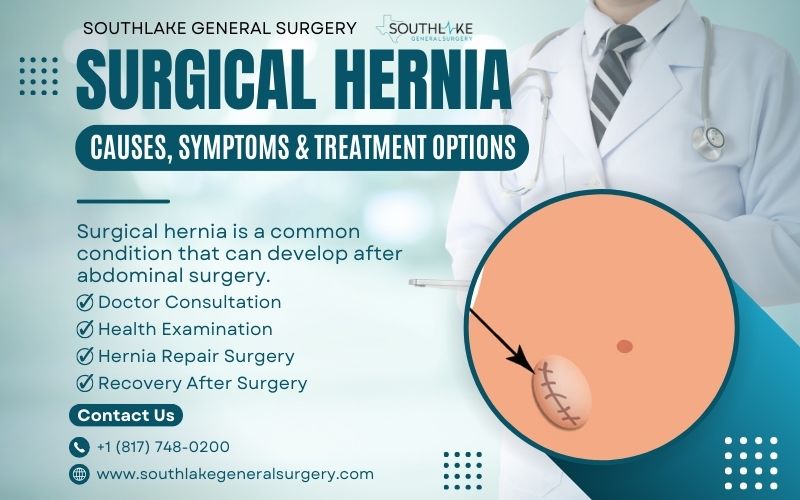
Surgical hernia is a common health condition that can develop after abdominal surgery. They occur when there is a weakening or opening in the abdominal wall, allowing tissue or organs to protrude.
Because of this, a lump or bulge near the site of the surgical incision may become apparent. Surgical hernias can cause discomfort and pain, and in some cases, they may lead to serious complications requiring medical intervention.
Understanding surgical hernias is important for individuals who have undergone abdominal surgery or who may be at risk for developing hernias. This blog will provide valuable information about the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for surgical hernias. We will also discuss the recovery process after hernia surgery and potential complications that may arise.
By understanding surgical hernias and their management, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and seek appropriate medical care when needed. For an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans, it is essential to speak with a medical professional.
Key Highlights
- Surgical hernia is a common condition that can develop after abdominal surgery.
- A prominent indication of a surgical hernia is the presence of a protrusion near the surgical incision site.
- Factors such as abdominal pressure and heavy lifting can contribute to the development of hernias.
- Non-surgical care and surgical repair are the treatment options available for surgical hernias.
- Recovery after hernia surgery involves a post-surgery hospital stay and a period of recovery at home.
- Potential complications of surgical hernias include bowel obstruction and long-term health considerations.
Understanding Surgical Hernias

Surgical hernia is a specific type of hernia that occurs after abdominal surgery. The abdominal wall, which is normally strong and intact, can become weakened or damaged during surgery, leading to the development of a hernia. This can happen due to factors such as the type of hernia repair performed, the location of the surgical incision, and individual patient factors.
Surgical hernias can manifest as different types, including incisional hernias and ventral hernias, depending on the location of the hernia along the surgical incision or abdominal wall.
What is a Surgical Hernia?
A surgical hernia is a condition where there is a protrusion of tissue or organs through a weakened area in the abdominal wall. It occurs because of a previous surgical incision that did not heal properly or a weakening of the abdominal muscles due to surgery.
Surgical hernias can develop after various types of abdominal surgeries, including open surgeries and laparoscopic procedures. The hernia may appear as a visible bulge or lump near the surgical incision site.
In some cases, surgical hernias can cause discomfort, pain, or other symptoms. If you think you may be suffering from a surgical hernia, you should consult a doctor immediately. Symptoms can be alleviated and problems can be prevented with treatment.
Different Types of Surgical Hernias
Different types of surgical hernias can occur after abdominal surgery, including:
- An incisional hernia develops at or near the site of a previous surgical incision
- Ventral hernia can form anywhere along the abdominal wall, caused by weakness in the abdominal muscles or tissues, and further classified as an Epigastric hernia, Umbilical hernia, or Flank hernia.
- Abdominal incisional hernias are a distinct form of surgical hernia that occurs at the location of a prior abdominal incision. These hernias can cause discomfort, pain, or other symptoms and may require treatment to prevent complications.
Causes of Surgical Hernias
Surgical hernia happens due to abdominal surgery, scar tissue, and some risk factors. Abdominal surgery weakens the abdomen and raises hernia risk. Scar tissue from earlier surgeries can also cause hernias by creating weak spots in the abdomen.
