Gallbladder sludge, also known as biliary sludge, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of small particles in the gallbladder.
This sludge is composed of cholesterol monohydrate crystals, calcium bilirubinate pigment, and other calcium salts that precipitate from bile.
While gallbladder sludge is not as well-known as gallstones, it can still cause significant discomfort and lead to complications if left untreated.
Bile production by the liver is mainly stored by the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver. Bile plays a crucial role in the digestion of fats, helping to break them down into smaller particles for absorption.
When the concentration of cholesterol or calcium salts in the bile is too high, these substances can form small particles that contribute to the formation of gallbladder sludge.
This article will delve into the reasons, signs, identification, and treatment possibilities for gallbladder sludge. It will also cover lifestyle changes that can prevent sludge formation and enhance gallbladder health.
If you suspect gallbladder sludge or are showing symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a medical professional for an accurate diagnosis and suitable treatment recommendations.
Key Highlights
- Biliary sludge is made up of crystals of cholesterol, calcium bilirubinate, and other precipitated calcium salts.
- Gallbladder sludge can cause nausea, abdominal pain, and stools that look like clay.
- Gallbladder sludge can be diagnosed through abdominal ultrasound and medical tests to determine the underlying cause.
- Treatment options for gallbladder sludge include medications to dissolve the sludge, lifestyle changes, and in severe cases, gallbladder removal.
- To avoid gallbladder sludge, it’s important to make lifestyle changes like eating a low-fat, low-cholesterol diet and exercising regularly.
- If you are experiencing symptoms of gallbladder sludge, it is important to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
What is Gallbladder Sludge?
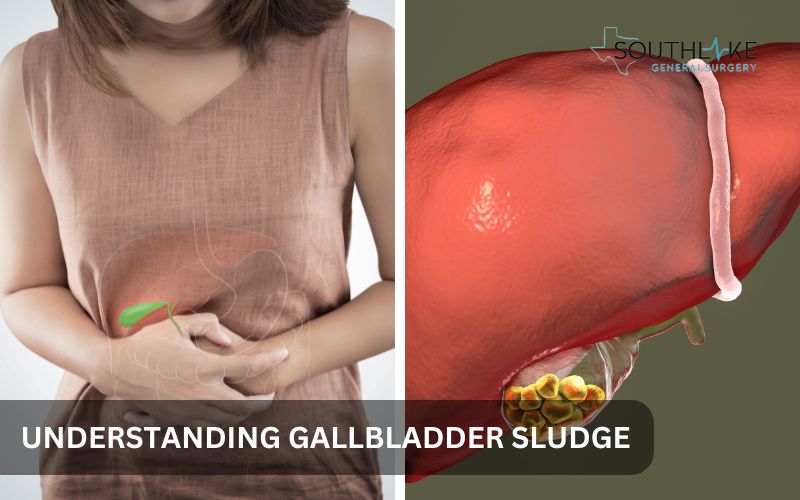
When bile and cholesterol build up in the gallbladder, the result is gallbladder sludge. It produces gastrointestinal problems and is a risk factor for gallstones. Understanding its composition is crucial for early detection and treatment.
Defining Gallbladder Sludge and Its Composition
Gallbladder sludge consists of microscopic particles, including cholesterol crystals, calcium salts, and other substances found in bile.
It is a viscous, mucus-like material that can accumulate in the gallbladder. This sludge can lead to the formation of gallstonesover time if not addressed.
Understanding the composition of gallbladder sludge is crucial in diagnosing and managing related conditions effectively.
Proper evaluation of gallbladder sludge composition can provide insights into the underlying causes and guide treatment decisions.
The Role of the Gallbladder in Digestive Health
The gallbladder plays a crucial role in digestive health by storing and concentrating bile produced by the liver. Bile, containing cholesterol, bile salts, and bilirubin, aids in digesting fats.
When fats enter the small intestine, the gallbladder releases bile through the bile duct to emulsify fats for better absorption.
This process supports nutrient assimilation and overall digestive function, highlighting the vital role of the gallbladder in maintaining a healthy digestive system.
Symptoms of Gallbladder Sludge
Abdominal pain, particularly in the upper right side, is a common symptom of gallbladder sludge. Other signs include:
- upper abdominal pain
- weight loss
- acute cholecystitis
- individuals may experience biliary colic or acute pancreatitis
It’s crucial to note any symptoms promptly and seek medical evaluation if needed. Symptoms indicating gallbladder issues should not be ignored, especially if accompanied by risk factors like obesity or high cholesterol levels.
