Laparoscopic appendectomy is a safe and effective surgical procedure that removes an inflamed appendix through small incisions, reducing recovery time, scarring, and post-operative pain, offering a modern alternative to traditional open surgery.
What is Appendicitis?
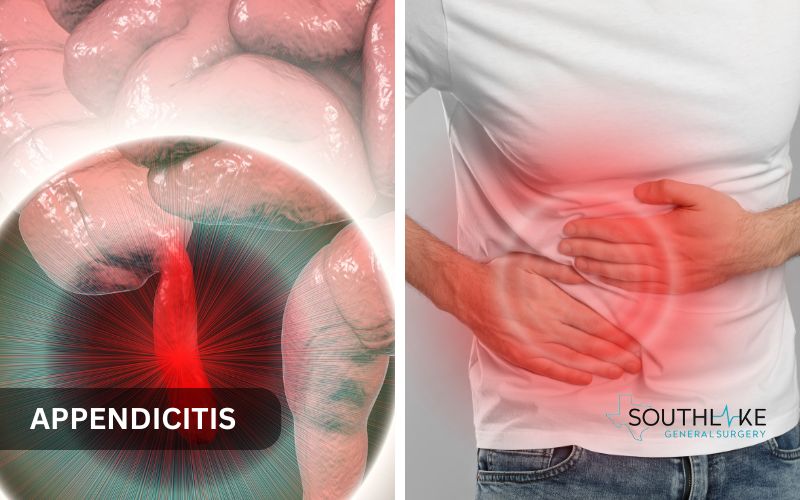
Appendicitis is a painful and potentially life-threatening condition that necessitates immediate attention. It occurs when the appendix becomes swollen. Surgery is needed to prevent serious issues, like a burst appendix.
A laparoscopic appendectomy is a less invasive choice than open appendectomy. It offers several advantages.
Understanding Laparoscopic Appendectomy
Laparoscopic appendectomy is a surgical procedure designed to remove an inflamed appendix using small incisions, usually ranging from 2 to 4, in the abdominal wall.
This method uses a laparoscope, which is a thin illuminated tube with a camera, to see the appendix and the nearby tissues.
Specialized instruments are gently inserted through separate incisions to carefully dissect and remove the appendix. A laparoscopic appendectomy is done while the patient is asleep with general anesthesia.
How Does it Differ from Traditional Open Surgery?
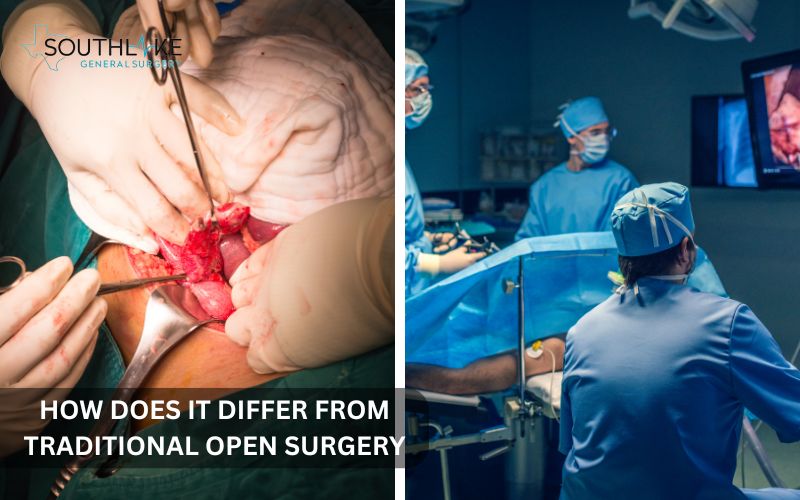
Laparoscopic appendectomy offers a fantastic option compared to traditional open surgery. Instead of a large incision of about 2-3 inches to reach the appendix, this method uses smaller incisions, which helps reduce tissue trauma and encourages a faster recovery.
This procedure helps to lessen post-operative pain, minimize scarring, and shorten recovery time, making it a great choice for patients looking for a more comfortable and convenient treatment option.
Types of Laparoscopic Appendectomy
There are three main categories of laparoscopic appendectomy:
- Single-incision laparoscopic appendectomy (SILA): This technique uses just one incision, usually situated near the belly button, to insert the laparoscope and necessary instruments.
- Three-port laparoscopic appendectomy: This method involves making three small incisions to allow for the insertion of the laparoscope and surgical instruments.
