Doctor?
If you feel a lot of pain in your upper right abdomen that doesn’t go away for several hours, you should see a doctor right away. This is very important if you also feel a fever, feel sick to your stomach, throw up, or see a yellow color in your skin or eyes.
What happens to your body when your gallbladder is bad?
When your gallbladder has problems from gallbladder disease, it may prevent bile from flowing the right way. This blockage can cause issues with digestion. If bile builds up in the liver or digestive tract, you may feel pain and discomfort.
Is there a link between gallbladder health and other digestive issues?
Yes, digestive and biliary functions are assisted by the gallbladder. Problems with the gallbladder can affect other organs that help with digestion. For example, if the bile duct is blocked, it might cause issues in the pancreas. This happens because the common bile duct and the pancreatic duct take the same path. Some people may also face digestive problems, like diarrhea, after gallbladder removal. This happens as their body gets used to living without the gallbladder.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
References:
- Jones, M. W., Small, K., Kashyap, S., & Deppen, J. G. (2023, May 1). Physiology, Gallbladder. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482488/
- Jones, M. W., Weir, C. B., & Ferguson, T. (2023, August 7). Porcelain Gallbladder. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK518979/
- Kalakonda, A., Jenkins, B. A., & John, S. (2022, September 12). Physiology, Bilirubin. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470290/
- Reynolds, W., Jr. (2001, March 1). The First Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3015420
- Jones, M. W., Weir, C. B., & Ghassemzadeh, S. (2024, August 17). Gallstones (Cholelithiasis). StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459370/
- He, L., Wang, J., Ping, F., Yang, N., Huang, J., Li, Y., Xu, L., Li, W., & Zhang, H. (2022). Association of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Use With Risk of Gallbladder and Biliary Diseases. JAMA Internal Medicine, 182(5), 513. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.0338
- Jones, M. W., Gnanapandithan, K., Panneerselvam, D., & Ferguson, T. (2023, August 8). Chronic Cholecystitis. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470236/
- Lee, J. M., & Boll, D. T. (2018). Disease of the Gallbladder and Biliary Tree. In IDKD Springer series (pp. 49–56). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-75019-4_5
- Naganuma, S., Ishida, H., Konno, K., Hamashima, Y., Hoshino, T., Naganuma, H., Komatsuda, T., Ohyama, Y., Yamada, N., Ishida, J., & Masamune, O. (1998). Sonographic findings of anomalous position of the gallbladder. Abdominal Radiology, 23(1), 67–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002619900287
- Meyer, G., Guizzardi, F., Rodighiero, S., Manfredi, R., Saino, S., Sironi, C., Garavaglia, M. L., Bazzini, C., Botta, G., Portincasa, P., Calamita, G., & Paulmichl, M. (2005). Ion Transport Across the Gallbladder Epithelium. Current Drug Targets – Immune Endocrine & Metabolic Disorders, 5(2), 143–151. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568008054064805