Gallbladder problems can cause a range of symptoms and discomfort, affecting the overall quality of life. Understanding the signs and symptoms of gallbladder problems is essential for early diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
The gallbladder is a small organ located in the abdomen, beneath the liver. Its main function is to store bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver, and release it into the small intestine to aid in the digestion of fats. However, various factors can lead to the development of gallbladder problems.
Gallbladder diseases, such as gallstones, cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder), biliary dyskinesia (functionality issues), and gallbladder polyps, can cause symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. These symptoms can be severe and may necessitate medical intervention.
In this blog, we’ll discuss gallbladder problem symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatments, and prevention. Remember, this material should not be considered a replacement for professional medical advice. Seek the guidance of a medical expert for a precise diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Key Highlights
- Gallbladder disease refers to any condition that affects the health of the gallbladder and can cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, and.
- Common gallbladder problems include gallstones, cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder), biliary dyskinesia (functionality issues), and gallbladder polyps.
- Symptoms of gallbladder problems can vary, but common signs include severe abdominal pain, right shoulder pain, fever, and nausea- Early diagnosis of gallbladder problems is important to prevent complications and determine the most appropriate treatment options.
- Imaging tests such as ultrasounds and CT scans, as well as non-imaging tests like blood tests, are commonly used to diagnose gallbladder problems.
- Treatment options for gallbladder problems range from non-surgical approaches, such as lifestyle changes and medications, to surgical interventions like gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy).
Understanding the Gallbladder and Its Function
The gallbladder, located beneath the liver in the abdomen, stores bile produced by the liver to aid digestion. When we eat, the gallbladder contracts, releasing bile into the small intestine to break down fats and assist in food digestion.
Bile is crucial for absorbing fat-soluble vitamins and nutrients. The gallbladder is linked to the liver and small intestine through bile ducts. Infections or blockages in these ducts can lead to gallbladder disease, impacting the digestive system.
Anatomy of the Gallbladder
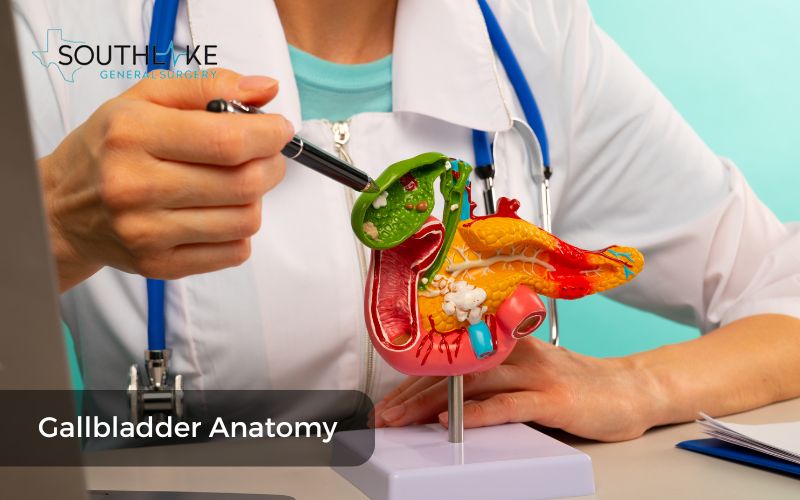
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located underneath the liver on the right side of your abdomen. It plays a crucial role in digesting food by storing and concentrating bile, which is produced by the liver. Bile aids in digesting fats in the small intestine.
The gallbladder is composed of three primary components: the fundus, body, and neck. It receives bile from the liver through the hepatic ducts and releases it through the cystic duct. The gallbladder contracts to release bile into the common bile duct to aid in digestion.
Understanding the anatomy of the gallbladder is essential in recognizing symptoms of gallbladder problems and seeking timely medical attention.
The Role of the Gallbladder in Digestion
The gallbladder has a vital role in digestion. After consuming a meal, particularly one high in fat, the gallbladder contracts to release bile into the small intestine. Bile salts within the bile aid in breaking down fats into easily absorbable, smaller molecules.