Factors that increase the likelihood of hernias include being overweight, smoking, and chronic coughing. Knowing these factors and taking precautions are vital to lower hernia risk.
Factors Leading to Hernia Development
Surgical hernias can be caused by many factors, such as:
- Increased abdominal pressure, which can occur due to factors such as obesity, pregnancy, or chronic coughing
- Heavy lifting, which can put excessive strain on the abdominal muscles
- Additional risk factors include characteristics such as age, gender, family history, and certain medical disorders
It is important to be aware of these risk factors and take appropriate measures to reduce the risk of hernia formation, such as:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Practicing proper lifting techniques
- Seeking medical advice for risk management
Role of Previous Surgeries in Hernia Formation
Previous surgeries can play a role in the development of surgical hernias. Abdominal surgeries can weaken the abdominal wall and increase the risk of hernia formation. The surgical incision and the healing process can create areas of weakness in the abdominal wall, making it more susceptible to hernia development.
Moreover, the choice of surgical technique and the level of proficiency in wound closure might also impact the likelihood of hernia development.
Individuals with a history of previous abdominal surgeries should be aware of the potential risk of hernias and take appropriate precautions to minimize the risk, such as practicing proper wound care and following post-surgical instructions from healthcare providers.
Identifying Symptoms of Surgical Hernias

Identifying the symptoms of surgical hernias is important for timely diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms of surgical hernias include a visible bulge or lump near the surgical incision site, abdominal discomfort or pain, and changes in bowel movements.
In some cases, surgical hernias can lead to complications such as bowel obstruction, which can cause severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Chronic pain in the abdominal area is also a possible symptom of surgical hernias.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms or suspect you may have a surgical hernia, it is important to seek medical advice for proper evaluation and treatment.
Common Symptoms to Watch For
Common symptoms of surgical hernias include:
- An observable protuberance or swelling close to the surgical incision location
- The bulge may become more noticeable when straining or during physical activity
- Abdominal pain or discomfort, which may exhibit varying degrees of severity
- Symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and changes in bowel movements if the hernia becomes trapped or obstructs part of the bowel
- Chronic pain in the abdominal area
If you notice any of these symptoms or have concerns, it is important to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you are experiencing severe pain, sudden changes in bowel movements, or any other concerning symptoms associated with a surgical hernia, it is important to seek immediate medical advice.
These symptoms may indicate complications such as bowel obstruction, which requires prompt medical attention. Additionally, if you notice a visible bulge or lump near a surgical incision site, it is important to have it evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Seeking medical help ensures correct diagnosis and treatment, leading to the best health outcome. A doctor will check symptoms, conduct tests, and suggest suitable treatments based on your needs.
Treatment Options for Surgical Hernias
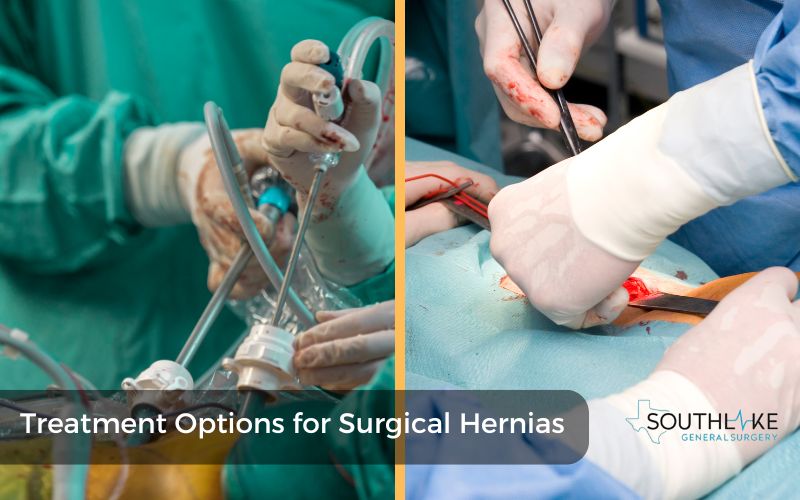
Treatment options for surgical hernias depend on the size, location, and severity of the hernia. Non-surgical methods are suggested for small hernias without symptoms. Lifestyle changes like no heavy lifting are recommended.
Surgical repair is needed for larger or symptomatic hernias. It can be open or laparoscopic surgery. Open surgery involves a cut at the hernia site, while laparoscopic surgery is minimally invasive. The choice of surgery depends on the case and the doctor’s advice.
