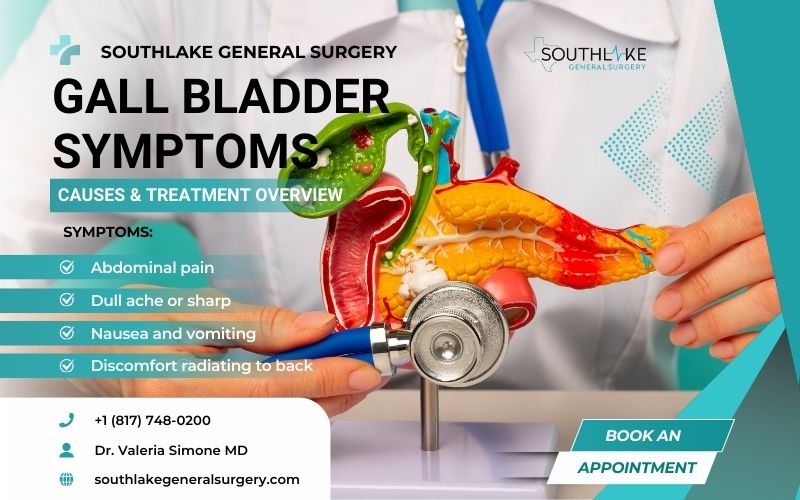
Gall bladder symptoms can significantly impact your health and overall well-being. The gallbladder plays a key role in our digestive system, breaking down fats. It contributes in breaking down fats. If you’re experiencing issues, you may notice some discomfort in your upper abdomen.
This discomfort can disrupt your everyday activities. Understanding how the gallbladder functions and being aware of the warning signs that something might be amiss is really important. This information is valuable for spotting issues early and improving management strategies.
Key Highlights
- Bile is stored in the small gallbladder. Bile is a digestive fluid that aids in the breakdown of lipids or fats.
- Gallstones frequently contribute to problems related to the gallbladder. These solid deposits have the potential to obstruct the bile ducts.
- A common symptom is severe upper right abdominal pain. That usually happens after a fatty meal. Symptoms may include a high temperature, nausea, and vomiting.
- Doctors use imaging tests for diagnosis. Gallbladder and stones can be seen on an abdominal ultrasound.
- The severity of the problem determines the course of treatment. It may involve lifestyle modifications, medication, or gallbladder removal.
Understanding Your Gallbladder: Key Functions and Importance
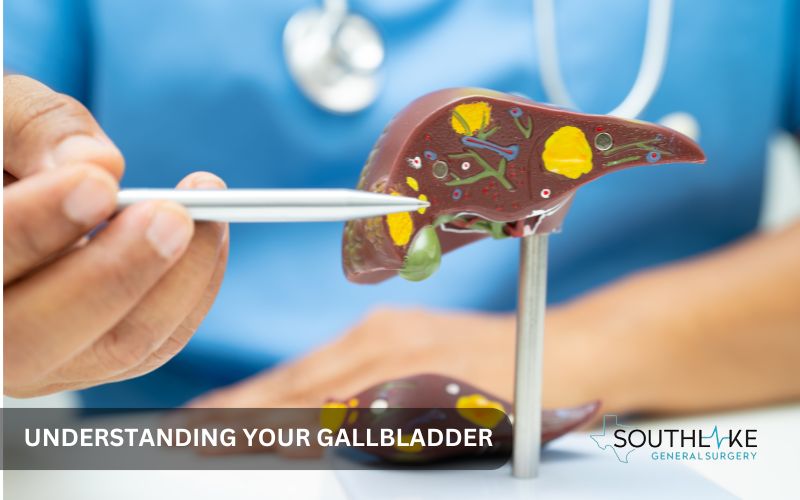
The gallbladder is a small, but significant organ located beneath the liver in the upper right region of the abdomen. The gallbladder plays a key role in digestion by storing and concentrating the bile produced by the liver.
