Open inguinal hernia repair usually takes place when the patient is under general anesthesia. Sometimes, doctors might use regional anesthesia instead. In surgery, the doctor makes a cut to reach and fix the hernia.
The most common location for tissue protrusion through the abdominal wall is the inguinal canal, which is why this condition is known as an inguinal hernia.
This can create a bulge in the groin area, causing pain and other problems. The success of your surgery often relies on your general health condition. Medical professionals often recommend surgical intervention for hernias to address the condition and avert potential complications down the line.
Key Highlights
- An inguinal hernia is a medical condition that develops when a portion of the intestines pushes through a small opening in the abdominal wall. This vulnerable area is located within the inguinal canal.
- Open inguinal hernia repair is a type of surgery that fixes this issue. As the procedure advances, the medical team carefully adjusts the tissues and reinforces the abdominal wall.
- The surgery might use synthetic mesh. This mesh provides additional support and aids in preventing the recurrence of the hernia.
- Usually, open repair procedures are performed with the patient under general anesthesia. Recovery can take several weeks.
- Dr. Valeria Simone, MD, is an expert in general surgery. She focuses on open inguinal hernia repair. Her utmost priority is offering individualized attention while achieving optimal patient outcomes.
Understanding Inguinal Hernia
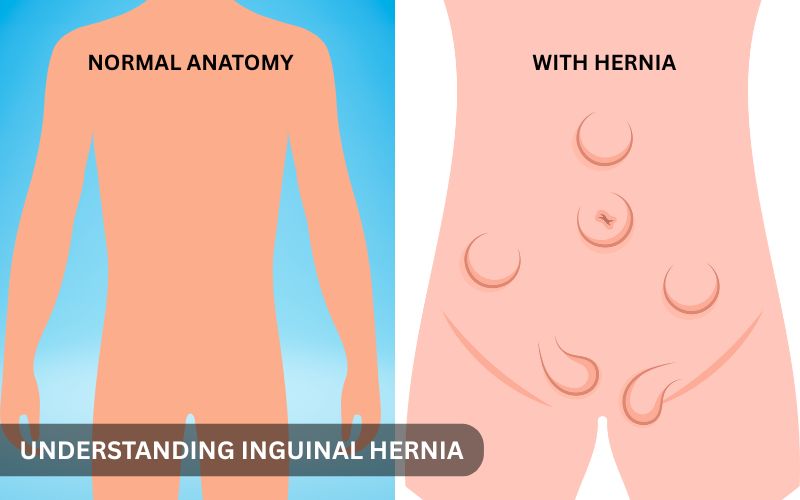
Inguinal hernias are a common problem. These happen when sections of your intestine or fatty tissue protrude through a vulnerable area in the abdominal wall.
The inguinal canal, located in the groin region, which includes the external inguinal ring and is a common site for this to happen. The inguinal canal is the location where the spermatic cord is located in males. The uterine ligament is located there in females.
Inguinal hernias frequently affect men rather than women. In the beginning, they may not be a big risk, but they can feel pain. If you do not treat them, they might lead to serious issues later.
Definition and Overview
In the inguinal region, a hernia can occur when an organ or piece of tissue, like the intestines, pushes through a hole in the abdominal wall. This can cause the inguinal region to become exposed. The groin region, more specifically the inguinal canal, is the typical location where this takes place.
Hernias form when a pouch of tissue forms. This pouch is called a hernia sac. It can hold part of the intestine, fatty tissue, or fluid. In a place known as the Hesselbach triangle, there are two main types of inguinal hernias: indirect and direct.
Furthermore, the inferior epigastric vessels and the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve are both included in this triangle. A direct hernia takes place in a delicate area within the transversalis fascia of this triangle. The indirect hernia occurs more frequently, particularly among men.
The abnormal protrusion or bulge that occurs in the groin region is the defining characteristic of an inguinal hernia. Experiencing pain or discomfort during activities like coughing, lifting, or straining is possible. A feeling of warmth or discomfort might also be felt. A significant number of individuals experience a sensation of weight or tightness in the groin region.
