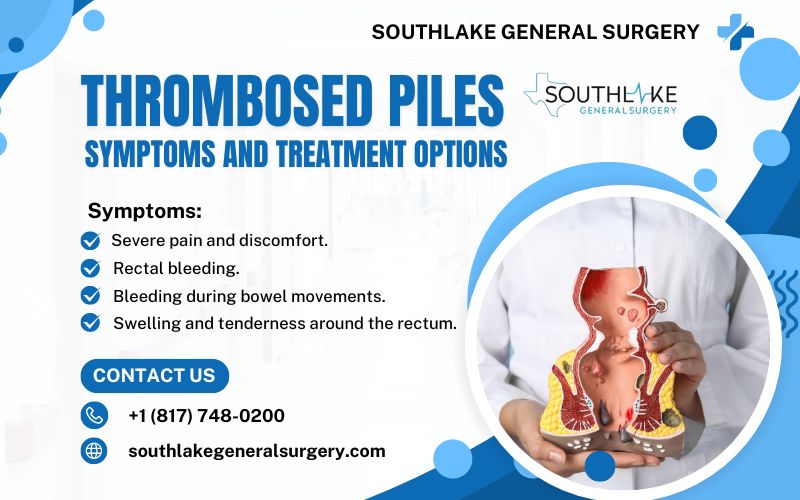
Thrombosed piles, also known as thrombosed hemorrhoids, is a common and painful condition that affects the rectum and anus. Hemorrhoids are swollen blood vessels in the anal canal and can occur internally or externally. When a blood clot forms within an external hemorrhoid, it is referred to as a thrombosed pile.
Thrombosed piles can cause severe pain, swelling, itching, and bleeding during bowel movements. The condition has the potential to be disabling and impact an individual’s quality of life. It is important to understand the symptoms and treatment options available for thrombosed piles to find relief and manage the condition effectively.
In this blog, we will discuss what thrombosed piles are, the symptoms associated with them, the causes and risk factors, as well as the various treatment options available. We will also explore the recovery process and management strategies for long-term health and prevention.
It is important to note that while there are home remedies and non-surgical treatments available, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Key Highlights
- Thrombosed piles are swollen vessels in the rectum and anus that can cause severe pain and discomfort.
- Symptoms of thrombosed piles include severe pain, swelling, itching, and bleeding during bowel movements.
- Common risk factors for thrombosed piles include constipation, pregnancy, and sitting for long periods of time.
- Treatment options for thrombosed piles range from at-home remedies and care to non-surgical and surgical interventions.
- Recovery and after treatment include post-treatment care and long-term prevention strategies.
- It is important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of thrombosed piles or if the condition worsens.
Understanding Thrombosed Piles
Thrombosed piles are a condition where there is a blood clot within an external hemorrhoid. Hemorrhoids are blood vessels located in the anal canal and can become swollen and inflamed, leading to various symptoms. Thrombosed piles can cause severe pain and discomfort, making it difficult to engage in daily activities.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for thrombosed piles is essential for managing this condition effectively.
What Are Thrombosed Hemorrhoids?
Thrombosed piles, also known as thrombosed hemorrhoids, occur when a blood clot forms within an external hemorrhoid. Enlarged blood vessels located in the anal canal are known as hemorrhoids. While everyone has hemorrhoids, they only become a problem when they become swollen or inflamed.
Thrombosed piles are characterized by severe pain and discomfort. The blood clot within the hemorrhoid causes the affected area to become swollen and tender. This can make it painful to sit, walk, or have a bowel movement.
Thrombosed piles usually occur suddenly and can last for several days or weeks. The pain and discomfort gradually subside as the body absorbs the blood clot. However, in some cases, medical intervention may be required to relieve the symptoms and promote healing.
The Difference Between Thrombosed and Regular Hemorrhoids
Thrombosed piles are a specific type of hemorrhoid that is characterized by the presence of a blood clot within an external hemorrhoid. While both regular hemorrhoids and thrombosed piles can cause similar symptoms such as pain, itching, and bleeding, there are a few key differences between the two.
Regular hemorrhoids, also known as internal or external hemorrhoids, occur when the blood vessels in the anal canal become swollen or inflamed. Internal hemorrhoids are situated within the rectum, whereas external hemorrhoids are situated outside the anus. They can cause discomfort and may bleed during bowel movements.
On the other hand, thrombosed piles are external hemorrhoids that have developed a blood clot. This blood clot can cause severe pain and swelling, making it difficult to sit or have a bowel movement. Thrombosed piles usually require medical intervention to relieve the symptoms and promote healing.
