Piles and hemorrhoids are health problems that many people face, regardless of their age. These enlarged veins in the rectal area can lead to pain and discomfort. This can make regular activities hard to do.
Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatments of these issues is really important. Doing so can help manage them better. Let’s take a closer look at piles and hemorrhoids to understand this common health concern.
Key Highlights
- Hemorrhoids, commonly referred to as piles, are enlarged veins that develop in the lower rectum and anus.
- Common indicators of hemorrhoids include rectal bleeding, itching, pain, and discomfort.
- Some risk factors include chronic constipation, pregnancy, obesity, and not eating enough fiber.
- Home remedies can help you feel more at ease. These solutions consist of warm baths, commercially available creams, and increasing fiber intake.
- If needed, medical treatments can range from simple procedures to surgery for more serious cases.
Exploring the Basics of Hemorrhoids and Piles
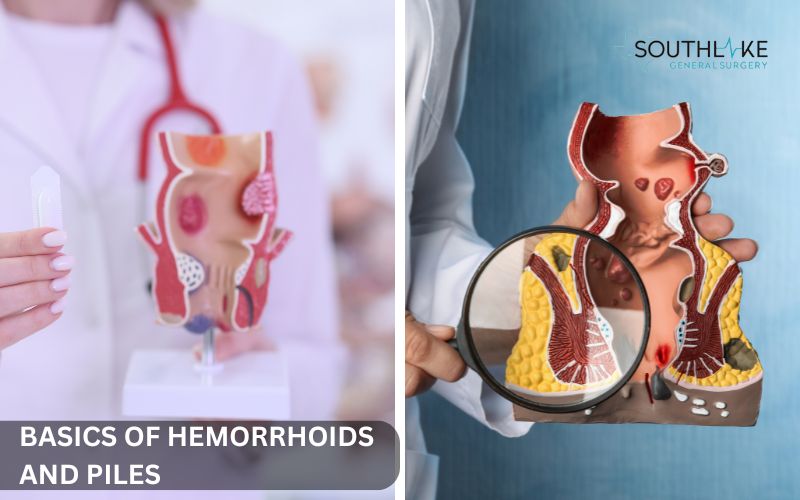
Hemorrhoids, or piles as they’re sometimes known, are generally swollen veins that can occur in the lower rectum and anus. They kind of feel like varicose veins in the legs. Swollen veins can really be a pain, causing discomfort and sometimes even leading to bleeding. A lot of people go through this kind of thing at some stage in their lives.
Hemorrhoids can occur for several reasons. Some of the common reasons are chronic constipation, sitting for a long time, being pregnant, and being overweight. If you find yourself straining in the bathroom or not getting enough fiber in your diet, you might end up with hemorrhoids.
Defining Hemorrhoids and Their Connection to Piles
Hemorrhoids and piles are just two names for the same problem. They both mean swollen veins in the anal canal. Being familiar with the various kinds is essential. You will be able to receive the correct diagnosis and treatment with this knowledge.
Internal hemorrhoids are located inside the anal canal. They usually don’t hurt, even if there’s some bleeding. This is because there are fewer pain receptors in that area. Sometimes, they can come out from the anus during bowel movements or when lifting heavy things.
External hemorrhoids develop beneath the skin near the rectum. This area has a lot of pain sensors, which can make them hurt more. You might feel some discomfort or itching, and there could be a slight sign of bleeding too.
How Common Hemorrhoids Are In The United States
Hemorrhoids are a common problem in the digestive system in the United States. Many people here have them. Anyone can get hemorrhoids, but they usually happen more often in older adults.
Research shows that almost half of adults over 50 in the United States have symptoms of hemorrhoids. The real number might be larger. Many people may feel embarrassed to talk about this private issue with their doctors.
If you think you might have hemorrhoids, it’s important to talk to a qualified healthcare provider. Accurate diagnosis can be facilitated by their assistance. They can also recommend treatment options and answer any questions you may have.
