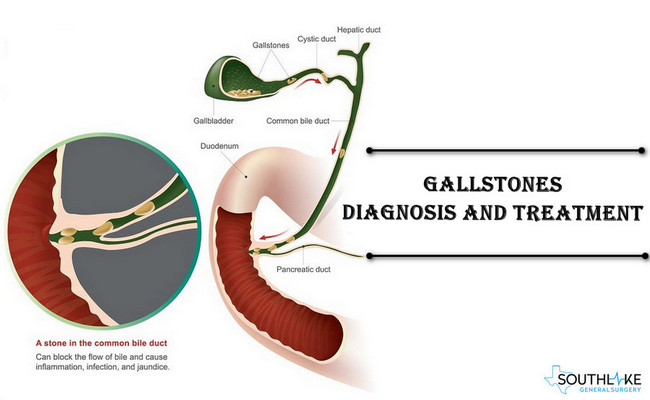
Gallstones are hardened digestive fluid deposits that are able to create in the gallbladder. Your Gallbladder is a small organ beneath the liver in the upper right abdomen area. It’s a pocket that stores bile, a green-yellow fluid that helps the body in digestion. Most gallstones form when there’s a lot of cholesterol in the bile.
Gallstones range in size from as small as a sand grain to as great as a golf ball. Some people only develop one gallstone while others also develop several gallstones.
Causes of Gallstones
In reference to a recent study, 80 percent of gallstones are made of cholesterol. And the remaining 20 percent of gallstones are made of calcium salts and bilirubin.
It’s not known precisely what makes gallstones to form, however there are a few speculations.
An excessive amount of cholesterol in bile
Having an excessive amount of cholesterol in bile can prompt yellow cholesterol stones. These hard stones may develop if liver produce more cholesterol than your bile can dissolve.
An excessive amount of bilirubin in bile
Bilirubin is a chemical generate when liver demolishes old red blood cells. In few conditions, damage liver and certain blood issue, cause liver to generate more bilirubin than it should. Pigmented gallstones form when gallbladder can’t separate the overabundance bilirubin. These hard stones are often dark brown colored or black.
Concentrated bile because of a full gallbladder
Gallbladder needs to purge its bile to be sound and to function appropriately. On the off chance that it fails to purge its bile content, the bile turns out to be excessively concentrated, which develops stones to structure.
Symptoms
Foods that are high in fat may cause Gallbladder pain, for example, fried foods. The pain doesn’t typically last in excess of a couple of hours.
Following symptoms may be experienced:
- nausea
- vomiting
- change in urine color -dark urine
- clay-colored stools
- pain in stomach
- burping
- diarrhea
- indigestion
These symptoms are also called as biliary colic.
Asymptomatic gallstones
Gallstones themselves don’t cause any pain or discomfort. However, pain usually happens when the gallstones hinder the bile movement from the gallbladder.
Gallstones risk factors
Several risk factors for gallstones are identified with diet, while a few variables are uncontrollable. Uncontrollable factors prone to risk include: age, gender, race, and family ancestry, which can’t be modified.
| Lifestyle factors | Uncontrollable factors | Clinical Risk factors |
| eating a meal that’s high in fat or cholesterol or low in fiber | being a female | being pregnant |
| Being obese or overweight | being 60 years or more above | having cirrhosis |
| Diabetes mellitus. | having a family ancestry of gallstones | taking certain drugs for bringing down cholesterol. |
| Rapid weight loss in a very short period of time. | being of Native American descent or Mexican-American descent | taking certain medications that have a high estrogen content |
Gallstones Diagnosis
Doctor will conduct a physical assessment that includes eyes check-up and any visible sign of change in skin color. A yellowish tint might be an indication of jaundice, the aftereffect of an excessive amount of bilirubin in the body.
The test may include using symptomatic tests that help primary care physician to examine the body. These tests include: Abdominal Ultrasound, Abdomen CT Scan, Gallbladder radionuclide examination, Blood Tests, Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP).
Consult our specialist for gallstones
In case you’re searching for specialists with the most experience treating gallstones, contact our healthcare expert for detailed discuss and remedy for Gallstones treatment in Southlake, Texas and book an appointment: https://www.southlakegeneralsurgery.com/make-an-appointment/
Treatment of Gallstones
More often, treatment for gallstones is not required except if they cause you pain. At times, people can pass gallstones without any hurdle. If a pain is experienced, doctor probably suggest surgery. In exceptional cases, medication is also a substitute of surgery for gallstones.
If the medical condition is at high risk for surgery difficulties, a drainage tube might be put into the gallbladder through the skin. And gallstone surgery might be delayed until complications are brought down by treating other health conditions.
Surgical Treatment for Gallstones
Doctor will prescribe one of two surgical treatments depending on medical condition:
Laparoscopic gallbladder removal: Laparoscopic surgery is very common procedure that requires general anesthesia with 3 or 4 small incisions on abdomen to remove the gallbladder. Post-surgery, Patient can go home on the day of the surgery or a day after if no complications are identified.
Open Surgery: Surgeon makes a 6-inch (15 centimetre) incision on abdomen beneath right ribs during an open cholecystectomy. It steps back the muscle and tissue to uncover the liver and gallbladder. Thereafter, surgeon removes the gallbladder.
What would I expect in the long term?
Patients need surgery to remove gallbladder or any stones from gallbladder, the viewpoint is often positive. In many cases of stone removal though surgery, stones don’t return.
The gallstones can return if the treatment carried out only with medications. This is fact in any event, when you’ve taken medicine to break down or dissolve the gallstones.
It wouldn’t require any treatment if gallstones don’t have symptoms. Although, it is recommended to make changes in way of life to keep them from getting bigger or causing issues.