Additionally, bile facilitates the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K. Poor gallbladder function can hinder fat digestion and absorption, leading to challenges in digesting fatty foods and potential symptoms like abdominal discomfort, bloating, and diarrhea.
Conditions like gallstones or inflammation can disrupt bile flow and impact digestion. Recognizing gallbladder issue symptoms promptly and seeking medical help is crucial.
Common Gallbladder Problems and Their Causes
Gallbladder problems like gallstones, cholecystitis, biliary dyskinesia, and polyps can be caused by factors such as high cholesterol levels and family history. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking medical care is crucial for managing these issues.
Gallstones: Types and Causes
Gallstones are one of the most common gallbladder problems. Gallstones are calcified concretions that can develop in the gallbladder. Gallstones can be classified into two primary categories: cholesterol stones and pigment stones.
- Cholesterol stones are the most common type and are made up of excess cholesterol in the bile.
- Pigment stones, on the other hand, are formed from bilirubin, a substance produced when red blood cells are broken down.
The exact cause of gallstones is not fully understood, but several factors can increase the risk of developing gallstones. These include having high levels of cholesterol in the bile, having excessive bilirubin in the bile, and having a gallbladder that does not empty properly.
Other risk factors include obesity, a diet high in fat and cholesterol, rapid weight loss, and certain medical conditions such as liver disease and diabetes. Additionally, a family history of gallstones can also increase the risk.
Cholecystitis: Acute and Chronic Inflammation
Cholecystitis is the medical term for inflammation of the gallbladder, which is commonly caused by the presence of gallstones. It can occur in two forms: acute cholecystitis and chronic cholecystitis.
Acute cholecystitis is a rapid and intense inflammation of the gallbladder, typically caused by a gallstone obstructing the cystic duct. This obstruction results in bile buildup and heightened gallbladder pressure, leading to discomfort and sensitivity in the upper abdomen. Signs of acute cholecystitis can encompass intense pain in the upper right abdomen, fever, nausea, and vomiting.
Chronic cholecystitis is characterized by repeated or persistent inflammation of the gallbladder, typically resulting from multiple acute cholecystitis episodes or prolonged gallbladder malfunction. Its symptoms, such as abdominal pain, bloating, and indigestion, are usually mild yet enduring.
If left untreated, both acute and chronic cholecystitis can lead to complications such as gallbladder rupture or infection.
Biliary Dyskinesia: Functionality Issues
Biliary dyskinesia is when the gallbladder struggles to contract and release bile, leading to symptoms like abdominal pain and digestive problems.
It is often linked to biliary colic, marked by recurring abdominal pain after eating fatty foods, and can be caused by issues like gallstones or gallbladder inflammation.
Managing biliary dyskinesia usually includes dietary changes, weight control, and potentially gallbladder removal.
Gallbladder Polyps and Their Implications
Gallbladder polyps are neoplastic formations that develop on the mucosal surface of the gallbladder. While many are harmless and asymptomatic, larger polyps or those linked to specific risk factors can elevate the chances of gallbladder cancer. Factors such as age, obesity, being female, and a family history of gallbladder issues contribute to the risk of gallbladder polyps.
Gallbladder polyps are typically found by chance during imaging tests for unrelated conditions. Treatment for a polyp depends on its size and characteristics. Small, harmless polyps may not need treatment, while larger ones or those linked to specific risk factors may necessitate evaluation and potential removal.
Regular monitoring is crucial for individuals with gallbladder polyps to catch any changes or cancer signs promptly.
Symptoms of Gallbladder Problems
It is crucial to identify the symptoms of gallbladder problems for prompt diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms can differ depending on the specific condition but commonly include:
- intense abdominal pain
- right shoulder, or back pain
- nausea
- vomiting
- bloating
- diarrhea
Additional signs may involve fever, jaundice, and alterations in bowel movements and urine color. Seeking medical help promptly is necessary if these symptoms of gallbladder problems arise, as they could signify a gallbladder issue necessitating medical care.