Identifying Different Types of Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids can be categorized into two primary types: those that are internal and those that are external. Understanding the difference is important for choosing the best treatment. Internal hemorrhoids form inside the rectum. Usually, you can’t see or feel them unless they’re sticking out.
External hemorrhoids are located just beneath the skin around the anus. They’re easier to notice than other kinds. Hemorrhoids can really be a pain, causing discomfort, itching, and annoying pain, especially when you’re using the bathroom.
Internal vs. External Hemorrhoids: What Sets Them Apart
Internal hemorrhoids happen when blood vessels in the lower rectum swell up. They come in four grades, which shows how serious they are.
- Grade 1 hemorrhoids are small and remain inside the rectum.
- Grade 2 hemorrhoids come out during a bowel movement but go back inside on their own.
- Grade 3 hemorrhoids come out and need to be pushed back in with your hand.
- Grade 4 hemorrhoids stay out all the time.
External hemorrhoids form under the skin that encircles the anus. They can feel more uncomfortable. Since they are in a sensitive area, they can get irritated easily. This discomfort may result in itching, pain, and occasionally bleeding.
It is key to understand the difference between these two types. This knowledge helps you pick the best treatment. A healthcare worker can help you see what the problem is. They can create a personalized plan that suits your needs perfectly.
Recognizing the Signs: Symptoms Associated with Each Type

It is important to recognize the symptoms of hemorrhoids. This helps you notice them early and get proper treatment. The symptoms can change depending on the type and seriousness. Here are some common signs:
Internal Hemorrhoids:
- You may observe bright red blood on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl following a bowel movement.
- A hemorrhoid might pop out from the anus when you’re using the bathroom. There are times when you might have to just push it back in.
- You may feel a sense of fullness or pressure in the rectal area.
External Hemorrhoids:
- Itching and irritation around the anus can be caused by swollen veins.
- You might feel a lot of discomfort or pain, particularly when you’re sitting down.
- A swollen area or a firm mass close to the anal area.
- A small amount of bleeding.
If you observe any signs of hemorrhoids, it is advisable to consult a physician. They can give you a correct diagnosis and help you create a treatment plan. Neglecting these symptoms could result in further complications. It is better to take action early.
Unveiling the Causes Behind Hemorrhoids

Hemorrhoids occur when there is too much pressure in the veins of the rectum. This added pressure might cause some swelling and inflammation. One usual reason is putting too much effort into bowel movements, which is often connected to constipation.
Other causes may include pregnancy, being overweight, sitting or standing for a long time, and not getting enough fiber in your diet. Getting to know what leads to hemorrhoids can really help you keep them at bay and handle them better.
Lifestyle and Dietary Factors Contributing to Hemorrhoid Development
Many choices about your diet and lifestyle can greatly affect your risk of getting hemorrhoids. It’s important to know these things so you can avoid them.
- Chronic constipation often causes hemorrhoids.
- A diet lacking in fiber may result in hard stools that are difficult to eliminate.
- Straining during bathroom trips can put pressure on the veins in the rectal area.
- Adding more fiber to your diet and drinking plenty of water can help you prevent constipation and hemorrhoids.
The Impact of Ageing and Pregnancy on Hemorrhoid Risk
Ageing and pregnancy are two stages in life when the risk of hemorrhoids can rise. As we get older, the tissues that hold the veins in our rectum and anus become weaker and stretch more. This makes it likely for those veins to swell when there is pressure. Because of this, the chance of getting hemorrhoids increases.
- When a woman is pregnant, her growing uterus puts pressure on veins in the pelvic area. This includes veins in the rectum. The pressure can block blood flow. This might make the veins swell and can lead to hemorrhoids.
- Pregnancy causes hormonal changes. These changes may slow down digestion. This can cause constipation and raise the risk of hemorrhoids.
- A healthy lifestyle can help. Eating a balanced diet and exercising often can prevent and ease hemorrhoid symptoms.