Identifying Symptoms of Thrombosed Piles
Identifying the symptoms of thrombosed piles is crucial for seeking appropriate medical attention and starting the necessary treatment. Symptoms may differ between individuals, but there are certain typical signs to be aware of.
Thrombosed piles are typically accompanied by severe pain and discomfort in the anal region. Activities like sitting, walking, or having a bowel movement can make this pain worse. Other symptoms may include swelling, itching, and bleeding during bowel movements.
It is crucial to seek advice from a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and suitable treatment plan if you encounter any of these symptoms.
Early Signs to Watch For
Early signs of thrombosed piles can vary from person to person, but there are some common symptoms to watch out for. These early signs may indicate the presence of a thrombosed hemorrhoid and the need for medical attention.
- Severe pain and discomfort in the anal region
- Swelling and tenderness around the anus
- Discomfort and itching in the impacted region
- Bleeding during bowel movements
If you experience any of these early signs, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can offer a precise diagnosis and suggest suitable treatment options, depending on the seriousness of your condition. Early intervention can help alleviate symptoms and promote faster healing.
When Symptoms Worsen
While thrombosed piles can cause significant pain and discomfort, there are instances when the symptoms worsen and require immediate medical attention. It is important to be aware of these signs and seek prompt medical care to prevent further complications.
- Severe and persistent pain that does not subside with home remedies or over-the-counter pain relievers
- Increasing swelling and tenderness around the anus
- Cough, fever, or other symptoms that can indicate an infection
- Rectal bleeding that is excessive or does not stop
If you experience any of these worsening symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical attention as soon as possible. Your healthcare provider can assess your condition, provide appropriate treatment, and address any potential complications. Do not delay seeking medical care if you are concerned about the worsening of your symptoms.
Causes Behind Thrombosed Piles
Understanding the causes behind thrombosed piles can help in taking preventive measures and managing the condition effectively. While the exact cause of thrombosed piles is not always clear, certain factors contribute to the development of this condition.
Some common causes of thrombosed piles include:
- Increased pressure on the veins situated in the rectum and anus
- Experiencing difficulty during defecation, particularly in cases of constipation
- Diarrhea or irregular bowel movements
- Pregnancy may result in heightened pressure on the veins
- Extended periods of sitting, like on lengthy car trips or during office hours
By identifying and addressing these causes, you can reduce the risk of developing thrombosed piles and manage the condition effectively.
Common Risk Factors
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing thrombosed piles. By understanding these risk factors, you can take preventive measures and manage the condition effectively.
Some common risk factors for thrombosed piles include:
- Chronic constipation or exerting pressure during defecation
- Pregnancy or childbirth, which can increase pressure on the veins in the rectum and anus
- Obesity or being overweight, can put extra strain on the veins
- Prolonged sitting or standing can lead to increased pressure in the anal region
- Aging occurs as the tissues in the rectum and anus become weaker over time
- Genetics, as some people may be more prone to developing hemorrhoids
By addressing these risk factors and making appropriate lifestyle changes, you can reduce the likelihood of developing thrombosed piles and manage the condition effectively.
How Lifestyle Affects Thrombosed Piles
Lifestyle factors can play a significant role in the development and management of thrombosed piles. By making certain changes to your lifestyle, you can reduce the risk of developing this condition and alleviate symptoms.
Some lifestyle factors that can affect thrombosed piles include:
- Diet: Consuming a high-fiber diet can help prevent constipation and promote regular bowel movements, reducing the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
- Hydration: Drinking an adequate amount of water can soften stools and make them easier to pass, reducing the strain on the rectum and anus.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can promote proper bowel function and prevent the development of hemorrhoids.
- Hygiene: Maintaining good anal hygiene, such as using moist wipes instead of dry toilet paper, can help prevent irritation and inflammation.
- Avoiding straining: Straining during bowel movements should be avoided, as it can put pressure on the veins in the anal region.
By incorporating these lifestyle changes into your daily routine, you can reduce the risk of developing thrombosed piles and manage the condition effectively.
Expert Diagnosis Procedures
When it comes to diagnosing thrombosed piles, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate assessment. Healthcare professionals have access to various diagnostic procedures to determine the severity of the condition and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Professional Assessment by Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Dr. Valeria Simone, a renowned healthcare provider in the field of colorectal medicine, can provide a professional assessment for thrombosed piles. Dr. Simone specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of various colorectal conditions, including hemorrhoids.