Accurate diagnosis and prompt treatment are possible outcomes of familiarity with and awareness of these symptoms.
Common Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Keep track of these symptoms for a better understanding of your health. Consult a physician if these symptoms continue to be present.
- Abdominal pain, especially on the upper right side, is a common indicator.
- Possible problems include unexplained weight loss and bloating or gas after eating.
- Look out for episodes of nausea and bloating after consuming fatty foods.
- Persistent indigestion and flatulence might point towards gallbladder problems.
- Beware of lighter-colored bowel movements.
How to Know If Your Gallbladder Needs Medical Attention
If you experience persistent abdominal pain, especially on the upper right side, along with other symptoms like nausea, vomiting, or jaundice, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention for gallbladder issues.
Additionally, if you notice sudden and unexplained weight loss, fever, or unusual changes in bowel habits, consulting a healthcare provider is recommended.
Early evaluation and diagnosis can help in preventing complications such as acute cholecystitis or acute pancreatitis. It’s vital to address any concerning symptoms promptly to avoid worsening of the condition.
Causes and Risk Factors of Gallbladder Sludge
Gallbladder sludge can develop due to various factors, including rapid weight loss, high levels of calcium salts, and underlying medical conditions such as liver disease.
Factors like obesity, pregnancy, and a diet high in cholesterol can also contribute to sludge formation. Those with a history of gallstone disease are at an increased risk.
Understanding these causes and risk factors is crucial in preventing the development of gallbladder sludge and associated complications.
Understanding the Main Causes of Gallbladder Sludge
The formation of gallbladder sludge primarily stems from imbalances in bile components, such as excessive cholesterol or calcium bilirubinate.
Factors like rapid weight loss, high cholesterol levels, and underlying liver diseases can contribute to sludge formation. Conditions like biliary microlithiasis or biliary colic may also escalate the risk.
Understanding these causes is vital for preventive measures and early intervention to manage gallbladder sludge effectively. Early detection through medical tests like CT scans and awareness of risk factors play a crucial role in addressing this condition.
Lifestyle and Health Conditions That Increase Risk
Factors like obesity, quick weight reduction, and cholesterol-rich diets can heighten the likelihood of developing gallbladder sludge.
Furthermore, health issues such as liver disease, pregnancy, and a genetic predisposition to gallstones can increase vulnerability to this condition.
People with existing medical problems like acute pancreatitis or acute cholecystitis are also at a greater risk. Adopting a healthy lifestyle with a well-rounded diet, consistent physical activity, and weight control can assist in reducing these risks.
Diagnosing Gallbladder Sludge
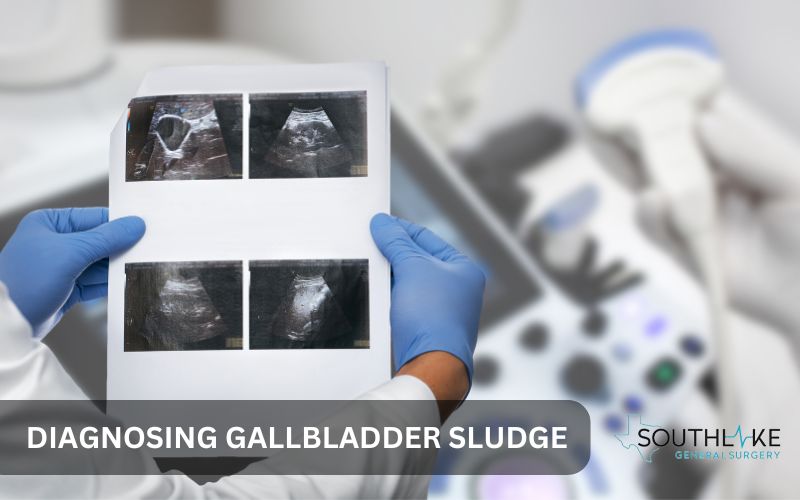
Medical tests like ultrasound and CT scans are used to diagnose gallbladder sludge accurately. These imaging methods can detect sludge or particles in the gallbladder.
A physical exam focusing on symptoms like abdominal pain is also helpful. Early diagnosis is key for effective treatment planning due to gallbladder sludge’s impact on overall health.
Medical Tests and Imaging for Detecting Gallbladder Sludge
Medical tests and imaging play a crucial role in detecting gallbladder sludge. Typically, ultrasound is the primary imaging modality used to visualize the gallbladder. It can detect thickened bile, stones, or sludge with remarkable accuracy.