Causes and Risk Factors

An inguinal hernia is experienced when a segment of tissue or an organ, such as the intestines, pushes through a weak place in the abdominal wall. This can cause the organ or tissue to rupture. From person to person, this vulnerability can differ. There may be a connection between certain factors and an increased probability of an inguinal hernia. These risk factors include:
- having a family history of hernias
- being male
- being born early
- have had an inguinal hernia before
Additional risk factors may contribute to increased stress on the abdominal wall. These include being overweight, having long-term constipation, coughing frequently, and lifting heavy things while working hard.
Not everyone who has these risk factors will get an inguinal hernia. However, it’s beneficial for you to be informed about them. Recognizing the early signs and symptoms can help you obtain an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Dr. Valeria Simone’s Approach to Hernia Repair

Dr. Valeria Simone is a skilled general surgeon. She focuses on open inguinal hernia repair. She is part of Southlake General Surgery in Texas, USA. Dr. Simone wants to give the best care for patients with inguinal hernias. Her main aim is to help people get good long-term results.
Dr. Simone knows that every patient is unique. She changes her approach to meet these needs. Communication is very important to her. She makes sure her patients understand their diagnosis, the treatment choices they have, and what they can expect during recovery.
Her Background and Experience
Dr. Simone is an expert in general surgery. She learned a lot from her tough practice in hernia surgery. She works hard to stay updated with the newest changes in her field. This allows her to provide her patients with the best and most advanced care.
Dr. Simone is good at fixing inguinal hernias through open surgery. One small incision is created in the groin region when this method of surgery is used. This cut helps her see the hernia and the surrounding areas clearly. Open surgery works well for complicated hernias or for people with certain health issues.
Dr. Simone is a member of a caring healthcare team. This team has nurses, anesthesiologists, and other medical experts. They work together to help patients receive good and complete care. This care starts at the first visit and goes on through follow-up appointments.
Techniques Employed by Dr. Simone
Dr. Simone often uses open repair methods for treating inguinal hernias. He likes the Shouldice repair technique. A groin incision is required for this type of surgery to access the hernia. With the open approach, the hernia and its surrounding tissues can be seen clearly. It is especially useful for complicated cases or for patients with specific health problems.
During the surgery, Dr. Simone carefully takes out the hernia sac. She restores the protruding tissue to its proper location within the abdomen. A synthetic mesh known as anterior oval polypropylene mesh might be utilized by the surgeon.
This mesh would be appropriate for the anterior rectus sheath. It strengthens the abdominal wall. It also decreases the chances of the hernia coming back. The mesh serves as a protective barrier to help prevent the hernia from recurring.
Dr. Simone likes open repair more than laparoscopic surgery. She feels that laparoscopic surgery affects some patients less. However, she believes that open repair is better over time. Open repair is also effective for more types of cases.
Preoperative Considerations
Before having an open inguinal hernia repair, patients need a full checkup. This checkup is important to confirm they are prepared for surgery. It typically involves examining the patient’s medical history and conducting a physical examination. In certain situations, individuals might also need to undergo imaging tests.
The assessment aims to find any health problems that could affect the surgery or the recovery process. While doing this, Dr. Simone will answer any questions or worries the patient may have about the procedure.
Patient Assessment and Diagnosis
Before we begin the open inguinal hernia repair, we need to examine the patient thoroughly. First, we look at the patient’s medical history. We need to know about any past surgeries, allergies, and current medications. A physical exam focuses on the groin area where the hernia is. Dr. Simone checks the bulge closely. He wants to find out its size, position, and whether it can be pushed back.
Sometimes, doctors recommend tests like an ultrasound or a CT scan. These tests help find the hernia and what is inside it. They provide essential information for planning surgery. This holds significance when the diagnosis is ambiguous or when it’s necessary to investigate additional health issues.
After Dr. Simone finds out the patient has an inguinal hernia, he discusses the treatment options. The most commonly selected approach is open inguinal hernia repair. This method is safe and effective.
Preparing for Surgery
Preparing for open inguinal hernia repair is important for your safety and to help the surgery go well. Dr. Simone provides clear instructions for you to follow before the operation. These instructions will tell you what to eat and drink. Normally, patients should not eat or drink anything for several hours before the surgery.