Identifying Gallstone Symptoms
Gallstones can cause severe symptoms, with the most common being intense pain known as a gallbladder attack. This pain is usually felt in the upper abdomen and can spread to the back or right shoulder, often triggered by fatty foods.
Other symptoms of gallstones include:
- abdominal pain that lasts several hours
- nausea
- vomiting
- fever
- jaundice
Not everyone with gallstones experiences symptoms; sometimes they are found incidentally during medical imaging for other conditions. Seek medical help if you have persistent or severe symptoms for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Recognizing Signs of Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis, which is the inflammation of the gallbladder, can result in various symptoms. The primary symptom of cholecystitis is intense abdominal pain, typically located in the upper abdomen and possibly tender to touch. The pain might extend to the back or right shoulder.
Additional symptoms may consist of fever, nausea, vomiting, and a sense of general unwellness (malaise). In more severe situations, cholecystitis can lead to complications like gallbladder rupture or infection, manifesting in jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) and dark urine.
If these symptoms occur, it is crucial to promptly seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of Biliary Dyskinesia
Biliary dyskinesia, also known as gallbladder dysfunction in contracting and releasing bile, can lead to various symptoms. The primary symptom is abdominal pain, particularly following meals, typically located in the upper right abdomen and can be accompanied by bloating, indigestion, and gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea.
Pain may be induced by fatty or oily foods, with other symptoms including nausea, vomiting, and a sense of unwellness (malaise). Seeking medical help for a correct diagnosis and treatment is crucial if these symptoms occur.
In certain instances, gallbladder removal may be suggested to relieve symptoms and enhance gallbladder function.
When to Worry About Gallbladder Polyps
Most gallbladder polyps are benign and do not cause symptoms. However, there are certain situations in which it is important to seek medical attention for gallbladder polyps. If a gallbladder polyp is larger than average (1 centimeter or more) or associated with certain risk factors, it may increase the risk of gallbladder cancer.
Additionally, if you experience symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, or changes in bowel movements, it is important to seek medical evaluation. Regular check-ups and monitoring are important for individuals with gallbladder polyps to detect any changes or signs of cancer early.
If necessary, your healthcare provider may recommend further testing or removal of the polyps to reduce the risk of complications.
Diagnosis of Gallbladder Problems
Diagnosing gallbladder issues usually involves a blend of medical history review, physical assessment, and various diagnostic examinations.
Your healthcare provider will inquire about your symptoms, medical background, and potential risk factors related to gallbladder problems. They will conduct a physical examination to identify any signs of gallbladder issues, such as inflammation or sensitivity.
Diagnostic procedures might include blood tests to identify inflammation or infection markers, imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to view the gallbladder and detect abnormalities, and occasionally specific tests like a HIDA scan or ERCP to assess gallbladder function and bile flow.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Timely detection of gallbladder issues is crucial for timely intervention and proper treatment. Identifying symptoms promptly enables healthcare professionals to address them effectively, reducing the risk of complications and enhancing patient outcomes.
Failure to diagnose promptly may result in exacerbated symptoms, heightened chances of complications like gallbladder infection or rupture, and prolonged patient discomfort.
Recognizing symptoms of gallbladder problems and promptly seeking medical assistance are essential for early detection. If you exhibit symptoms like intense abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or jaundice, consulting a healthcare provider promptly for a comprehensive assessment and accurate diagnosis is vital.
Imaging Tests and Their Roles

Imaging tests are essential for diagnosing gallbladder problems, offering detailed images to detect abnormalities and inflammation. Ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI are commonly used for this purpose.
- Ultrasound is initially preferred due to its non-invasiveness and availability, using sound waves to identify gallbladder issues.