Non-Surgical Management Techniques
Non-surgical management techniques may be recommended for small, asymptomatic hernias or in cases where surgery is not an immediate option. These techniques focus on:
- Lifestyle modifications such as avoiding heavy lifting or straining the abdominal muscles
- Continuously observing the hernia for any alterations or progression of symptoms
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Making appropriate dietary and activity modifications to reduce abdominal pressure
Working closely with a healthcare provider is essential for closely monitoring the hernia and effectively managing symptoms.
While non-surgical management techniques may provide temporary relief, it is important to note that surgical repair is often necessary for long-term resolution and to prevent potential complications.
Your healthcare provider will be able to determine the most suitable treatment approach based on your individual needs and circumstances.
Surgical Treatment Approaches: Laparoscopic Hernia Repair & Open Surgery
There are two main surgical treatment approaches for surgical hernias: laparoscopic hernia repair and open surgery.
- Laparoscopic hernia repair is a minimally invasive procedure that involves making small incisions and using a camera and surgical tools to repair the hernia.
- Benefits of laparoscopic hernia repair include smaller incisions, reduced risk of infection, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery times.
- Open hernia repair involves making a larger incision at the hernia site to repair the hernia. This technique may be necessary for larger or more complex hernias.
A comparison of laparoscopic hernia repair and open hernia repair is summarized in the table below:
| Surgical Treatment Approach | Laparoscopic Hernia Repair | Open Hernia Repair |
| Incision Size | Small incisions (about 0.5-1 inch) | Large incision at the hernia site |
| Surgical Technique | Minimally invasive | Traditional open surgery |
| Benefits | Smaller incisions, reduced risk of infection | Suitable for larger or more complex hernias |
| Recovery Time | Shorter hospital stay, quicker recovery | Longer recovery period |
| Potential Risks and Complications | Risk of surgical complications, hernia recurrence | Risk of surgical complications, hernia recurrence |
The surgical treatment for a hernia depends on factors like size, complexity, and health. Discuss options with your healthcare provider to choose the best treatment for you.
Preparing for Hernia Surgery
Preparing for hernia surgery involves several important steps to ensure a successful procedure and recovery. Prior to surgery, your healthcare provider will conduct a thorough evaluation of your medical history, including any underlying health conditions or medications you are taking.
They may also order additional tests, such as blood work or imaging studies, to assess your overall health and the severity of the hernia. It is important to follow any preoperative instructions provided by your healthcare provider, which may include fasting before surgery and discontinuing certain medications.
Discuss any concerns or questions you have with your healthcare provider to ensure you are fully prepared for the surgical procedure.
Steps Before Your Surgery
Before your hernia surgery, it is essential to follow a few steps to ensure a smooth and successful procedure.
- Talk to your doctor about your health history, including any preexisting problems, current medications, and any other medications you’re taking.
- Your healthcare provider may order preoperative tests, such as blood tests or imaging studies, to assess your overall health and the severity of the hernia.
- Follow any preoperative instructions provided by your healthcare provider, which may include fasting before surgery, discontinuing certain medications, or adjusting your daily routine.
- Contact a medical professional if you have any inquiries or apprehensions.
By taking these necessary steps before your surgery, you can help ensure a successful outcome and promote a smooth recovery process.
What to Anticipate on the Day of Your Surgical Procedure
On the day of your hernia surgery, you can expect to be admitted to the hospital or surgical center. You will be prepared for the procedure by the medical staff, who will review your medical history, verify any preoperative instructions, and answer any last-minute questions you may have.
Once you are ready for surgery, you will be taken to the operating room, where the surgical team will prepare you for the procedure. This may include administering anesthesia, monitoring your vital signs, and ensuring your comfort and safety throughout the surgical process.
During the surgery, the surgeon will repair the hernia by pushing the protruding tissue back into place and reinforcing the abdominal wall with sutures or a mesh. The specific details of the surgical procedure will depend on the approach chosen by your healthcare provider, such as laparoscopic or open surgery.
After the surgery, you will be transferred to a recovery area where you will be closely monitored by the medical staff. Depending on the complexity of the surgery and your individual needs, you may need to stay in the hospital for some time to ensure a smooth recovery and proper post-operative care.