General anesthesia is the most popular choice. It keeps the patient asleep and pain-free during surgery. Local anesthesia with sedation can also be a good option sometimes.
Patients might have to stop taking some medications, like blood thinners, several days before surgery. Patients must ensure they inform Dr. Simone about every medicine or supplement they are currently using. This will assist in preventing any issues that may arise during or following the surgery.
Surgical Procedure Explained
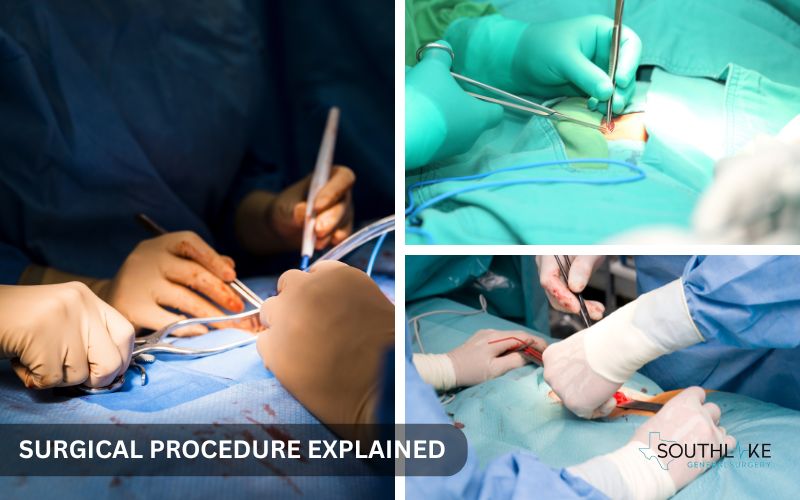
Open inguinal hernia repair is a straightforward procedure consisting of several steps. The surgeon administers anesthesia to numb the area, then proceeds to make an incision in the groin to directly access and repair the hernia.
They locate and push back the hernia sac and the anterior wall of distal sac, before strengthening the weak spot in the abdominal wall using a mesh.
Step-by-Step Process of Open Inguinal Hernia Repair
In the process of addressing an inguinal hernia through open repair, the surgeon begins by making an incision in the groin area. Next, they carefully go through the layers of tissue to find the inguinal canal and the hernia.
The surgeon must check if it is an indirect hernia or a direct hernia. They need to be careful to avoid damaging the ilioinguinal nerve during this process. Once they find the hernial sac, they gently separate its front wall and posterior wall from the nearby structures.
Next, the surgeon will fix the hernia. They will push the bulging tissue or organ back into the right spot in the abdomen. They might use sharp and dull tools to free the hernia sac. If needed, they will also take care of a strangulated hernia. They will be careful not to harm the nearby tissues.
Sometimes, watchful waiting can be a good choice before going for surgery. There are general types of hernia surgeries needed based on the specific situation.
In the last step, the surgeon strengthens the weak spot in the abdominal wall that led to the hernia. This often involves making the back part of the inguinal ligament stronger, including the conjoined tendon region. The inguinal ligament is a strong structure that plays an important role in supporting the internal inguinal ring and the abdominal wall.
The surgeon might employ sutures or a mesh implant to address the issue. Feel free to inquire with your surgeon regarding the most suitable surgical option for your needs. This extra support makes the repair even stronger.
Tools and Technologies Used
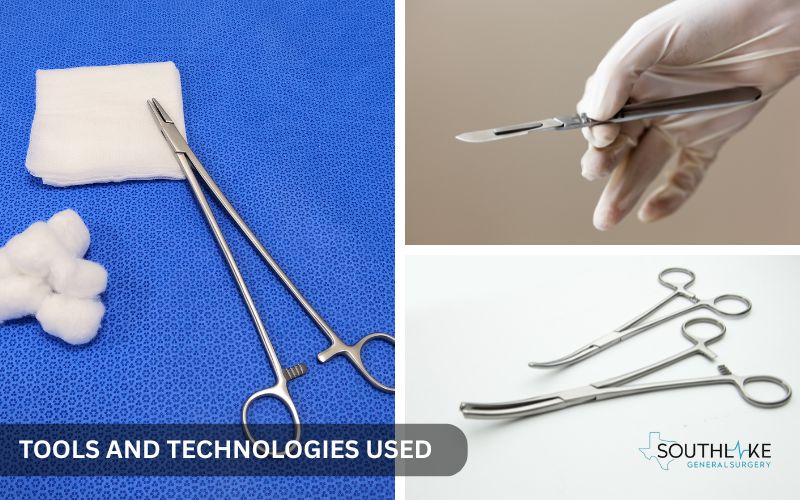
Open inguinal hernia repair involves using specialized tools and modern technology. This helps the surgery be successful. During the procedure, surgeons use certain tools and techniques. They ensure that the hernia repair goes well.