- CT scans and MRI offer more detailed images to assess function, complications, and disease extent, often used alongside other tests for a comprehensive evaluation.
Non-imaging Tests for Gallbladder Function Assessment
Non-imaging tests, along with imaging tests, play a crucial role in evaluating gallbladder function and diagnosing related issues. These tests focus on assessing bile flow and overall gallbladder performance.
- Blood tests are commonly employed to check liver function, and detect inflammation or signs of infection.
- Liver function tests offer valuable insights into gallbladder and bile duct health.
- Specialized tests like a HIDA scan and ERCP may also be utilized to evaluate gallbladder function and bile flow, using radioactive tracers or contrast agents to visualize and detect abnormalities.
Treatment Options for Gallbladder Issues
The treatment options for gallbladder problems vary depending on the specific condition and symptom severity. Non-surgical approaches and lifestyle modifications may be suggested for certain issues, like biliary dyskinesia or mild cholecystitis, which can involve dietary changes, weight control, and symptom-relieving medications.
However, surgery is often required, with gallbladder removal surgery (cholecystectomy) being the most common procedure. This can be done through minimally invasive methods like laparoscopic cholecystectomy or open surgery for more complex cases.
Your healthcare provider will decide on the best treatment based on your condition, symptoms, and overall health.
Non-surgical Treatments and Lifestyle Changes
Non-invasive treatments and lifestyle changes might be suggested for specific gallbladder issues, particularly those that do not necessitate immediate action or are not serious.
For instance, dietary modifications and weight control could be used to manage biliary dyskinesia, a disorder marked by impaired gallbladder contraction and bile release. This may involve steering clear of fatty foods, consuming smaller, more frequent meals, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Medications might be recommended to alleviate symptoms like stomach pain or digestive problems. Incorporating regular physical activity and stress management into one’s lifestyle can also promote overall gallbladder well-being.
Collaborating closely with your healthcare provider to create a tailored treatment regimen that targets your condition and symptoms is crucial.
Surgical Options: Exploring Cholecystectomy
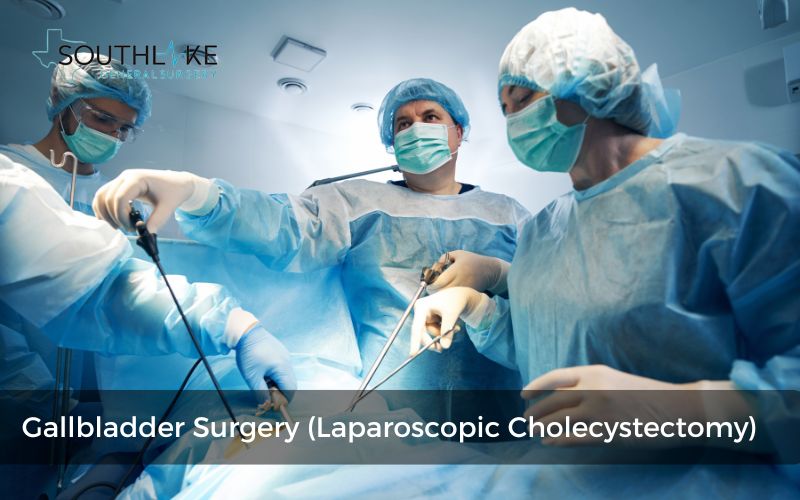
Gallbladder removal surgery, also known as cholecystectomy, is the most common surgical treatment for gallbladder problems. It involves the removal of the gallbladder through minimally invasive techniques or, in more complex cases, open surgery. The goal of cholecystectomy is to alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and improve overall health and quality of life.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the preferred approach for most cases. It involves making several small incisions in the abdomen and using a laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera) to guide the surgical instruments. This approach offers a shorter recovery time, less pain, and a lower risk of complications compared to open surgery.
In some cases, open surgery may be necessary, such as when there are complications, or the gallbladder cannot be safely removed through laparoscopic techniques. Your healthcare provider will determine the most appropriate surgical option based on your specific condition and overall health.