- Robotic-assisted laparoscopic appendectomy: This procedure uses a robotic system to enhance the surgeon’s accuracy and skill throughout the operation.
Your surgeon will go over the pros and cons of each method with you in detail, helping to find the best approach tailored to your specific situation.
Preparation and Procedure for Laparoscopic Appendectomy
Before getting a laparoscopic appendectomy, you’ll go through:
- Pre-operative testing: Blood tests, imaging studies, and other tests are important for confirming the diagnosis and evaluating overall health.
- Patient education: Your surgical team will share clear and helpful instructions regarding preparation, the procedure itself, and what to expect for post-operative care.
- Anesthesia options: To keep you comfortable during the procedure, the doctor will administer either general anesthesia or conscious sedation.
The surgical procedure usually lasts about 1 to 2 hours and includes:
- Abdominal inflation: Carbon dioxide gas is introduced to help create a clear visual field.
- Laparoscope insertion: A laparoscope is carefully inserted through a small incision to allow for a clear view of the appendix.
- Appendix removal: Surgeons utilize specialized instruments that gently dissect and remove the inflamed appendix with precision.
- Incision closure: The incisions are carefully closed using sutures or staples.
Benefits and Advantages of Laparoscopic Appendectomy

Laparoscopic appendectomy provides many benefits compared to traditional open surgery, making it a popular option for treating appendicitis. This procedure, which is minimally invasive, offers patients a faster, safer, and more comfortable recovery experience.
Key Benefits:
- Reduced recovery time: Patients usually get back to their normal activities in just 1-2 weeks.
- Less post-operative pain: Less tissue trauma leads to lower discomfort levels.
- Smaller incisions: You’ll experience minimal scarring along with enhanced cosmetic results.
- Lower risk of complications: Reduced risk of infection, bleeding, and bowel injury.
- Shorter hospital stay: Usually done on an outpatient basis, which helps to shorten the time spent in the hospital.
- Fewer adhesions: There is a lower risk of experiencing intestinal obstruction and potential future complications.
- Improved accuracy: The use of a laparoscope for enhanced visualization helps ensure a precise removal of the appendix.
- Reduced risk of hernias: Using smaller incisions can help reduce the risk of hernias.
Risks and Complications of Laparoscopic Appendectomy
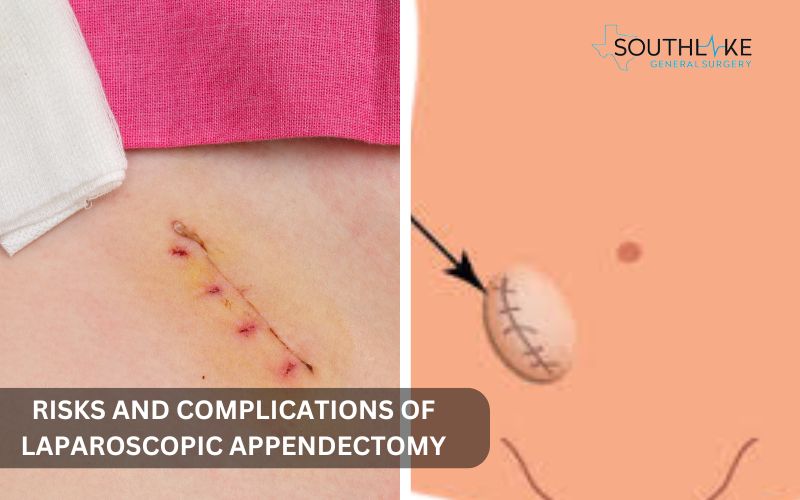
Laparoscopic appendectomy is usually considered a safe procedure, but it’s important to be aware that there can be potential risks and complications involved.
It’s really important to talk about these things with your surgeon so that you can ensure sure you have all the information you need for informed consent.
Possible complications:
- Infection: A wound or internal infection that may need antibiotics or additional surgery.
- Bleeding: Bleeding that is more than usual during or after surgery.
- Bowel injury: Accidental damage to surrounding intestines.
- Adhesions: There may be internal scarring that could lead to bowel obstruction.
- Hernias: There may be some weakness in the abdominal walls at the sites of the incisions.
- Organ damage: Injuries to surrounding organs, such as the bladder and ureter, can occur.
- Anesthesia risks: Reactions to anesthesia that may not be favorable.