- Scalpel: This instrument creates the initial incision in the groin area.
- Forceps: There are several types, such as tissue forceps and hemostats. They hold and position tissues throughout the surgical procedure.
- Scissors: Surgical scissors are crafted to precisely cut tissues and remove stitches.
- Needle Holder: This tool keeps the needle steady when sewing stitches.
- Synthetic Mesh: A synthetic mesh is often used in the weak abdominal wall. It helps lower the chance of a hernia coming back.
In open inguinal hernia repair, doctors do the surgery without special laparoscopic tools. These tools enhance the safety of surgical procedures and improve outcomes.
Postoperative Care and Recovery

After an open inguinal hernia repair, patients need good care to recover and feel better. Right after surgery, nurses will check vital signs. They will also help with any pain management. Patients might feel some discomfort and swelling in the area where the surgery took place. Medications can assist in alleviating these feelings.
At home, you can begin to return to your normal activities. After surgery, there might be some limits on what you can do. For a few weeks, stay away from heavy lifting and certain movements.
It’s important to avoid tough activities. Do not lift heavy things. Also, be careful not to push too hard when using the bathroom to keep from having any issues.
Immediate Post-Surgery Care
After the open inguinal hernia repair, patients go to a recovery area. A healthcare team checks important signs like blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen levels. It is important to manage pain, so patients get medication to help with any discomfort.
The surgical team looks at the area of the cut. They check for bleeding or signs of infection. This step is key for healing. When patients feel better and wake up, they can eat regular food again. They are also encouraged to walk as much as they feel comfortable.
Waking up early and walking a little in your room can be good for your blood flow. This helps stop blood clots and can help you heal faster. Nurses will show you how to look after your wound, take your medications properly, and when to call the doctor if you feel concerned.
Long-Term Recovery Tips
The recovery time after open inguinal hernia repair can be different for each person. Some things can affect how fast someone heals. Age, overall health, and hernia severity are all relevant considerations.
In the first weeks, it’s important to follow Dr. Simone’s advice closely. Patients might feel ready to do more activities. However, they need to avoid heavy lifting, intense exercises, and quick movements. These can put stress on the surgery area.
Walking is a simple activity. Improving circulation and speeding up the healing process are two possible outcomes. You should pay attention to your body and take breaks when you need to. Most patients can return to their normal activities in a few weeks as their cuts heal.
After your surgery, you should avoid lifting heavy things or doing tough activities for 6 to 8 weeks. It is important to follow Dr. Simone’s advice during this time.
You should also go to regular check-up visits with him. These visits will help you see how well you are healing. They will answer your questions and make sure your recovery is good.
Potential Complications and Management
Open inguinal hernia repair, like any surgery, has some risks. Although problems can arise, they do not happen very often. It is important to understand that each person reacts to surgery in their own way. Even with successful surgery and smooth recovery, problems can still occur.
Learning about these possible problems helps you spot them early. This way, you can get help quickly and lessen any negative effects. Dr. Simone wants to educate his patients. He clearly describes the risks and benefits of the surgery. He also shares tips on how to identify warning signs.
Common Post-Surgery Complications
Open inguinal hernia repair done by a skilled surgeon like Dr. Simone, usually has good results. However, you should know about the risks that come with it. A typical concern associated with any surgical procedure is the possibility of developing an infection.
Another issue, though not very common, is chronic pain. Some individuals experience lasting pain or discomfort in areas where they had surgery or in the groin, which may be a cause of significant postherniorrhaphy pain. Most of the time, medication or other methods can help manage the pain.
