Lipomas are common benign tumors that develop in the fatty tissue just below the skin. These lumps are usually painless and moveable, making them distinguishable from other types of growth. While lipomas are generally harmless and don’t require treatment, they can sometimes cause discomfort if they press on nerves or blood vessels.
It’s important to understand the causes, symptoms, and types of lipomas to ensure proper diagnosis and management. Lipomas can occur at any age, but they are more commonly found in middle-aged adults. They can develop anywhere on the body but are often found on the torso, shoulders, neck, and arms.
In this blog, we will delve into the details of lipoma, starting with an overview of what lipomas are and their prevalence in adults. We will then discuss the common symptoms of lipoma and when to be concerned. The causes behind lipoma formation, including genetic factors and lifestyle triggers, will also be explored.
We will delve into the various types of lipomas, the diagnostic techniques used to identify them, and the comprehensive treatment options available.
Additionally, we will discuss the role of diet and lifestyle in managing lipoma and the recovery and post-treatment care involved. Finally, we will provide a note from Southlake General Surgery and information on how to schedule an appointment.
Key Highlights
- Lipomas are benign lumps of fatty tissue that usually develop between the skin and underlying muscle.
- Soft tissue tumors are frequently found in adults.
- Lipomas are typically painless and don’t cause symptoms unless they press on nerves or blood vessels.
- While the exact cause of lipoma formation is unknown, genetic factors and lifestyle factors such as obesity may play a role.
- There are various types of lipomas, including conventional lipomas and atypical lipomas.
- Diagnosis of lipomas involves physical examination and, in some cases, imaging tests or biopsies.
- Treatment options for lipomas include surgical removal and minimally invasive alternatives such as steroid injections or liposuction.
- Preventive measures for lipoma formation include maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing weight.
- Recovery after lipoma treatment is usually smooth, and follow-up care is important for monitoring any recurrence or complications.
Understanding Lipoma: An Overview
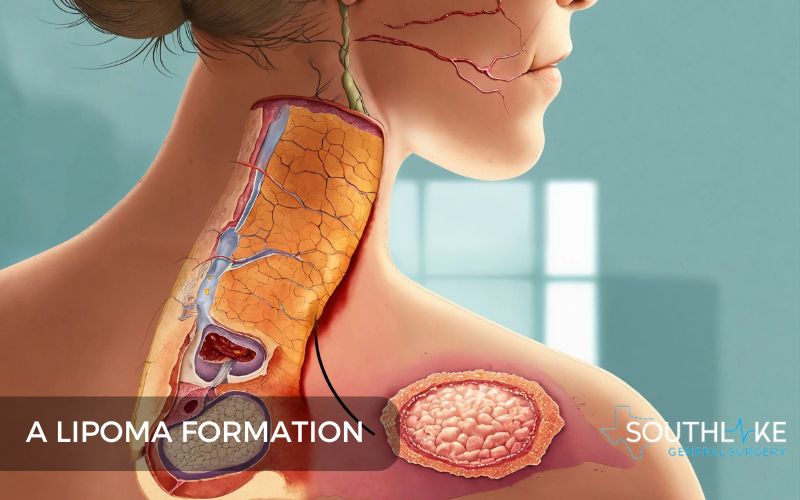
Lipomas are benign lumps of fatty tissue that typically form between the skin and the underlying muscle. They are the most common soft tissue tumors found in adults, with a higher prevalence in middle-aged individuals.
Lipomas are usually painless and don’t produce symptoms unless they press on nerves or blood vessels. While the exact cause of lipoma formation is unknown, genetic factors and lifestyle triggers such as obesity may play a role. Understanding lipomas is crucial for proper diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
What Is Lipoma?