Bile plays a crucial role in breaking down fats, making digestion easier and supporting nutrient absorption and overall digestive health. When problems with the gallbladder are left untreated, they can create unpleasant symptoms and even complications.
The Role of the Gallbladder in Digestion
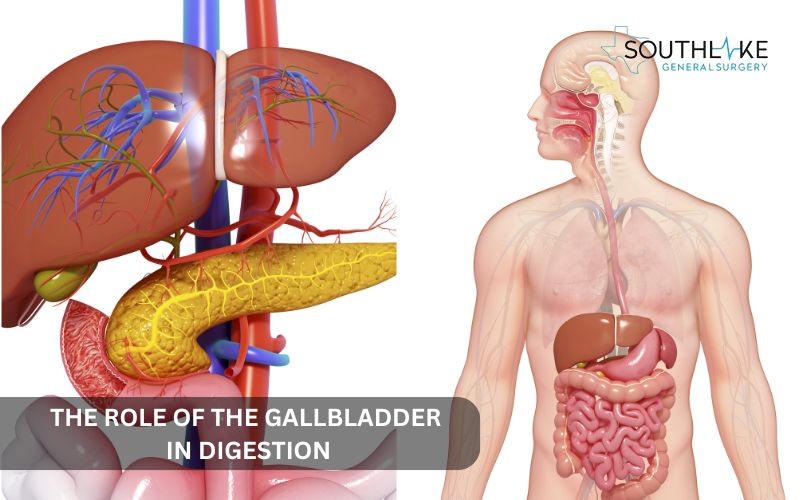
To facilitate digestion, the gallbladder is a necessary organ for fatty foods. When you enjoy a meal, your body gets to work by releasing stored bile to help break down fats in the small intestine. This detailed process includes:
How the Gallbladder Works:
- Contracts when fats enter the digestive system
- Releases bile through the bile duct
- Bile facilitates the emulsification of fats within the small intestine
- Facilitates digestive enzymes’ work
- Enables effective fat absorption
Understanding the Impacts of Gallbladder Failure:
- Difficulty processing fats
- Digestive issues arise
- Possibility of more significant health issues
How Gallbladder Issues Can Affect Your Health
Gallbladder problems can range from being a bit uncomfortable to quite serious. If left untreated, they may result in significant health concerns.
Many people deal with gallstones on a regular basis. They cause severe gallbladder pain that can spread to other parts of the body, including the back and shoulders.
- The natural flow of bile might be interrupted if the bile duct becomes clogged due to gallstones or swelling.
- Bile accumulation in the gallbladder can result in significant discomfort, including intense pain, nausea, and vomiting.
- When the gallbladder is quite inflamed or infected, a doctor may suggest gallbladder removal as a treatment option.
Your body can continue to work effectively even without a gallbladder, although you may want to make some dietary adjustments.
Seeking timely medical attention for diagnosis and treatment is crucial, as gallbladder issues can greatly affect your daily activities.
Identifying Common Gall Bladder Symptoms

Being aware of the early signs or symptoms of gall bladder issues is quite important! Taking swift action can help avoid bigger issues down the road.
While symptoms can differ from person to person, feeling discomfort after eating fatty foods might suggest there could be an issue with the gallbladder.
If you’re feeling a bit uneasy, it’s a great idea to reach out to your healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and the right care you need.
Recognizing issues early on is essential for keeping your gallbladder healthy and avoiding potential complications down the line.
Recognizing Early Signs of Gallbladder Problems
Is your body sending you signals about gallbladder trouble? Know the warning signals that are most often encountered:
Early Gall Bladder Symptoms to Watch For:
- Abdominal pain located in the upper right area, just beneath the ribs
- Dull ache or sharp, stabbing sensation
- Pain worsens after eating, especially fatty foods
- Nausea and vomiting
- Discomfort radiating to back, right shoulder, or chest
Red Flags: Seek Medical Attention Immediately
- Severe, persistent pain
- Fever
- Chills
- Yellowing of skin or eyes (jaundice)
- Sudden, intense pain in the abdomen or back
If you are noticing any of these symptoms, it is advisable to seek guidance from your healthcare provider. Effective management of gallbladder problems is possible with early diagnosis and treatment, which also reduces the risk of complications.
