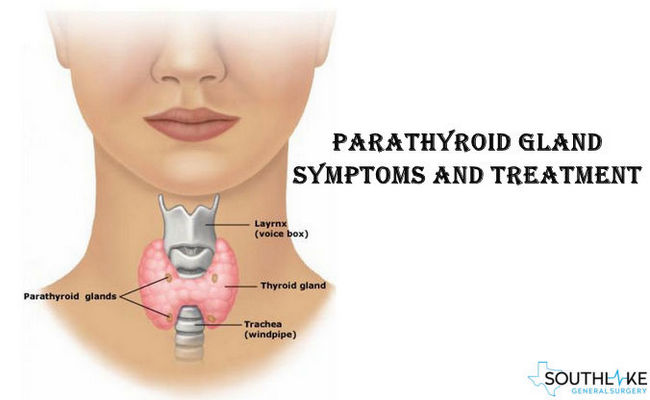
The parathyroid gland comprise of four individual pieces that are small and round. They’re appended to the rear of the thyroid gland in neck. These glands are a piece of the endocrine system. Endocrine system produces and directs the hormones that influence the human growth, advancement, body capacity, and state of mind.
Parathyroid gland control the measure of calcium in our blood. At the point when the calcium level is low in circulatory system, these glands discharge parathyroid hormone (PTH), which collects calcium from bones.
Parathyroid gland removal is a type of surgery to remove these glands. It’s also called a Parathyroidectomy. This surgery may be performed if the blood has a high level of calcium in it. This is a condition called as Hypercalcemia. It is a result of overactive parathyroid glands.
Why parathyroid gland removal is required?
Hypercalcemia happens when blood calcium levels are unusually high. The most well-known reason for hypercalcemia is an overproduction of PTH in at least one parathyroid organs. This is a type of hyperparathyroidism called essential hyperparathyroidism. Primary hyperparathyroidism is twice as basic in women for what it’s worth in men. Many people diagnosed to have primary hyperthyroidism are more than 45 years of age. The average age of finding is around 65 years.
Under following circumstance it might require to remove parathyroid glands:
- Tumors known as adenomas, which are often amiable and once in a while transform into cancer
- Cancer prone tumors on or near the glands
- Parathyroid hyperplasia, a condition where every one of the four of the parathyroid glands are enlarged.
Levels of calcium in blood can rise regardless of whether just a single gland is influenced. Just a single parathyroid gland is associated with around 80 to 85 percent of cases.
Symptoms of Hypercalcemia
Symptoms can be ambiguous in the initial stage of hypercalcemia. As the condition advances, it may cause:
- Weakness
- depression
- muscle aches or cramps
- a loss of appetite
- nausea
- vomiting
- excessive thirst
- frequent urination
- abdominal pain
- constipation
- muscle weakness
- confusion
- kidney stones
- bone fractures
Individuals without any symptoms may just need observation. Mellow cases can be overseen therapeutically. In any case, if hypercalcemia is because of primary hyperparathyroidism, surgery is the only treatment option that removes the influenced parathyroid gland(s).
The major consequences of hypercalcemia are:
- kidney failure
- hypertension
- arrhythmia
- coronary artery disease
- an enlarged heart
- atherosclerosis (arteries with calcified greasy plaques that solidified and anomalous function)
This may because of the development of calcium in the arteries and heart valves.
Types of Surgeries
There are different approaches to locate and remove the infected parathyroid glands.
Radio-guided parathyroidectomy
In a radio-guided parathyroidectomy, surgeon uses radioactive material that every one of the four parathyroid organs will absorb. A special test can find the wellspring of the radiation from every organ so as to orient and locate the parathyroid gland(s). If only a couple on a similar side are unhealthy, surgeon just needs to make a small incision to remove the ailing gland(s).
Video-assisted parathyroidectomy (also known as endoscopic parathyroidectomy)
Under video-helped parathyroidectomy, surgeon uses a mini camera on an endoscope. Through this methodology, surgeon form 2-3 small incisions for the endoscope and the surgical instruments in the sides of the neck and one incision over the breastbone. This limits obvious scarring.
A minimum intrusive parathyroidectomy allows for a quick recover. In any case, if not all of the infected glands are found and removed, the high calcium levels will proceed, and there might be requirement for a subsequent surgery.
Individuals with parathyroid hyperplasia (influencing every one of the four glands) will mainly have three and a half parathyroid glands removed. The surgeon will leave the rest of the tissue to control calcium levels in blood. In any case, the parathyroid gland tissue that should stay in the body will be removed from the neck area and embedded in an available spot, similar to the lower arm, in the event that it should be removed later.
Post-surgery
You may get back home same day of surgery or might spend a night in the hospital. There’s might be some pain or inconvenience after surgery, for example, a sore throat. Many people can come back to their normal routine possibly in 14 days, however it can differ from individual to individual.
As a safety measure, blood calcium and PTH levels will be checked for at least a half year post surgery. You may take supplements for a year after surgery to reconstruct bones that have been burglarized of calcium.
For more information on Parathyroid, please feel free to contact our healthcare expert and book an appointment: https://www.southlakegeneralsurgery.com/make-an-appointment/