- Intestinal obstruction: A bowel blockage that requires additional surgery.
- Abscess formation: Infected fluid accumulation near the surgical site.
- Wound complications: Slow healing, separation of tissue, or internal organs protruding.
- Conversion to open surgery: There has been an unexpected change to traditional open surgery.
Minimizing these risks requires strict adherence to your surgeon’s instructions and regular attendance at follow-up appointments. If you see anything unusual, please reach out to your doctor as soon as possible.
Recovery and Post-Operative Care
To ensure optimal healing and minimize complications, it is crucial to carefully follow the post-operative instructions when recovering from a laparoscopic appendectomy. The usual length of stay for a patient in the hospital is one or two days.
Immediate Post-Operative Recovery
Right after surgery, patients are brought to the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) for monitoring that involves close monitoring by medical professionals.
The Initial recovery process includes:
- Vital sign monitoring: The patient’s temperature, heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation levels are monitored continuously.
- Pain management: Medication to help manage discomfort and ease any pain.
- Wound care: Incisions will be bandaged, and any signs of bleeding or leakage will be checked.
- Hydration: Staying properly hydrated is crucial for your recovery and contributes significantly to your overall health. Intravenous fluids and electrolytes will be replenished.
- Rest: It’s essential for patients to take some time to rest and avoid any strenuous activities. This helps their bodies heal and recover effectively.
- Breathing exercises: Exercises that involve deep breathing and coughing can aid in the prevention of pneumonia and the general improvement of lung function.
- Mobility: Gradual mobilization is effective in preventing blood clots, facilitating healing, and minimizing the risk of complications.
- Nausea and vomiting management: It’s quite common for individuals to experience nausea and vomiting following a laparoscopic appendectomy. Managing your health effectively includes taking medication, making dietary changes, and adopting lifestyle modifications.
- Urinary catheter removal: It is removed once a patient can urinate normally.
- Diet initiation: Starting a diet after laparoscopic appendectomy is all about taking it step by step. You’ll begin with clear liquids and gradually move on to solid foods. This approach helps ensure you get the right nutrition while keeping complications at bay.
- Discharge preparation: Patients are provided with information about post-operative care, medication, and follow-up appointments.
Short-Term Recovery
After a laparoscopic appendectomy, the short-term recovery period usually lasts about 1-2 weeks. During this time, patients can expect to see a gradual improvement in their physical condition and overall well-being.
Physical Recovery Milestones:
- Initial 24-48 hours: Many patients may feel some discomfort, fatigue, and sleepiness because of anesthesia.
- 2-4 days: You can expect to see a gradual improvement in appetite, bowel movements, and urination over time.
- 5-7 days: You will have increased mobility, you will feel less discomfort, and your overall well-being will improve.
- 1-2 weeks: It’s time to ease back into light activities, whether that’s work or school!
Post-Operative Precautions:
- Avoid heavy lifting: It is recommended that patients avoid lifting anything more than 10-15 pounds (4.5-6.8 kg) for a period of four to six weeks.
- Bending and straining: When it comes to preventing hernias and wound problems, it is necessary to minimize bending and straining. It is especially important for patients to refrain from doing anything that can put a strain on their abdominal wall during the first four to six weeks after surgery.
- Driving: It is recommended that patients refrain from driving for at least two to four weeks following surgery, or until the patient has gotten their doctor’s explicit consent.
- Sexual activity: Engaging in sexual activity following a laparoscopic appendectomy necessitates careful consideration and approval from a healthcare professional. It is advisable for patients to refrain from engaging in sexual activity until they receive clear approval, which usually occurs 2-6 weeks following the surgical procedure.
Follow-Up Care:
- Post-operative appointments: Regular check-ups facilitate the assessment of recovery progress, allow for the discussion of any concerns, and help in the prevention of potential complications.
- Wound care: It is important to keep the wound clean and look out for signs of infection or problems.
- Medication management: The goal of medication management following laparoscopic appendectomy is to facilitate a safe and effective recovery by controlling pain, reducing the risk of complications, and modifying medications as required.
- Lifestyle guidance: Post-operative guidance following laparoscopic appendectomy includes suggestions on nutrition, physical activity, and stress reduction to ensure a seamless recovery, reduce the risk of complications, and enhance overall health.
Long-Term Recovery After Laparoscopic Appendectomy
Recovering from a laparoscopic appendectomy takes time and following your doctor’s advice is important for a successful outcome. Usually, a full recovery can take around 6 to 12 weeks.