Decoding Abdominal Pain: Gallbladder vs. Other Issues
Abdominal pain can be a bit confusing but figuring out where it’s coming from is really important. Gallbladder pain has some unique features that set it apart:
Identifying Gallbladder Pain:
- Experiencing a sharp pain on the right side of the upper abdomen, which may be related to biliary colic
- May be induced by the consumption of meals rich in fats
- Could potentially spread to the right shoulder or back.
- Continue for several hours before gradually easing
What’s Behind Gallbladder Pain?
A temporary blockage in the cystic duct, which is often due to a gallstone, leads to this pain.
Don’t Self-Diagnose – Seek Expert Care
Although these signs might suggest gallbladder problems, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a precise diagnosis. There are various other causes of abdominal pain, including:
- Appendicitis
- Ulcers
- IBS
- Pancreatitis
Different treatments are necessary. Make certain you obtain appropriate care – seek advice from a healthcare provider for tailored recommendations.
Causes Behind Gallbladder Disorders
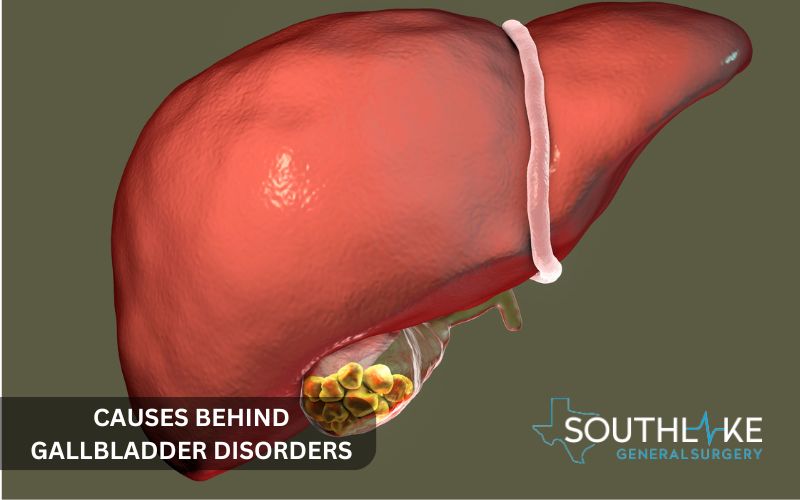
Multiple factors can influence the health of the gallbladder, such as the presence of gallstones and other contributing causes. Grasping these causes is important for preventing issues and finding the right care.
You can reduce your chance of gallbladder problems by optimizing your diet and maintaining a healthy weight. If you’re looking for personalized advice on prevention, it’s an ideal choice to reach out to a healthcare provider for support!
The Formation of Gallstones: A Primary Culprit
The common culprits behind gallbladder problems are gallstones. Let’s investigate their forms and available types:
Types of Gallstones:
- Cholesterol Stones: A buildup of cholesterol in the bile can cause the formation of stones, the size of which can range from a sand grain to a golf ball.
- Pigment Stones: Stones can form in the bile ducts because of excess bilirubin, which is typically caused by problems with the liver or blood.
The Risks:
- Asymptomatic or severe symptoms
- Gallstone attacks can cause significant discomfort when stones get stuck in the bile ducts
- There is a possibility of experiencing complications like infection or inflammation
Take Control of Your Gallbladder Health
Learning about how gallstones form and the associated risk factors helps you make better choices for your health. It’s beneficial to have a conversation with a healthcare professional about:
- Prevention strategies
- Risk assessment
- Early detection and treatment
By knowing the causes and types of gallstones, you can take proactive steps to safeguard your health.