In some cases, a hernia might return. If this occurs, you might require an additional surgical procedure. After the surgery, you can be at risk for deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVT is when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, often in the legs. This can hurt the blood supply and damage the blood vessels.
Strategies to Minimize Risks
To reduce problems after an open inguinal hernia repair, several steps are important, such as talking about the patient’s health and risk factors is helpful. Discussing their treatment expectations is also important. This conversation can help find the best way to proceed.
Careful surgery is very important to prevent problems, including a low recurrence rate of issues. Many studies show that this is true. This means handling the tissues gently. The mesh should be placed correctly. Moreover, it is essential to regulate the circulation of blood to halt any bleeding.
Caring for patients after surgery is very important. It is beneficial to begin the process of movement again at the earliest opportunity. It’s also crucial to manage pain and take care of wounds.
If you listen to Dr. Simone’s advice after your surgery, you can lower the chance of getting an infection and aid in your recovery.
Benefits of Open Inguinal Hernia Repair
Open inguinal hernia repair offers clear benefits. Surgeons have a precise view of the hernia, reducing risks during the procedure. New research indicates that this method is more effective in preventing hernia recurrence than non-surgical alternatives.
Patients undergoing successful open inguinal hernia repair often experience improved outcomes, including reduced pain and complications.
Effectiveness and Success Rates
Open inguinal hernia repair is an established method for addressing inguinal hernias. Many studies indicate that this method is effective in fixing the hernia. It can also help lessen symptoms and stop the hernia from coming back in most cases.
Skilled surgeons in the United States can fix over 95% of open inguinal hernias using Lichtenstein hernioplasty. This means that more than 95% of patients typically get their hernia repaired successfully as noted in an audit of Lichtenstein hernioplasty. Also, there is a very low chance that the hernia will return.
Open repair doesn’t have many problems with hernias coming back. The reason for this is the technique applied during the surgical procedure. This way, patients can return to their everyday lives without fear of the hernia coming back.
Comparisons with Other Hernia Repair Methods
Open hernia repair is a common method to fix an inguinal hernia. But laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair is becoming more popular. This is mostly because it is easier on the body. When deciding between open hernia repair and laparoscopic repair, several factors are important. You should consider if there is a recurrent hernia, the size and type of hernia, the person’s overall health, and the surgeon’s choice.
In laparoscopic hernia repair surgery, also known as keyhole surgery, the doctor makes several small cuts in the abdomen. A flexible instrument known as a laparoscope is utilized. This tube has a camera to help the doctor see the hernia.
There are two ways to do mesh repair of inguinal hernia: the open method and the laparoscopic method. Both methods use surgical mesh to strengthen the weak spots in the abdominal wall.
In the end, the best way to treat a hernia depends on each person. It is important to discuss the risks and benefits of all options.
When to Call the Doctor
After open inguinal hernia repair, look for any problems. Most people heal well. If you notice anything unusual, contact Dr. Simone right away. You can also reach out to another doctor if you feel it is needed.
If you feel extra pain or see redness and swelling around your cut, call your doctor right away. If you notice signs like fever, chills, feeling unwell, vomiting, or having trouble urinating, seek help. You should also let your doctor know quickly if you see any bulging or if the hernia comes back.
When Should I Contact My Healthcare Provider
After an open inguinal hernia repair, most people feel better pretty fast. However, be aware of any problems. If something doesn’t feel right, see a doctor right away. If you notice any of these issues, contact your healthcare provider quickly:
- Fever or chills: This might mean you have an infection that needs quick help.
- Increased pain at your incision site: A little pain is normal, but it shouldn’t be getting worse.
- Redness, swelling, warmth, or drainage from the incision: These signs can indicate an infection.
- Nausea, vomiting, or a swollen belly: These could mean you have a bowel obstruction. This condition is critical, and immediate assistance is required.
- Pain, swelling, or tenderness in your calf or leg: These symptoms could show deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which is a type of blood clot.
- Trouble urinating or blood in your urine: This might mean you have a urinary tract infection (UTI) or other issues with your urine.