Effective Strategies for Hemorrhoid Prevention
To avoid hemorrhoids, you should practice good habits for digestion. Eat a lot of fiber to make your stool soft. This helps you go to the bathroom regularly and reduces the need to strain. Also, make sure to exercise often. It helps you stay at a healthy weight and improves how your bowels work. These actions can lower the risk of hemorrhoids.
Diet and Exercise for Hemorrhoids Prevention
A balanced diet with plenty of fiber is key to preventing hemorrhoids. You should eat a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Some good examples of whole grains are brown rice, oatmeal, and whole-wheat bread. Fiber helps make your stool larger. This makes it easier for you to go to the bathroom and lessens the need to strain.
- Drinking enough water keeps your stool soft. It helps with regular bowel movements. Try to consume a minimum of eight glasses of water daily.
- Staying active is important too. Exercise regularly, like walking fast. This can prevent constipation. It helps you keep a healthy weight, reduces pressure on your veins, and lowers the risk of hemorrhoids.
Importance of Regular Health Check-Ups and Early Detection
Regular health check-ups are key for spotting and treating hemorrhoids early. At your check-up, your doctor may perform a physical exam. This could include a digital rectal exam to assess your risk and identify any potential issues.
- Finding problems early with regular check-ups helps your doctor suggest ways to stop issues.
- These could be changes to your daily habits and what you eat.
- Taking these steps can lower the chance of getting hemorrhoids.
If you notice any symptoms, your doctor may recommend extra tests. This can involve a flexible sigmoidoscopy or a colonoscopy. These tests look for other health issues.
Getting problems diagnosed early and beginning treatment can greatly improve your health. It can also lower the chance of problems in the future.
Treatment of Hemorrhoids
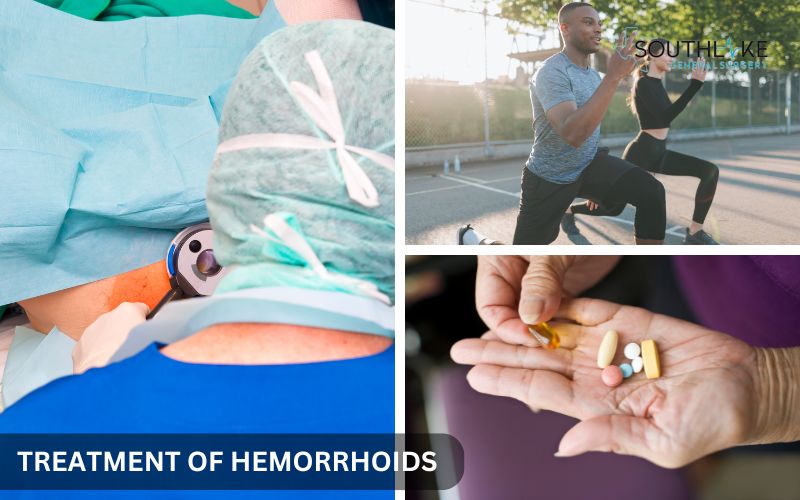
Hemorrhoid treatment includes home remedies and surgery. The choice relies on how severe your case is. Simple treatments work well for mild symptoms.
On the other hand, surgery may be needed for severe hemorrhoids that do not improve. Your physician will assess your symptoms and medical background. They will also check what type of hemorrhoid you have. This will help them determine the best treatment for you.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Many people can feel relief from hemorrhoid symptoms without surgery. Here are some non-surgical treatments that may help improve their lives:
- Lifestyle Changes: Eating more fiber, drinking enough water, and exercising often can help your bowel movements and reduce strain.
- Topical Creams: Over-the-counter creams, ointments, and suppositories with hydrocortisone or witch hazel can help ease itching, pain, and swelling temporarily.
- Sitz Baths: Soaking the affected area in warm water for 10-15 minutes every day can reduce swelling and support healing.
- If these choices do not work, your doctor might suggest some simple procedures, like:
- Rubber Band Ligation: A small rubber band gets placed around the base of the hemorrhoid. This stops its blood supply. Because of this, the hemorrhoid shrinks and will fall off later.
- Sclerotherapy: A chemical solution is administered to the hemorrhoid. This helps to make it smaller.