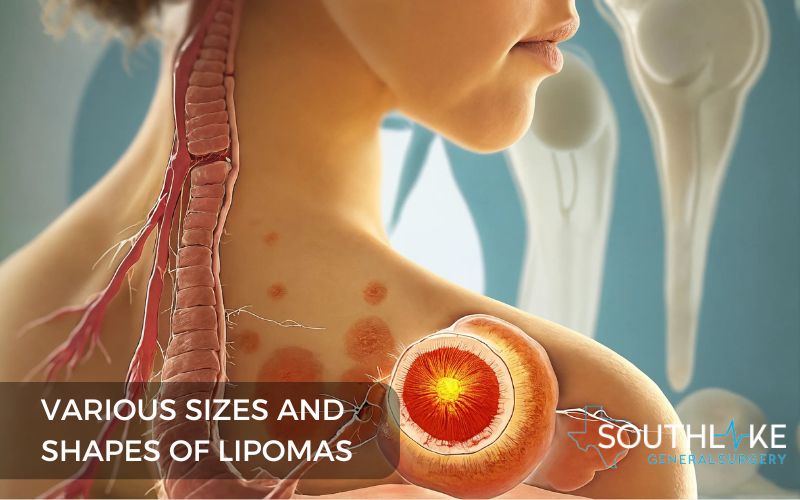
A lipoma is a noncancerous growth made up of fatty tissue that forms between the skin and the muscle beneath. It is comprised of fat cells and is typically encapsulated, meaning it does not spread to surrounding tissues.
Lipomas are usually soft, moveable, and feel doughy or rubbery to the touch. Benign soft tissue tumors are the most frequently encountered type in adults. Lipomas can occur anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the torso, shoulders, neck, and arms.
In rare cases, lipomas can be associated with conditions such as adiposis dolorosa, also known as Dercum’s disease, which causes painful lipomas to form.
However, most lipomas are asymptomatic and do not require treatment unless they are causing discomfort or affecting a person’s quality of life. Lipomas are typically harmless and do not pose any health risks. But, it is important to have any new or changing lumps evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out other potential causes.
Prevalence of Lipoma
The most prevalent soft tissue tumors discovered in adults are lipomas. The incidence of lipoma formation increases with age, with a higher prevalence in middle-aged individuals. While lipomas can develop at any age, they are more commonly seen in adults between the ages of 40 and 60.
Studies have shown that lipomas occur in approximately 2.1 per 1,000 individuals each year. Men are slightly more likely to have them compared to women. It is estimated that lipomas affect about 1% of the population. However, these numbers may vary depending on the population studied and the criteria used for diagnosis.
In the United Kingdom (UK), lipomas are also a common occurrence. They are often identified during routine physical examinations or when individuals seek medical attention for other reasons. Lipomas can occur in people of all ethnicities and backgrounds.
It is important to note that while lipomas are benign and usually do not cause harm, they should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to confirm the diagnosis and rule out any other potential conditions.
Identifying Lipoma: Symptoms and Signs
Identifying lipomas involves recognizing their symptoms and signs. Lipomas are usually painless and do not produce symptoms unless they press on nerves or blood vessels. The typical characteristics of a lipoma include a soft, rubbery lump that can be moved easily under the skin.
Lipomas are usually round or oval-shaped and can vary in size from small to large. While lipomas can occur anywhere on the body, they are often found on the torso, shoulders, neck, and arms. Being aware of these symptoms and signs can help individuals recognize and seek medical attention for lipomas if necessary.
Common Symptoms of Lipoma
Lipomas are often asymptomatic and don’t cause any symptoms. However, in some cases, lipomas can cause discomfort or pain if they press on nerves or blood vessels.
The most common symptom of a lipoma is the presence of a soft, moveable lump under the skin. This lump is usually round or oval-shaped and can vary in size.
Lipomas are typically painless, but they can cause discomfort if they grow large or press on nearby structures. Some individuals may also experience swelling or tenderness in the area where the lipoma is located.
It is important to note that these symptoms are not specific to lipomas and can also occur with other conditions. If you have a lump or any concerning symptoms, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
When Should You Be Concerned?
In most cases, lipomas are benign and don’t require immediate medical attention. However, there are certain situations where you should be concerned and seek medical advice.
If a lipoma is causing pain, discomfort, or affecting your quality of life, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional. Additionally, if you notice any changes in the size, shape, or appearance of the lipoma, or if it grows rapidly, it is important to have it evaluated.
While rare, complications can occur with lipomas, such as infection, bleeding, or interference with nearby nerves or blood vessels. If you experience any of these complications or have concerns about your lipoma, it is best to seek medical advice for proper evaluation and management.
Your healthcare professional can assess the lipoma and recommend appropriate treatment options based on your specific situation.
Causes Behind Lipoma Formation
The exact cause of lipoma formation is not well understood. However, research suggests that there may be both genetic and lifestyle factors that contribute to the development of lipomas.
Genetic factors play a role in certain cases, as lipomas can run in families. Lifestyle factors, such as obesity, have also been associated with an increased risk of developing lipomas.
Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as familial multiple lipomatosis and Gardner syndrome, have been linked to an increased risk of lipoma formation.
While the specific mechanisms behind lipoma formation are still being studied, understanding these potential causes can help individuals recognize their risk factors and take preventive measures.
Genetic Factors and Lipoma
Genetic factors have been found to play a role in lipoma formation. Some individuals have a genetic predisposition to developing lipomas, and the condition can run in families.
In certain cases, lipomas are associated with genetic syndromes such as familial multiple lipomatosis and Gardner syndrome.
Familial multiple lipomatosis is a rare condition in which multiple lipomas develop throughout the body. Gardner syndrome, a variant of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), is characterized by the development of benign and malignant tumors, including lipomas.
While the specific genetic risk factors for lipoma formation are not fully understood, research is ongoing to further explore the underlying mechanisms. Understanding the genetic factors involved in lipoma formation can provide valuable insights into the development, diagnosis, and management of this condition.
Lifestyle and Environmental Triggers
In addition to genetic factors, lifestyle, and environmental triggers may contribute to lipoma formation.
Obesity has been linked to a higher likelihood of developing lipomas. Excess body fat and adipose tissue may create an environment that promotes the growth of lipomas.
Alcohol use disorder has also been linked to lipoma formation, particularly in the case of Madelung’s disease, a condition characterized by the development of multiple lipomas around the neck and shoulders.
Environmental factors such as exposure to certain chemicals or toxins may also play a role, although further research is needed to fully understand the impact of these factors.
Making healthy lifestyle choices, maintaining a balanced diet, and managing weight can potentially reduce the risk of developing lipomas.
Various Types of Lipoma
Lipomas can vary in their characteristics and can be classified into different types based on their composition and appearance under a microscope.
The most common type of lipoma is a conventional lipoma, which consists of an overgrowth of mature fat cells.
Atypical lipomas, on the other hand, have a more irregular appearance and can be associated with adiposis dolorosa or Madelung’s disease.
Other types of lipomas include hibernomas, myelolipomas, spindle cell lipomas, pleomorphic lipomas, and fibro-lipomas. Understanding the various types of lipomas can provide insights into their nature and help guide appropriate diagnosis and treatment options.
Conventional Lipomas
The most prevalent form of lipoma is conventional lipoma. They are characterized by an overgrowth of mature fat cells. These lipomas usually present as soft, moveable lumps under the skin.
Conventional lipomas are typically encapsulated and do not spread to surrounding tissues. They can occur in various parts of the body, including the torso, shoulders, neck, and arms.
While conventional lipomas are generally benign and do not cause symptoms, they may be surgically removed if they become bothersome or affect a person’s quality of life. The diagnosis of a conventional lipoma is usually made based on physical examination and imaging studies.
Treatment options for conventional lipomas include surgical removal and minimally invasive procedures such as liposuction or steroid injections, depending on the size, location, and individual circumstances.
Atypical Lipomas
Atypical lipomas are a less common type of lipoma that can exhibit different characteristics compared to conventional lipomas. These lipomas have a more irregular appearance and can be associated with conditions such as adiposis dolorosa and Madelung’s disease.
Adiposis dolorosa, also known as Dercum’s disease, is a rare condition that presents with painful lipomas. Madelung’s disease, also known as multiple symmetric lipomatosis, primarily affects men who consume alcohol excessively. It is characterized by the formation of multiple lipomas in the neck and shoulder area.
Atypical lipomas have distinctive pathological features that differentiate them from conventional lipomas. Treatment options for atypical lipomas may include surgical removal or other interventions, depending on the individual case.
Professional Diagnosis Techniques
Professional diagnosis of lipomas involves a combination of physical examination and diagnostic tests. During the physical examination, a healthcare professional will assess the characteristics of the lipoma, such as size, shape, and consistency.
In some cases, the healthcare provider may order diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other conditions. Common diagnostic tests for lipomas include imaging studies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, computed tomography (CT) scans, and ultrasounds.
These imaging techniques can help visualize the lipoma, determine its location, and assess its impact on surrounding structures. To get a better look at the lipoma under a microscope, a biopsy might be suggested in certain instances.
The choice of diagnostic tests may vary depending on the individual case and the healthcare provider’s assessment.
Initial Examination by Dr. Valeria Simone
The initial examination by Dr. Valeria Simone, a healthcare professional specializing in lipoma diagnosis, involves a comprehensive physical exam.
