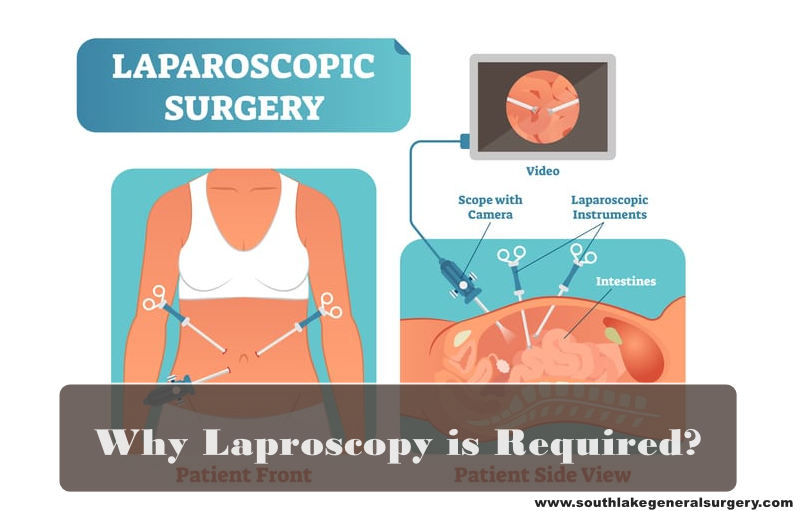
Laparoscopy is also called diagnostic laparoscopy, it is a surgical diagnostic method used to inspect the organs inside the abdomen. Laparoscopic surgery is a low-risk, minimally invasive method that can be completed with just a small 3-4 incision.
In Laparoscopic procedures, the surgeon uses equipment called a laparoscope to view the internal organs of the abdomen. A laparoscope is a long cylindrical tube with a high-resolution mini camera with light at the front top of the tube. The instrument is passed through a small incision in the abdominal wall. As the laparoscope moves along, the camera sends pictures to a video screen.
Laparoscopy helps surgeons to view inside the abdomen and examine the condition in real-time, without open surgery. Your doctor likewise can get biopsy tests during this procedure.
What is the need for laparoscopy surgery?
To identify and diagnose the root of pelvic or abdominal pain doctors often use laparoscopy. It’s mainly performed when noninvasive procedures can’t help with diagnosis.
In certain cases, abdominal problems and complications can easily be diagnosed through imaging methods such as:
- Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to male pictures of the body
- CT Scan is a special X-ray technique that captures cross-sectional images of the body
- MRI scan uses radio waves and magnets to create images of the body.
Laparoscopy is performed when these tests don’t give enough data or knowledge for a diagnosis. The method may likewise be used to take a biopsy, or sample of tissue, from a specific organ in the abdomen.
Your doctor may prescribe laparoscopy to analyze the following organs:
- Gallbladder
- appendix
- liver
- spleen
- pancreas
- stomach
- reproductive organs or pelvic
- small intestine and large intestine (colon)
After examining these areas with a laparoscope, your surgeon can distinguish:
- mass or tumor in the abdomen
- fluid in the abdominal cavity
- liver disease
- the adequacy of certain treatments
- the degree to which specific cancer has advanced
Also, your doctor might have the option to do mediation to treat your condition immediately after diagnosis.
How is Laparoscopic Surgery Performed?
Before this procedure tagged along, a doctor who worked on the patient’s abdomen needed to make an incision 6-to-12 inches in length. That gave them sufficient space to perceive what they were doing and reach whatever they needed to work on.
In the laparoscopic surgical procedure, the surgeon makes 3-4 small incisions. Typically, everyone is close to a half-inch in length. This procedure is also known as a keyhole surgery. They embed a cylindrical tube attached with a camera on top through each opening, and surgical instruments enter inside the body through these cuts to perform surgery.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Surgery
Working this way has many benefits compared with conventional surgery. Since it includes fewer incisions:
- Small scars of an incision.
- Short stay at the hospital.
- Less Pain and faster recovery.
- Resume normal activities in a short time.
- Less internal scarring.
For example, with the customary procedure, you may go through up to seven days in the hospital for the intestinal surgical procedure, and your complete recovery may take 4 to 8 weeks. If you go for laparoscopic surgery, you might have to stay in the hospital for 24hours based on the medical condition, and recovery time is about 2 or 3 weeks. Furthermore, a shorter stay in the hospital eventually reduces hospital expenses.
Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Procedure
In a few surgeries, the surgeon can get the camera and the surgical instrument through the same opening in the skin. This implies less scarring. However, it’s complex for the surgeon on the grounds that the instruments are very close to each other.
In some cases, the surgeon may choose to use a special instrument that lets them reach in with a hand. This is classified as “hand assisted” laparoscopy. The incision in the skin must be longer than a half-inch, however, it actually can be smaller than in customary surgery. This technique has made it conceivable to use laparoscopic surgery for the liver and other organs.
When a Robotic Surgery Helps
Innovation can enable the clinical group to be precise. In the robotic adaptation of laparoscopic surgery, the initial step of the surgeon is to make cuts into the skin and insert the camera. Rather than grabbing surgical instruments, they programmed a robot’s mechanical arms. Thereafter, they move to a computer close by.
Many doctors think robotic surgery is particularly useful for working on individuals who weigh a ton, and for gynecology and urology surgical procedures. Many prostate removal surgery use robots.
In robotic surgery, the surgeon will be able to view the screen that gives a 3-D, high-resolution, magnified picture inside the body. As they watch the screen, they use hand controls to work the robot and surgical instruments. This allows the surgeon to be more precise, and it leads to less bleeding and a rare possibility of any impact on the body. You may likewise have less uneasiness after the surgery.
Recovery After Laparoscopic Surgery
Once the surgery is over, your health will be monitored for several hours before you get discharged from the hospital. Your vital signs, like your breathing and pulse, will be observed closely. Hospital staff will likewise check for any unfriendly responses to the anesthesia or the surgery, just as a screen for prolonged bleeding.
The duration of discharge may vary. It relies upon:
- overall medical condition
- the type and effect of anesthesia used in surgery
- your body’s response to the surgery
In a few cases, you might have to stay in the hospital overnight.
A relative or companion should drive you home if are dosed off because of general anesthesia. The impacts of general anesthesia generally take a few hours to get normal, so it is not advised and considered unsafe to drive home after surgery.
Day after your laparoscopic surgery, you may feel slight pain and pulsate in the area where entry points (incision) were made. Any pain or distress ought to get better within a couple of days. Your surgeon may prescribe medicine to feel better and relieve any pain.
It’s likewise common to have shoulder pain after your surgery. The pain is typically an aftereffect of the carbon dioxide gas used to expand your abdomen to make a surgical space for the surgical instruments. The gas can disturb your diaphragm, which connects nerves with your shoulder. It might likewise cause some swelling. The distress should disappear within two or three days.
After the consultation with the surgeon, you can resume all normal activities within in a week after laparoscopic surgery. You’ll have to go to a subsequent consultation with your surgeon around 2 weeks after laparoscopy.
Here are a few tips you can follow to ensure faster recovery:
- Start with small activity as soon as you feel better and comfortable, in order to reduce any risk of blood clots.
- Take more rest than usual.
- Use throat lozenges to reduce or relieve the pain of a sore throat.
- Wear comfortable and loose-fitting clothes.
Appointment
For more information on Laparoscopic Surgery, please contact our healthcare expert today at +1(817) 748-0200.