Surgical Treatment
Non-surgical treatments are often the first option. But, if piles or hemorrhoids are severe and don’t get better with other treatments, surgery may be needed. These surgeries are usually done as outpatient procedures. This means you won’t have to stay overnight in the hospital.
- Hemorrhoidectomy: This is a surgery to take out the hemorrhoid. The procedure can be performed using local anesthetic, general anesthesia, or spinal anesthesia.
- Hemorrhoidopexy: This method uses staples to keep the hemorrhoid in place and stop it from sticking out. It can also be performed using local anesthetic, general anesthesia, or spinal anesthesia.
Choosing the best surgery for your case depends on how bad your hemorrhoids are and which type you have. It’s important to talk to your doctor about this. They can tell you the risks and benefits of each type of surgery.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is important to know about piles and hemorrhoids to stay healthier. Understanding the signs and risk factors can help people choose the right treatment, whether it is surgery or another option. Making simple changes in your life, like eating more fiber, drinking enough water, and exercising often, can greatly reduce your chances of getting hemorrhoids.
If you see ongoing problems like rectal bleeding or anal itching, you should see a doctor. A correct diagnosis and proper care are vital. Finding out early and acting quickly can help manage hemorrhoid issues before they get worse. This can make your life and health better.
Don’t feel shy to talk with a healthcare provider for advice that suits your needs. Make an appointment today for thorough care and support.
Make an Appointment
You can get help with your piles and hemorrhoids by going to see Dr. Valeria Simone, MD, at Southlake General Surgery in Texas, USA. To book an appointment, just call +1 (817) 748-0200.
Dr. Simone knows a lot about colorectal issues. She will listen to your symptoms and create a treatment plan for you. Getting expert help is important to reduce your pain. You can talk about options like lifestyle changes or surgery if needed. Start feeling better by making your appointment today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Piles and Hemorrhoids the Same Thing?
Hemorrhoids and piles are the same thing. They happen when the blood vessels in the anal canal become swollen and inflamed. This can cause symptoms such as rectal bleeding, pain, and discomfort in the anal area.
Can Diet Influence the Risk of Developing Hemorrhoids?
Diet is important when it comes to piles or hemorrhoids. Consuming foods that are low in fiber may result in constipation. When you are constipated, you may strain while using the bathroom. Straining can raise the risk of hemorrhoids. However, having a diet rich in fiber, like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help lower the risk of hemorrhoids.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
References:
- Gallo G, Lori E, Goglia M, Dezi A, Picciariello A, Grossi U. Effectiveness of preoperative micronized purified flavonoid fraction treatment and sucralfate-based rectal ointment on hemorrhoidal disease: A case-matched analysis. Tech Coloproctol. 2024 Sep 17;28(1):126. doi: 10.1007/s10151-024-02998-0. PMID: 39287845; PMCID: PMC11408642.
- Wang Y, Su W, Zeng X, Liu Z, Zhu J, Wang M, Li L, Shen W. Surprising diversity of new plasmids in bacteria isolated from hemorrhoid patients. PeerJ. 2024 Aug 30;12:e18023. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18023. PMID: 39224828; PMCID: PMC11368089.
- Cristea C, Lewis CR. Hemorrhoidectomy. [Updated 2024 Feb 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549864/
- Kestřánek J. Hemorrhoid management in women: the role of tribenoside + lidocaine. Drugs Context. 2019 Sep 13;8:212602. doi: 10.7573/dic.212602. PMID: 31555338; PMCID: PMC6752749.
- Fontem RF, Eyvazzadeh D. Internal Hemorrhoid. [Updated 2023 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537182/
- Lawrence A, McLaren ER. External Hemorrhoid. [Updated 2023 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK500009/
- Kibret AA, Oumer M, Moges AM. Prevalence and associated factors of hemorrhoids among adult patients visiting the surgical outpatient department in the University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. PLoS One. 2021 Apr 20;16(4):e0249736. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249736. PMID: 33878128; PMCID: PMC8057569.