Dr. Simone will carefully examine the characteristics of the lipoma, including its size, shape, and consistency. She will also assess the location of the lipoma and its potential impact on surrounding structures.
This thorough physical examination will help Dr. Simone determine the nature of the lipoma and its potential complications. Dr. Simone’s expertise in lipoma diagnosis ensures accurate assessment and appropriate treatment recommendations.
In some cases, Dr. Simone may recommend additional diagnostic tests, such as imaging studies or biopsies, to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other conditions. The initial examination by Dr. Simone is an essential step in the diagnostic process and plays a crucial role in developing a personalized treatment plan for everyone.
Advanced Diagnostic Tools Used
In addition to the physical examination, advanced diagnostic tools are often used to aid in the diagnosis of lipomas. These tools include imaging studies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, computed tomography (CT) scans, and ultrasounds.
- MRI scans provide detailed images of the lipoma and surrounding tissues, helping to determine the size, location, and impact of the lipoma on nearby structures.
- CT scans use X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the body, providing valuable information about the lipoma’s characteristics.
- Ultrasounds use high-frequency sound waves to create images of the lipoma, assisting in the evaluation of its size, shape, and composition.
Doctors may recommend a biopsy to obtain a small sample of the lipoma for further examination under a microscope in some cases. These advanced diagnostic tools, along with the physical examination, contribute to an accurate diagnosis and the development of an appropriate treatment plan.
Comprehensive Treatment Options
The treatment options for lipomas depend on various factors, including the size, location, and individual circumstances. In most cases, lipomas do not require treatment unless they are causing symptoms or affecting a person’s quality of life.
If treatment is required, there are various choices accessible. The most common treatment for lipomas is surgical removal, which involves making an incision and removing the lipoma from the underlying tissue.
Minimally invasive procedures, such as liposuction or steroid injections, may also be considered, depending on the specific case. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the size and location of the lipoma, the individual’s overall health, and the preferences of the healthcare provider and patient.
Surgical Removal Procedures
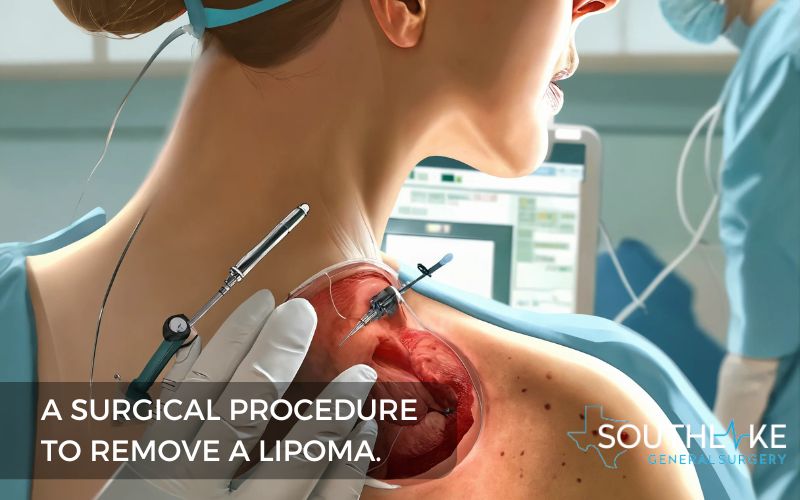
Surgical excision is a frequently used treatment choice for lipomas. This procedure involves making an incision in the skin and removing the lipoma from the underlying tissue.
The surgeon typically performs the surgery under local anesthesia, which numbs the area and allows the patient to remain awake during the procedure. In some cases, general anesthesia may be used, especially if the lipoma is large or located in a sensitive area.
During the surgery, the healthcare provider will carefully remove the lipoma, minimizing scarring and preserving the surrounding tissues.
After removing the lipoma, the surgeon closes the incision using sutures or stitches. Recovery from lipoma removal surgery is usually relatively quick, with minimal discomfort and scarring.
The healthcare provider will provide post-operative instructions and monitor the patient’s progress during follow-up appointments.
Minimally Invasive Alternatives
In some cases, minimally invasive alternatives to surgical removal may be considered for the treatment of lipomas. Doctors may utilize steroid injections to reduce the size of the lipoma. This procedure involves injecting a steroid medication directly into the lipoma, which can help reduce its size and alleviate symptoms.