Additionally, CT scans and MRIs may provide detailed images to confirm the presence of sludge. Blood tests to check liver function and assess for signs of inflammation can also aid in diagnosis.
Combining these diagnostic tools helps healthcare providers formulate an effective treatment plan.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of gallbladder sludge is crucial for effective management. Detecting sludge in its initial stages enables timely intervention to prevent complications like acute pancreatitis or cholecystitis.
Medical tests such as CT scans play a key role in diagnosing sludge formation accurately. Asymptomatic patients may benefit from early detection through routine screenings, ensuring prompt medical attention if needed.
Early diagnosis not only aids in formulating appropriate treatment plans but also contributes to a smoother recovery process.
Treatment Options for Gallbladder Sludge

Non-surgical approaches and lifestyle modifications are initial steps for managing gallbladder sludge. These include dietary adjustments and maintaining a healthy weight.
It is possible to dissolve small particles with the help of medications such as ursodeoxycholic acid. However, if symptoms persist or complications arise, surgical intervention such as gallbladder removal might be necessary.
Consulting a healthcare provider to discuss personalized treatment plans is crucial for addressing gallbladder sludge effectively.
Non-Surgical Treatments and Lifestyle Changes
Non-surgical treatments for gallbladder sludge focus on lifestyle adjustments and medication.
- Lifestyle changes include maintaining a balanced diet low in cholesterol and high in fiber, staying hydrated, and achieving a healthy weight.
- Ursodeoxycholic acid and similar medications may help in the dissolution of the sludge.
- Avoiding rapid weight loss is crucial, as it can worsen the condition.
These approaches aim to manage symptoms and prevent complications without the need for surgery. Lifestyle modifications play a key role in promoting overall digestive health.
Surgical Options: When Gallbladder Removal is Necessary
Surgical intervention, particularly gallbladder removal, becomes essential in severe cases of gallbladder sludge. When symptoms persist despite non-surgical treatments or complications like acute cholecystitis emerge, surgical options are considered.
The presence of large gallstones obstructing the bile duct or recurrent episodes of biliary colic may also warrant gallbladder removal.
Surgeons may opt for laparoscopic cholecystectomy to extract the gallbladder. It is crucial to discuss the necessity of this procedure with a healthcare provider to address the underlying cause effectively.
Recovery After Gallbladder Surgery
Following gallbladder surgery, expect a recovery period of about 4-6 weeks. During this time, gradual resumption of normal activities is recommended. As your body adjusts to life without the gallbladder, you might feel some short-lived changes in your digestive system.
It’s crucial to adhere to post-operative instructions provided by your healthcare provider to ensure a smooth recovery process.
Contact your doctor immediately if you encounter severe abdominal pain, fever, or unusual symptoms during recovery.
What to Expect During the Recovery Period
After gallbladder surgery, patients can expect a gradual recovery process. Initially, some discomfort and fatigue are common. It is critical to carefully adhere to the postoperative care instructions. Patients may resume light activities within a few days but should avoid heavy lifting.
A healthy diet rich in fiber with a gradual reintroduction of fats is recommended. Follow-up appointments will monitor progress and ensure proper healing.
Overall, the recovery period varies, but most individuals can return to normal routines within a few weeks.
Ways to Recover Efficiently Following Gallbladder Removal
- Stay hydrated and follow a balanced diet post-surgery to aid recovery
- Gradually increase physical activity as advised by your doctor to regain strength
- Be mindful of incision care to prevent infections
- Attend follow-up appointments to monitor progress closely
- To enhance blood flow, incorporate mild exercises like short walks into your routine
- Get ample rest to allow your body to heal efficiently
- Follow medical guidance strictly for optimal recovery and avoid strenuous activities during the initial healing phase
Preventing Gallbladder Sludge

Maintaining a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can help prevent gallbladder sludge formation. Avoiding rapid weight loss and gradually shedding excess weight, if needed, is beneficial.
Stay hydrated and limit cholesterol-rich foods. Healthy gallbladder function may be achieved by dietary consumption of olive oil. Regular physical activity and maintaining a healthy weight are essential preventive measures.