Recovery Process After Hernia Surgery

The recovery process after hernia surgery is an important time for healing and regaining strength. Following your surgery, your healthcare provider will provide specific instructions for post-surgery care, including wound care, pain management, and restrictions on physical activity. Thoroughly following these recommendations is essential to promote effective recovery and minimize the risk of problems.
During the recovery period, it is normal to experience some discomfort, swelling, or bruising around the surgical site. It is essential to engage in rest and avoid engaging in physically demanding activities during this period. Gradually, you will be able to increase your physical activity levels as directed by your healthcare provider.
As you recover, you will likely notice improvements in your overall quality of life and a reduction in symptoms related to the hernia. If you have any concerns or questions during the recovery process, do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for guidance and support.
Post-Surgery Hospital Stay
After hernia surgery, the length of your hospital stay will depend on various factors, including the complexity of the surgery and your individual needs. In some cases, hernia surgeries can be performed as outpatient procedures, allowing you to go home the same day.
However, more complex surgeries or the presence of certain risk factors may require a longer hospital stay for proper monitoring and post-operative care.
During your hospital stay, the medical staff will closely monitor your recovery, including the healing of the surgical incision, pain management, and the return of normal bowel function.
They will also guide wound care, medication management, and any necessary dietary modifications. Your healthcare provider will ensure that you are comfortable and that all your needs are met during your hospital stay.
If you have any concerns or questions, do not hesitate to communicate with your healthcare provider or the nursing staff. They are there to support your recovery and address any issues that may arise.
Recovery at Home
Once you are discharged from the hospital, the recovery process continues at home. Your healthcare provider will provide specific guidelines and instructions for your post-operative care, including
- wound care
- pain management
- restrictions on physical activity
Following these guidelines exactly is essential to promoting appropriate healing and lowering the risk of problems.
During the initial phase of recovery at home, it is normal to experience some discomfort, swelling, or bruising around the surgical site. It is imperative to engage in relaxation and refrain from engaging in physically demanding activities during this period.
Gradually, you will be able to increase your physical activity levels as directed by your healthcare provider. It is essential to pay close attention to your body’s signals and avoid overexerting yourself prematurely.
As you continue to recover at home, you will likely notice improvements in your overall quality of life and a reduction in symptoms related to the hernia.
However, it is essential to attend all follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider to ensure that your recovery is progressing as expected.
If you have any concerns or questions during the recovery process, do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for guidance and support.
Potential Complications and Risks
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential complications and risks associated with hernia surgery. These can include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- wound healing problems
- pain, or numbness at the surgical site
- adverse reactions to anesthesia
While these complications are relatively rare, it is important to be aware of them and to discuss them with your healthcare provider before undergoing surgery.
In addition to short-term surgical risks, there are also long-term health considerations to be aware of. These can include chronic pain, the rate of hernia recurrence, and potential long-term effects on overall health and well-being.
It is important to have a thorough discussion with your healthcare provider to understand the potential risks and benefits of hernia surgery and to make an informed decision about your treatment options.
Long-Term Health Considerations
Long-term health considerations after hernia surgery can include chronic pain, the rate of hernia recurrence, and potential long-term effects on overall health and well-being.
Chronic pain is a possible complication of hernia surgery, and it can vary in severity and duration. If you experience persistent or worsening pain after surgery, it is important to notify your healthcare provider for further evaluation and management.
The rate of hernia recurrence, or the hernia coming back after surgery, can vary depending on various factors, such as the size and location of the hernia, the approach used for repair, and individual patient factors. Your healthcare provider will discuss the specific risks associated with your hernia and guide how to minimize the risk of recurrence.
It is also important to consider the potential long-term effects of hernia surgery on your overall health and well-being. Although hernia surgery is typically effective in relieving symptoms and enhancing quality of life, it is necessary to schedule regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare professional to track your progress and handle any potential issues.
Outlook
The outlook for individuals who undergo hernia surgery is generally positive. Most people experience a significant improvement in their quality of life because of the surgery, with a reduction in symptoms and a return to normal daily activities.
Prospective studies and systematic reviews have shown high success rates for hernia repair, with low rates of complications and a low likelihood of hernia recurrence. However, it is important to attend all follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider and to communicate any concerns or issues that may arise during your recovery process.
By actively participating in your care and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, you can help promote a successful outcome and long-term well-being.
Make An Appointment
If you are experiencing symptoms of a hernia or need further information about hernia surgery, you can make an appointment with Dr. Valeria Simone MD at Southlake General Surgery in Texas, USA.