Liposuction is another minimally invasive option for lipoma removal. This procedure involves using a small, thin tube called a cannula to suction out the fatty tissue of the lipoma through a small incision in the skin.
Liposuction is particularly effective for smaller lipomas and can result in minimal scarring. The choice of minimally invasive treatment depends on factors such as the size and location of the lipoma, the individual’s overall health, and the preferences of the healthcare provider and patient.
The Role of Diet and Lifestyle in Managing Lipoma

Although the specific reason for lipomas is still a mystery, there are a number of lifestyle choices that may impact the progression and treatment of these tumors.
Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle can play a role in managing lipomas and reducing the risk of their formation.
Weight management and maintaining a balanced diet that includes an adequate intake of dietary fiber and reduced fat intake can help promote overall health and potentially reduce the risk of lipoma development.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized dietary recommendations and guidance.
Engaging in regular physical activity and adopting a healthy lifestyle can also contribute to overall well-being and potentially aid in the management of lipomas.
Preventive Measures
While it may not be possible to prevent the development of lipomas entirely, there are preventive measures that individuals can take to potentially reduce the risk.
Engaging in consistent physical activity and following a well-rounded diet can decrease the chances of developing lipomas by maintaining a healthy weight.
Regular exercise promotes weight management and contributes to overall health and well-being. Following a healthy lifestyle that includes a well-rounded diet, stress management, and proper hydration can also potentially reduce the risk of lipoma formation.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations and guidance on preventive measures that are appropriate for individual circumstances.
Recommended Dietary Changes
Making dietary changes can potentially help manage lipomas and reduce the risk of their formation. A diet rich in dietary fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, can help promote regular bowel movements and maintain a healthy weight.
Maintaining a healthy weight requires eating a wide variety of nutrient-dense foods, including complex carbs, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Reducing fat intake, particularly saturated and trans fats, may also be beneficial. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized dietary recommendations and guidance. They can provide specific recommendations tailored to individual needs and goals.
Implementing these dietary changes as part of a healthy lifestyle can have a positive impact on overall well-being and potentially aid in the management of lipomas.
Recovery and Post-Treatment Care

The recovery and post-treatment care after lipoma removal involve proper wound care and monitoring for any signs of infection or complications. It is important to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions for wound care, which may include keeping the incision clean and dry, changing dressings as instructed, and avoiding activities that may strain the incision site.
The healthcare provider advises limiting physical activity to promote proper healing. It is also essential to attend follow-up appointments to monitor the healing process and ensure that the lipoma does not recur.
The healthcare provider will provide specific guidelines for recovery and post-treatment care based on the individual’s situation.
What to Expect After Treatment
After lipoma removal treatment, individuals can expect a recovery period during which the incision site heals. The length of the recovery period may vary depending on factors such as the size and location of the lipoma, the individual’s overall health, and the nature of the surgical procedure.
The healthcare provider will provide specific instructions for post-operative care, which may include keeping the incision clean and dry, avoiding strenuous activities, and taking any prescribed medications as directed.
It is important to monitor the incision site for any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or increased pain. We will schedule follow-up sessions to evaluate the healing process and keep an eye out for any indications of problems or recurrence.
It is essential to attend these appointments and communicate any concerns or questions to the healthcare provider.
Tips for Speedy Recovery
To promote a speedy recovery after lipoma removal, it is important to follow the healthcare provider’s recommendations and take appropriate self-care measures. Engaging in light physical activity, such as walking, can help promote circulation and aid in the healing process.
However, it is important to avoid strenuous activities or heavy lifting until cleared by the healthcare provider. Proper wound care is crucial during the recovery period. This may include keeping the incision site clean and dry, changing dressings as instructed, and avoiding activities that may strain the incision site.
It is essential to attend follow-up appointments as scheduled to monitor the healing process and address any concerns or questions. By following these tips and taking care of themselves, individuals can support a speedy recovery after lipoma removal.
A Note From Southlake General Surgery
At Southlake General Surgery, our dedicated team of healthcare professionals specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of lipomas. Each patient will receive the individualized attention and thorough treatment they need from our team.
Our medical team utilizes advanced diagnostic techniques and treatment options to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective management of lipomas. We prioritize patient care and work closely with everyone to develop personalized treatment plans that meet their specific needs and goals.