Dietary Choices to Prevent Gallbladder Issues
- Opt for a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables to prevent gallbladder issues
- Limit saturated fats and cholesterol-heavy foods
- Choose olive oil for cooking
- Avoid rapid weight loss to reduce the risk of gallstones
- To maintain proper hydration, drink lots of water every day
- Incorporate fiber into meals for improved digestion and overall gallbladder health
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding gallbladder sludge is crucial for early detection and appropriate treatment. Recognizing the symptoms, causes, and available treatments can help manage this condition effectively.
Whether through non-surgical approaches or, in some cases, surgical intervention, addressing gallbladder sludge promptly is essential for maintaining digestive health.
Remember to prioritize a healthy lifestyle and dietary choices to prevent gallbladder issues. If you suspect any gallbladder-related symptoms, seek medical attention promptly to receive proper diagnosis and care.
For personalized guidance and support, feel free to get in touch with Dr. Valeria Simone MD at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Make An Appointment
For more information on Gallbladder sludge and treatment. You can contact our healthcare expert today to make an appointment at +1 (817) 748-0200 with Dr. Valeria Simone MD, at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Gallbladder Sludge Go Away on Its Own?
Gallbladder sludge can sometimes dissolve on its own with dietary changes and increased physical activity. However, if symptoms persist or worsen, medical intervention may be necessary for complete resolution. Early detection and lifestyle modifications play a key role in managing gallbladder sludge.
How is Gallbladder Sludge Different from Gallstones?
When bile becomes too thick, it forms gallbladder sludge, which can lead to gallstones. Sludge forms before solidifying into stones, which are hardened deposits. While sludge can be managed with lifestyle changes, gallstones may require surgical intervention. To effectively treat a patient, one must first understand the difference.
Are There Any Natural Remedies for Gallbladder Sludge?
Some natural remedies for gallbladder sludge include dietary changes, such as increasing fiber intake and staying hydrated. Herbal supplements like milk thistle and dandelion may also help. Before attempting any natural remedies, talk to your doctor.
What are the Long-Term Effects of Gallbladder Removal?
Long-term effects of gallbladder removal may include changes in bowel habits and digestion, as bile is not stored for release. Some individuals may experience diarrhea or fat malabsorption.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
References:
- Figueiredo JC, Haiman C, Porcel J, et al. Sex and ethnic/racial-specific risk factors for gallbladder disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017;17(1):153. Published 2017 Dec 8. doi:10.1186/s12876-017-0678-6
- Catalano OA, Sahani DV, Kalva SP, Cushing MS, Hahn PF, Brown JJ, Edelman RR. MR imaging of the gallbladder: a pictorial essay. Radiographics. 2008 Jan-Feb;28(1):135-55; quiz 324. doi: 10.1148/rg.281065183. PMID: 18203935.
- Chatterjee A, Lopes Vendrami C, Nikolaidis P, Mittal PK, Bandy AJ, Menias CO, Hammond NA, Yaghmai V, Yang GY, Miller FH. Uncommon Intraluminal Tumors of the Gallbladder and Biliary Tract: Spectrum of Imaging Appearances. Radiographics. 2019 Mar-Apr;39(2):388-412. doi: 10.1148/rg.2019180164. Epub 2019 Feb 1. PMID: 30707646.
- Shaffer EA. Gallbladder sludge: what is its clinical significance? Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2001 Apr;3(2):166-73. doi: 10.1007/s11894-001-0015-6. PMID: 11276386.
- Wang HH, Portincasa P, Liu M, Tso P, Wang DQ. Similarities and differences between biliary sludge and microlithiasis: Their clinical and pathophysiological significances. Liver Res. 2018;2(4):186-199. doi:10.1016/j.livres.2018.10.001
- Elta GH. Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction and bile duct microlithiasis in acute idiopathic pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Feb 21;14(7):1023-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1023. PMID: 18286682; PMCID: PMC2689403.
- “Acute Cholecystitis.” StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf, 22 May 2023, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459171.
- Baad M, Lu ZF, Reiser I, Paushter D. Clinical Significance of US Artifacts. Radiographics. 2017 Sep-Oct;37(5):1408-1423. doi: 10.1148/rg.2017160175. Epub 2017 Aug 4. PMID: 28777700.
- “Gallstones (Cholelithiasis).” StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf, 24 Apr. 2023, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459370.
- Pazzi P, Gamberini S, Buldrini P, Gullini S. Biliary sludge: the sluggish gallbladder. Dig Liver Dis. 2003 Jul;35 Suppl 3:S39-45. doi: 10.1016/s1590-8658(03)00093-8. PMID: 12974509.