During a professional assessment, Dr. Simone may perform a flexible sigmoidoscopy, a procedure that allows for the visualization of the lower part of the colon and rectum. This procedure can help identify the presence of thrombosed piles and assess their severity.
Consulting with a healthcare professional such as Dr. Simone is crucial for receiving an accurate diagnosis and suitable treatment plan. Dr. Simone’s expertise and experience can ensure that you receive the best possible care for your thrombosed piles.
Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
Diagnostic tools and techniques are essential for accurately diagnosing thrombosed piles and determining the appropriate treatment options. Healthcare professionals have access to various tools and techniques to assess the condition and provide the best possible care.
Some common diagnostic tools and techniques for thrombosed piles include:
- Physical examination: Healthcare professionals may perform a physical examination to assess the anal region and identify any visible signs of thrombosed piles.
- Digital rectal exam: This procedure involves the insertion of a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to feel for any lumps or abnormalities. This can help determine the presence and severity of thrombosed piles.
These diagnostic tools and techniques, along with the expertise of healthcare professionals, can ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment for thrombosed piles.
Comprehensive Treatment Options
Treatment options for thrombosed piles range from at-home remedies and care to non-surgical and surgical interventions. Treatment options are based on the patient’s preferences and the severity of their condition. Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and the right treatment plan.
At-Home Remedies and Care
For mild cases of thrombosed piles, at-home remedies, and care can often provide relief and promote healing. These remedies can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further irritation.
Some at-home remedies and care options for thrombosed piles include:
- Warm sitz baths: Immersing in lukewarm water for 10-15 minutes multiple times daily can aid in decreasing pain and swelling.
- Over-the-counter creams or ointments: Applying topical creams or ointments that contain ingredients like witch hazel or aloe vera can soothe the affected area and reduce discomfort.
- Ice packs: Applying a cold compress or ice pack to the anal region can help numb the area and reduce pain and swelling.
- High-fiber diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can soften stools and make them easier to pass, reducing strain on the rectum and anus.
These at-home remedies and care options can provide temporary relief and help manage the symptoms of thrombosed piles. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and to discuss the best treatment options for your specific condition.
Non-Surgical Thrombosed Piles Treatments
In cases where at-home remedies and care are not sufficient, non-surgical treatments may be recommended to provide relief and promote healing. Healthcare professionals typically perform these treatments and can offer long-term solutions for thrombosed piles.
Some non-surgical treatment options for thrombosed piles include:
- Hemorrhoid creams or ointments: Over-the-counter creams or ointments that contain ingredients like hydrocortisone or lidocaine can help reduce pain, itching, and swelling.
- Rubber band ligation: In this process, a tiny rubber band is placed around the hemorrhoid’s base to stop its blood flow, leading it to shrink and detach.
- Sclerotherapy: During this process, a chemical solution is inserted into the hemorrhoid, leading it to reduce in size and eventually vanish.
Non-surgical treatments can provide effective relief for thrombosed hemorrhoids and are often less invasive than surgical interventions. It is important to discuss these options with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific condition.
Surgical Interventions by Dr. Valeria Simone
When non-surgical treatments are not effective, or the thrombosed piles are severe, surgical interventions may be recommended. Dr. Valeria Simone, a highly skilled colorectal and general surgeon, offers surgical interventions for thrombosed piles.
Some common surgical interventions for thrombosed piles include:
- Local anesthesia: Dr. Simone can perform a surgical excision of the thrombosed hemorrhoid under local anesthesia. This procedure involves making a small incision to remove the blood clot and relieve the symptoms.
- General anesthesia: In some cases, general anesthesia may be required for more complex surgical interventions. Dr. Simone can provide expert care and ensure your comfort throughout the procedure.
By consulting with Dr. Simone, you can discuss the surgical options available, understand the potential risks and benefits, and make an informed decision regarding your treatment. Dr. Simone’s expertise and compassionate approach to patient care ensures that you receive the highest quality treatment for your thrombosed piles.
Recovery Process and Management
The recovery process and management of thrombosed piles are crucial for long-term healing and prevention of recurrence. It is important to follow the recommended post-treatment care and incorporate lifestyle changes to promote healing and reduce the risk of future episodes.
Post-Treatment Care
After treatment for thrombosed piles, it is important to follow a comprehensive post-treatment care plan to promote healing and prevent complications.