Recovery Timeline:
- 6-8 weeks: You can resume light physical activities
- 8-12 weeks: Patients can gradually move towards moderate exercise, which helps improve physical fitness and supports overall well-being.
- 3-6 months: Patients can concentrate on rebuilding abdominal strength, improving core stability, and fostering overall physical fitness.
- 6-12 months: Internal healing is finished by the body, and organ function and tissue integrity are restored to their optimal levels.
For a successful recovery after laparoscopic appendectomy, it’s important to consider these four essential factors:
- adhere to your personalized medical advice,
- focus on self-care and managing stress,
- watch for any potential complications such as adhesions or bowel obstruction, and
- make sure to attend regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider to discuss any concerns and monitor your progress.
Why Choose Southlake General Surgery?
- Expertise: Our team specializes in minimally invasive surgery.
- Personalized care: Compassionate, individualized attention.
- State-of-the-art facilities: Advanced surgical equipment.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic appendectomy offers a modern and minimally invasive way to effectively address appendicitis.
When patients take the time to learn about the procedure, its benefits, and any potential risks, they can feel more confident in making choices about their care.
It’s a great idea to consult with a qualified surgeon or medical professional to find out if a laparoscopic appendectomy is the right option for you.
Expert Care for Appendicitis and Stomach Concerns
If you’re experiencing stomach discomfort or worried about appendicitis, trust the expertise of Dr. Valeria Simone, MD, at Southlake General Surgery in Texas, USA. Dr. Simone provides top-notch care for patients seeking relief from stomach issues.
Why Choose Dr. Simone?
- Board-certified general surgeon: Ensuring the highest standards of care
- Laparoscopic appendectomy specialist: Minimally invasive procedures for optimal recovery
- Compassionate care: Provide tailored support that focuses on your individual requirements
- Friendly environment: Relaxing atmosphere for a stress-free experience
Services Offered:
- Appendicitis diagnosis and treatment
- Laparoscopic appendectomy surgery
- Stomach pain evaluation and management
- Digestive health guidance
- Preventative care and education
Schedule Your Appointment Today!
If you would like to talk about appendicitis, or any stomach concerns, or schedule a consultation, please feel free to call us at +1 (817) 748-0200.
We’re here to help! Dr. Simone provides compassionate and comprehensive care. Book your appointment today and embark on the journey to a healthier, happier you!
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
References:
- He, J., Han, Y., Hang, T., Lin, Z., Lu, S., Wang, J., & Hong, Z. (2022). <Editors’ Choice> Advantages of gasless single-port transumbilical extracorporeal laparoscopic-assisted appendectomy in the treatment of uncomplicated acute appendicitis in children in China: a multi-institutional retrospective study. PubMed, 84(4), 848–856. https://doi.org/10.18999/nagjms.84.4.848
- Chang, H. K., Han, S. J., Choi, S. H., & Oh, J. (2013). Feasibility of a Laparoscopic Approach for Generalized Peritonitis from Perforated Appendicitis in Children. Yonsei Medical Journal, 54(6), 1478. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.6.1478
- Nguyen, A., & Lotfollahzadeh, S. (2023, June 3). Appendectomy. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK580514/
- Kumar, M., Mohan, L., & Singh, M. (2013). Suprapubic approach for laparoscopic appendectomy. Journal of Natural Science Biology and Medicine, 4(2), 389. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-9668.116987
- Shimoda, M., Maruyama, T., Nishida, K., Suzuki, K., Tago, T., Shimazaki, J., & Suzuki, S. (2019). <p>Preoperative high C-reactive protein level is associated with an increased likelihood for conversion from laparoscopic to open appendectomy in patients with acute appendicitis</p> Clinical and Experimental Gastroenterology, Volume 12, 141–147. https://doi.org/10.2147/ceg.s196471
- Di Saverio, S., Birindelli, A., Kelly, M. D., Catena, F., Weber, D. G., Sartelli, M., Sugrue, M., De Moya, M., Gomes, C. A., Bhangu, A., Agresta, F., Moore, E. E., Soreide, K., Griffiths, E., De Castro, S., Kashuk, J., Kluger, Y., Leppaniemi, A., Ansaloni, L., . . . Andersson, R. (2016). WSES Jerusalem guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of acute appendicitis. World Journal of Emergency Surgery, 11(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13017-016-0090-5