If you observe any of these indicators, reach out to your physician immediately. Seeking assistance promptly can enhance your well-being.
A note from Dr Valeria Simone, MD, Southlake General Surgery
At Southlake General Surgery, we prioritize personalized care for every patient. With extensive experience in surgery and a focus on innovative hernia treatments, we provide top-notch care.
Our goal is to ensure that patients are well-informed about their health, surgical procedures, and recovery process. We value transparency and dedicate time to address all questions and concerns, aiming to offer the best care in a welcoming environment.
If you’re experiencing discomfort or issues from an inguinal hernia, schedule a consultation with us for a tailored treatment plan to enhance your well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, you must prioritize your health. This is even more crucial if you have problems like bowel obstruction or deep vein thrombosis. Watch for warning signs.
These signs can be swelling in your legs, difficulty peeing, or pain. Be quick to respond if you see these symptoms. Dr. Valeria Simone from Southlake General Surgery highlights the importance of making smart health choices.
She emphasizes that getting the right care is essential, especially for open inguinal hernia repair. Don’t wait to get help. Make today the first step toward a healthier future.
Make an Appointment
If you are thinking about open inguinal hernia repair, you should talk to Dr. Valeria Simone, MD, at Southlake General Surgery in Texas, USA. Dr. Simone is very knowledgeable about hernia surgery. She can give you the advice you need.
To make an appointment, call Southlake General Surgery at +1 (817) 748-0200. Speaking with Dr. Simone is the first step towards your successful hernia repair. You will receive the most appropriate treatment and information based on this discussion.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the success rate of open inguinal hernia repairs?
Open repair of inguinal hernias is really effective. The success rate is over 95%. This shows that most people who undergo hernia surgery see excellent results. They also have a small chance of their hernia returning.
When can I expect to return to my normal routine after the surgery?
The duration for recovery after hernia surgery can differ from one individual to another. Many people can begin light activities a few weeks after surgery. A complete recovery, where you can do more intense activities, usually takes about 6 to 8 weeks or sometimes longer. This can change based on personal factors and how well you take care of yourself after surgery.
Are there any lifestyle restrictions on post-surgery?
After your open inguinal hernia repair, you will need to make some changes in your life. It’s important to stay away from heavy lifting and hard activities for several weeks after the surgery. It’s a good idea to gradually start resuming your regular activities. It is critical that you follow your surgeon’s instructions carefully while you are recovering.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
References:
- Akyol, C., Kocaay, F., Orozakunov, E., Genc, V., Bayram, I. K., Cakmak, A., Baskan, S., & Kuterdem, E. (2013). Outcome of the patients with chronic mesh infection following open inguinal hernia repair. Journal of the Korean Surgical Society, 84(5), 287. https://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2013.84.5.287
- HerniaSurge Group. International guidelines for groin hernia management. Hernia. 2018 Feb;22(1):1-165. doi: 10.1007/s10029-017-1668-x. Epub 2018 Jan 12. PMID: 29330835; PMCID: PMC5809582.
- Hakeem, A. (2011). Inguinodynia following Lichtenstein tension-free hernia repair: A review. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 17(14), 1791. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i14.1791
- Paajanen, H., & Varjo, R. (2010). Ten-year audit of Lichtenstein hernioplasty under local anaesthesia performed by surgical residents. BMC Surgery, 10(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2482-10-24
- Viscusi, E., Minkowitz, H., Winkle, P., Ramamoorthy, S., Hu, J., & Singla, N. (2019). HTX-011 reduced pain intensity and opioid consumption versus bupivacaine HCl in herniorrhaphy: results from the phase 3 EPOCH 2 study. Hernia, 23(6), 1071–1080. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-019-02023-6
- Kark, A. E., Kurzer, M., & Waters, K. J. (1995, July 1). Tension-free mesh hernia repair: review of 1098 cases using local anaesthesia in a day unit. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2502328/
- Gianetta, E., Cuneo, S., Vitale, B., Camerini, G., Marini, P., & Stella, M. (2000). Anterior Tension-Free repair of recurrent inguinal hernia under local anesthesia. Annals of Surgery, 231(1), 132. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-200001000-00019