Some post-treatment care recommendations for thrombosed hemorrhoids include:
- Sitz baths: Taking warm sitz baths several times a day can help soothe the affected area, reduce pain and swelling, and promote healing.
- Using topical creams or ointments: Applying prescribed or over-the-counter creams or ointments can help alleviate discomfort and reduce inflammation.
- Taking pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help manage pain and discomfort.
- Maintaining good hygiene: Keeping the anal area clean and dry can prevent infection and promote healing.
- Eating a high-fiber diet: Consuming foods rich in fiber can prevent constipation and promote regular bowel movements, reducing the risk of recurrence.
By following these post-treatment care recommendations, you can ensure a smooth recovery and reduce the risk of complications. Consulting your healthcare provider for personalized post-treatment care instructions is crucial.
Long-Term Health and Prevention

Long-term health and prevention strategies are essential for managing thrombosed piles and reducing the risk of recurrence. By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can promote bowel health and prevent future episodes.
Some long-term health and prevention strategies for thrombosed hemorrhoids include:
- Maintaining a high-fiber diet: Consuming foods rich in fiber can soften stools and make them easier to pass, reducing the risk of constipation and straining.
- Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help prevent dehydration and promote regular bowel movements.
- Avoiding prolonged sitting: Taking breaks from prolonged sitting can reduce pressure on the veins in the anal region.
- Practicing good hygiene: Keeping the anal area clean and dry can prevent irritation and inflammation.
- Engaging in regular exercise: Regular physical activity can promote proper bowel function and prevent the development of hemorrhoids.
By incorporating these strategies into your lifestyle, you can reduce the risk of developing thrombosed piles and promote long-term bowel health.
Conclusion
Thrombosed piles can cause discomfort and pain, but timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment can offer relief. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options outlined by Dr. Valeria Simone is crucial for effective management.
Whether opting for at-home remedies, non-surgical treatments, or surgical interventions, seeking professional guidance ensures a tailored approach to your care. Remember, post-treatment care and preventive measures play a significant role in long-term health.
If you have concerns or need personalized advice, do not hesitate to make an appointment for expert evaluation and assistance. Your well-being is our priority. Contact us today for complete assistance.
Make an Appointment
If you are experiencing symptoms of thrombosed piles or if your condition worsens, it is important to make an appointment with our healthcare expert at +1 (817) 748-0200. They will be able to evaluate your health, diagnose you correctly, and suggest treatments that will work.
Relieving symptoms, preventing complications, and promoting faster recovery can all be achieved with early management. Don’t hesitate to seek medical attention if you are concerned about your symptoms or if they are impacting your quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Thrombosed Piles Heal on Their Own?
Thrombosed piles may resolve on their own within a week or two as the body absorbs the blood clot. However, medical intervention may be required to relieve pain and promote healing in severe cases.
How Can I Prevent Thrombosed Piles in the Future?
To prevent thrombosed piles, it is important to maintain a high-fiber diet, drink plenty of water, engage in regular exercise, practice good anal hygiene, and avoid prolonged sitting or straining during bowel movements.
Are there any complications associated with untreated thrombosed piles?
Untreated thrombosed piles can lead to complications such as rectal bleeding, which may be a sign of colorectal or anal cancer. Severe pain and chronic discomfort can also impact a person’s quality of life.
What should one do if hemorrhoids burst?
If a hemorrhoid bursts, immediate care should be sought from a healthcare provider. They can provide appropriate treatment, such as local anesthesia, to relieve pain and prevent further complications.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
References:
- Lohsiriwat, Varut. “Hemorrhoids: From Basic Pathophysiology to Clinical Management.” World Journal of Gastroenterology, vol. 2009, no. 17, 1 Jan. 2012, https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i17.2009
- Picciariello A, Rinaldi M, Grossi U, et al. Management and Treatment of External Hemorrhoidal Thrombosis. Front Surg. 2022;9:898850. Published 2022 May 3. https://doi:10.3389/fsurg.2022.898850
- Sun Z, Migaly J. Review of Hemorrhoid Disease: Presentation and Management. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2016;29(1):22-29. https://doi:10.1055/s-0035-1568144
- “Hemorrhoidectomy for Thrombosed External Hemorrhoids.” AAFP, 15 Apr. 2002, www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2002/0415/p1641.html.
- Jayne, David, and Karen Nugent. “Diagnosis of Hemorrhoids and ODS.” Springer eBooks, vol. 31–41, 1 Jan. 2009, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-84800-905-9_4.