Risks and Benefits of Gallbladder Removal
Gallbladder removal, or cholecystectomy, is a common surgical procedure that offers several benefits for individuals with gallbladder problems. The main benefit of gallbladder removal is the relief of symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, and digestive issues.
After the gallbladder is removed, bile flows directly from the liver to the small intestine, bypassing the gallbladder. This allows for the normal digestion of fats and reduces the risk of gallstone formation.
Gallbladder removal is generally safe and well-tolerated, but like any surgical procedure, it carries some risks. These can include bleeding, infection, injury to surrounding organs, and complications from anesthesia.
However, the overall risk of these complications is low. Your healthcare provider will discuss the risks and benefits of gallbladder removal with you and address any concerns or questions you may have.
Living Without a Gallbladder
Living without a gallbladder is generally well-tolerated, and most people can lead a normal and healthy life after gallbladder removal surgery. After the gallbladder is removed, bile flows directly from the liver to the small intestine to aid in the digestion of fats.
Without a gallbladder, some individuals may experience changes in their digestion, particularly after consuming fatty or greasy foods. To minimize any discomfort or digestive issues, it is important to follow a healthy diet that includes a balance of nutrients and limits the intake of high-fat or fried foods.
Your healthcare provider can provide guidance on dietary adjustments and lifestyle changes to ensure optimal digestion and overall health after gallbladder removal.
Dietary Adjustments Post-Surgery

After gallbladder removal surgery, it is important to make dietary adjustments to support digestion and overall health. While the gallbladder is no longer present to store and release bile, the liver continues to produce bile, which is essential for the digestion of fats.
To minimize any discomfort or digestive issues, it is recommended to follow a healthy diet that includes a balance of nutrients and limits the intake of high-fat or fried foods. Focus on consuming lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats such as olive oil. Consider eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day to aid in digestion.
It may also be helpful to limit or avoid foods that are known to trigger digestive symptoms, such as fatty or spicy foods. Your healthcare provider can provide personalized dietary recommendations based on your specific needs and overall health.
Long-term Health Management
Long-term health management after gallbladder removal surgery is important to maintain overall health and prevent any complications. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet is recommended. This can help support optimal digestion and reduce the risk of developing certain conditions, such as gallstones or fatty liver disease.
It is also important to attend regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your overall health and address any concerns or symptoms that may arise. Be sure to follow any recommended follow-up appointments or screenings to ensure early detection and intervention if any issues arise.
By adopting a healthy lifestyle and staying proactive in managing your health, you can continue to lead a normal and fulfilling life without a gallbladder.
Preventing Gallbladder Problems
While some risk factors for gallbladder problems, such as age and genetics, cannot be controlled, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk and promote gallbladder health. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet is key.
Aim to consume a diet that is low in saturated fat, cholesterol, and processed foods, and high in fiber-rich fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Avoid rapid weight loss or crash diets, as these can increase the risk of gallstones. You should also minimize your alcohol consumption and make sure to stay hydrated.
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help monitor your gallbladder health and address any concerns or symptoms.
Diet and Lifestyle Recommendations
Adopting a healthy diet and lifestyle can significantly prevent gallbladder problems and promote overall gallbladder health.
- Focus on consuming a balanced diet that is low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and processed foods, and high in fiber-rich fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Incorporate lean proteins, such as fish or poultry, and healthy fats, such as olive oil or avocados, into your meals.
- Stay hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water and limiting alcohol consumption.
- Regular exercise can also support gallbladder health by promoting digestion and maintaining a healthy weight.
- A higher incidence of gallstones is associated with crash diets and other forms of fast weight loss.
If you have any concerns about your diet or lifestyle, consult with your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
Regular Check-ups and Risk Assessment
Regular check-ups and risk assessments are important for maintaining gallbladder health and preventing potential problems. Attend regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your overall health, including the health of your gallbladder.