Dr. Simone is a highly skilled and experienced general surgeon specializing in hernia repair and offers personalized care to meet your specific needs.
To schedule an appointment or gather additional information regarding hernia surgery, please reach us at +1 (817) 748-0200. Dr. Simone and her dedicated team are committed to providing comprehensive and compassionate care to help you achieve optimal health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can I Prevent a Hernia From Reoccurring?
To prevent a hernia from recurring, it is important to engage in regular physical activity to strengthen your abdominal muscles and maintain a healthy weight. Avoid activities that put excessive strain on your abdomen and follow any post-surgery guidelines provided by your healthcare provider. In certain instances, surgical intervention may be required to mitigate the risk of hernia recurrence.
What is the duration of the recovery period following hernia surgery?
The recovery period after hernia surgery can vary depending on individual factors, such as the type of hernia, the surgical approach, and your overall health. In general, most people can expect to return to normal daily activities within a few weeks, although specific restrictions on physical activity may apply during the initial recovery period. Your healthcare provider will provide detailed post-surgery care instructions to ensure a smooth recovery process.
Can Hernias Be Treated Without Surgery?
While some small hernias may not require immediate surgical intervention, long-term management typically involves surgical repair. Non-surgical management options, such as lifestyle changes, weight management, and physical therapy, may help alleviate symptoms but cannot fully repair the hernia or prevent potential complications. It is important to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment approach for your specific case.
Can a recurrent hernia be successfully treated with surgery?
Yes, surgery is an effective treatment for a recurrent hernia. However, the surgical approach may need to be tailored based on the specific circumstances of the patient and the characteristics of the hernia to ensure a successful outcome and reduce the risk of recurrence.
What is the best surgical treatment for incisional hernia?
Choosing the most effective surgical option for incisional hernias involves considering factors like size, location, and overall health. Treatment options include open repair, laparoscopic repair, and robotic repair. Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized treatment recommendations.
What is an interstitial hernia?
Interstitial hernias occur within the body’s muscle or tissue layers due to factors like heavy lifting, obesity, or past surgeries. Symptoms include pain, swelling, or a bulge. Treatment usually involves surgery to repair and strengthen the affected area.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
References:
- Edwards, Chris, et al. “Laparoscopic Transperitoneal Repair of Flank Hernias: A Retrospective Review of 27 Patients.” Surgical Endoscopy/Surgical Endoscopy and Other Interventional Techniques, vol. 2692–2696, no. 12, 22 May 2009, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0477-4.
- Gurusamy, Kurinchi Selvan, and Victoria B. Allen. Wound Drains After Incisional Hernia Repair. 17 Dec. 2013, https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd005570.pub4.
- Matapurkar, B. G., et al. “Regeneration of Abdominal Wall Aponeurosis: New Dimension in Marlex Peritoneal Sandwich Repair of Incisional Hernia.” World Journal of Surgery, vol. 446–451, no. 5, 1 May 1999, https://doi.org/10.1007/pl00012326.
- Flum DR, Horvath K, Koepsell T. Have outcomes of incisional hernia repair improved with time? A population-based analysis. Ann Surg. 2003;237(1):129-135. doi:10.1097/00000658-200301000-00018
- Nguyen SQ, Divino CM, Buch KE, et al. Postoperative pain after laparoscopic ventral hernia repair: a prospective comparison of sutures versus tacks. JSLS. 2008;12(2):113-116.
- Bucknall TE, Cox PJ, Ellis H. Burst abdomen and incisional hernia: a prospective study of 1129 major laparotomies. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1982;284(6320):931-933. doi:10.1136/bmj.284.6320.931
- LeBlanc KA, Elieson MJ, Corder JM 3rd. Enterotomy and mortality rates of laparoscopic incisional and ventral hernia repair: a review of the literature. JSLS. 2007;11(4):408-414.
- Hope, William W., and Faiz Tuma. “Incisional Hernia.” StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf, 12 June 2023, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK435995
- “Hernias: Learn More – How Are Incisional Hernias Treated?” InformedHealth.org – NCBI Bookshelf, 13 Dec. 2023, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK395550.
- Bunting DM. Port-site hernia following laparoscopic cholecystectomy. JSLS. 2010;14(4):490-497. doi:10.4293/108680810X12924466007728
- Hope, William W., and Faiz Tuma. “Incisional Hernia.” StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf, 12 June 2023, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK435995.