We, at Southlake General Surgery, dedicate ourselves to delivering high-quality care and achieving exceptional outcomes for our patients. For scheduling a consultation or obtaining further details about our services, kindly get in touch with our office.
Outlook
In conclusion, lipomas are benign fatty tumors that are simple to detect and treat. Understanding the symptoms, causes, types, and treatment options can help you make informed decisions about managing lipomas.
Whether opting for surgical removal or minimally invasive alternatives, it’s essential to consider your lifestyle and dietary choices for long-term management. Regular check-ups and post-treatment care play a crucial role in ensuring a smooth recovery process.
If you have any concerns or want professional advice, don’t hesitate to reach out to schedule an appointment for expert guidance on lipoma management.
Make An Appointment

Make an appointment with your doctor if you want to talk about your concerns regarding lipomas or get some medical advice. Skincare specialists, general surgeons, and others in the medical industry can diagnose and treat lipomas.
To make an appointment, contact our healthcare expert at +1 (817) 748-0200 and inquire about scheduling a consultation. You can also book an online appointment with us.
During the consultation, the healthcare provider will assess your specific situation, perform a physical examination, and recommend appropriate diagnostic tests or treatments. It is important to communicate any symptoms, concerns, or questions to the healthcare provider during the appointment to ensure a comprehensive evaluation and personalized care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What can cause lipomas in humans?
Genetic factors or lifestyle triggers can cause lipomas in humans. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, along with environmental influences. Lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise, may also contribute to their development. Understanding these causes is crucial for effective management.
Can Lipomas Turn Cancerous?
Lipomas are typically benign tumors and do not turn cancerous. However, in rare cases, a lipoma can transform into a liposarcoma, which is a malignant tumor of the fatty tissue. It is important to have any new or changing lumps evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out liposarcoma and other potential malignancies.
How Often Should Lipoma Sites Be Checked?
The frequency of checking lipoma sites depends on individual factors and the recommendations of the healthcare professional. It is common practice to arrange for follow-up visits to assess the patient’s progress toward recovery and identify any potential problems or recurrences. It is important to attend these appointments and communicate any concerns or changes to the healthcare professional.
Is Lipoma Surgery Covered by Insurance in Texas?
Insurance coverage for lipoma surgery in Texas may vary depending on the specific insurance policy and the medical necessity of the procedure. If the healthcare provider determines that lipoma surgery is medically necessary, insurance may cover it. Cosmetic coverage may be limited or excluded. It is important to check with the insurance provider and healthcare professional to understand the coverage and potential out-of-pocket costs.
How can I differentiate between a lipoma and other similar conditions?
A healthcare professional can differentiate between a lipoma and other similar conditions through a process called differential diagnosis. They will perform a physical examination and assess the characteristics of the lump. Other conditions that may resemble lipomas include epidermoid cysts and skin tags. If necessary, imaging tests or biopsies may be ordered for further evaluation.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
References:
- Fisher SB, Baxter KJ, Staley CA 3rd, et al. The General Surgeon’s quandary: atypical lipomatous tumor vs lipoma, who needs a surgical oncologist?. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;217(5):881-888. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2013.06.003
- Charifa, A., Azmat, C. E., & Badri, T. (2022, December 5). Lipoma Pathology. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482343
- Guler O, Mutlu S, Mahirogulları M. Giant lipoma of the back affecting quality of life. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2015;4(3):279-282. Published 2015 Aug 11. doi:10.1016/j.amsu.2015.08.001
- Charifa, A., Azmat, C. E., & Badri, T. (2022, December 5). Lipoma Pathology. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482343/
- Lee YJ, Jeong YJ, Lee JH, Jun YJ, Kim YJ. Liposarcoma in the axilla developed from a longstanding lipoma. Arch Plast Surg. 2014;41(5):600-602. doi:10.5999/aps.2014.41.5.600
- Peev I, Spasevska L, Mirchevska E, Tudzarova-Gjorgova S. Liposuction Assisted Lipoma Removal – Option or Alternative?. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017;5(6):766-770. Published 2017 Oct 14. doi:10.3889/oamjms.2017.186
- Xiong Y, Yang L, Zhen W, Fangyong D, Feng W, Ting L. Conservative and surgical treatment of pediatric asymptomatic lumbosacral lipoma: a meta-analysis. Neurosurg Rev. 2018 Jul;41(3):737-743. doi: 10.1007/s10143-016-0796-6. Epub 2016 Oct 28. PMID: 27796602.