Your healthcare provider can assess your risk factors for gallbladder problems, such as age, family history, and medical conditions, and provide appropriate guidance and screening recommendations.
Be sure to inform your healthcare provider about any symptoms or concerns you may have regarding your gallbladder. They can perform relevant tests or imaging studies to evaluate the health of your gallbladder and detect any potential issues early.
By staying proactive and addressing any concerns promptly, you can reduce the risk of developing gallbladder problems and ensure optimal gallbladder health.
Conclusion
Gallbladder problems can manifest through various symptoms, indicating issues like gallstones, cholecystitis, biliary dyskinesia, or polyps. To effectively manage a condition, early diagnosis is essential.
Treatment options range from non-surgical interventions to cholecystectomy. After surgery, dietary adjustments are necessary for optimal health post-cholecystectomy.
Prevention involves maintaining a healthy diet, lifestyle, and regular check-ups. Don’t ignore warning signs, your gallbladder health matters.
Make An Appointment

If you are experiencing symptoms of gallbladder problems or have any concerns about your gallbladder health, it is important to seek medical attention.
Dr. Valeria Simone MD, at Southlake General Surgery in Texas, USA, specializes in gallbladder surgery and can provide expert care for your gallbladder concerns. To make an appointment, call +1 (817) 748-0200.
Dr. Simone and her team will evaluate your symptoms, perform necessary tests or imaging studies, and develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
With their expertise and compassionate care, you can receive the appropriate diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up care for your gallbladder issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Early Signs of Gallbladder Problems?
Early signs of gallbladder problems may include abdominal pain, especially after eating fatty foods, chronic cholecystitis (recurring inflammation of the gallbladder), bloating, indigestion, and nausea. It is essential to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and treatment if you encounter these signs.
What Can Mimic Gallbladder Pain?
Several conditions can mimic gallbladder pain, such as pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas), heart attack, peptic ulcer, rib cage pain, and liver disease. If you are experiencing severe abdominal pain, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
How can you differentiate between the symptoms of gallbladder issues and other digestive problems?
Differentiating between the symptoms of gallbladder issues and other digestive problems can be challenging. However, specific symptoms such as a gallbladder attack (severe abdominal pain), biliary colic, pain in the upper right side of your abdomen, and changes in bowel movements can indicate gallbladder issues. Consulting with a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation is recommended for an accurate diagnosis.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
References:
- Jones, Mark W., et al. “Porcelain Gallbladder.” StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf, 7 Aug. 2023, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK518979
- Wanjara, Samuel, and Sarang Kashyap. “Bile Duct Stricture.” StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf, 23 Jan. 2023, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559217.
- Descoteaux-Friday, Garrett J., and Isha Shrimanker. “Chronic Diarrhea.” StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf, 7 Aug. 2023, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544337.
- Virgile, Jennifer, and Rachana Marathi. “Cholangitis.” StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf, 3 July 2023, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK558946.
- Jones, Mark W., et al. “Acute Cholecystitis.” StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf, 22 May 2023, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459171.
- Turner, Anisha R., et al. “Gallstone Ileus.” StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf, 19 Sept. 2022, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430834.
- Jones, Mark W., et al. “Chronic Cholecystitis.” StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf, 8 Aug. 2023, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470236.
- Kashyap, Sarang, et al. “Gallbladder Empyema.” StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf, 10 Apr. 2023, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459333.
- Morimoto M, Matsuo T, Mori N. Management of Porcelain Gallbladder, Its Risk Factors, and Complications: A Review. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021;11(6):1073. Published 2021 Jun 10. doi:10.3390/diagnostics11061073
- “Dieting & Gallstones.” National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 22 Feb. 2024, www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/gallstones/dieting
- “Definition & Facts for Gallstones.” National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 22 Feb. 2024, www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/gallstones/definition-facts.
- “Treatment for Gallstones.” National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 30 Aug. 2022, www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/gallstones/treatment.