Risk Factors for Developing Gallbladder Diseases
Anyone can develop gallstones, but there are certain risk factors that make it more likely. Take control of your gallbladder health by understanding these risks:
Gallstone Risk Factors:
- Family History: Genetic predisposition increases the probability
- Being overweight, especially around the abdomen
- Rapid weight loss affecting cholesterol levels
- Age: Risk increases after 40
- Gender: Gallstones more commonly occur in women
- Diet: High-fat, high-cholesterol, or low-fiber diet
- Health Conditions: Such as diabetes, liver disease, or the use of specific medications
Reduce Your Risk:
- Maintain a healthy weight by embracing a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity
- Enjoy foods that are rich in fiber and try to reduce your intake of saturated fats
- Stay hydrated and limit sugary drinks
- Manage stress and get regular check-ups
Take Proactive Steps:
Talk to your doctor about your specific needs if you’re concerned about any potential risks, such as a history in your family. Taking prompt action helps avoid:
- Serious complications
- Gallbladder damage
- Related health issues
Being informed about the potential risks and maintaining a healthy lifestyle will help protect the health of your gallbladder.
Diagnostic Approaches for Gallbladder Issues
To diagnose gallbladder issues, healthcare professionals will examine your body, talk about your symptoms, and perform some medical tests. Your physician will inquire about your medical background, dietary habits, and symptoms to gain a clearer insight into your condition.
Next, they might suggest some tests to help identify and evaluate how serious the issue is, ensuring you receive the right treatment. Noticing issues early on is essential for managing them well and avoiding any complications down the line.
Key Tests and Procedures for Accurate Diagnosis
Getting an accurate diagnosis is extremely crucial when you’re dealing with gallbladder symptoms. Healthcare providers often recommend imaging tests like:
- An abdominal ultrasound helps to see if there are gallstones or any inflammation present.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) for providing detailed images of the bile ducts
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) for detailed images of the bile ducts
Blood tests may reveal:
- Elevated liver enzymes indicate gallbladder issues
Your medical history, symptoms, and physical examination play a key role in choosing the right tests for you. To reach a definitive diagnosis, doctors might carry out:
- HIDA scan to assess gallbladder function
- Liver biopsy to rule out other conditions
These tests are really helpful in figuring out the best treatment plan, whether that means managing it with medication or considering gallbladder surgery.
When it comes to gallbladder issues, it’s critical to get medical help quickly so you may get an appropriate diagnosis.
Comprehensive Treatment Options for Gall bladder Symptoms
Treatment for gall bladder symptoms varies based on their severity and your specific needs. If gallstones aren’t causing any symptoms, you might not need to seek treatment right away.
If you start to notice any gall bladder symptoms, it’s usually a good idea to reach out for medical assistance.
There are several treatment options available, such as making lifestyle changes, taking medications, or, in more serious situations, undergoing surgery like gallbladder removal.
Non-Surgical Treatments and Their Effectiveness
For people who have gallbladder problems, there are non-surgical treatments that can help control their symptoms and stop further issues. Some medical treatment options could include:
- Pain relievers can be helpful in alleviating discomfort during gallbladder attacks.
- Antibiotics can be important to consider if there’s an infection present.
Making lifestyle changes is important, especially with your diet, for healthy gallbladder function. It is key to:
- Avoid fatty foods
- Eat more high-fiber foods
- Keep a healthy weight
- Drink enough water to stay hydrated
For many people, a gradual approach to weight loss can be a more helpful option. Rapid weight loss can raise the likelihood of forming gallstones.
The effectiveness of non-surgical treatments can differ from one individual to another. The seriousness of their condition also has an impact on this. Usually, these treatments are tried out first before considering more serious options.
When Surgery Becomes Necessary: Exploring Cholecystectomy
Although certain gallbladder problems might benefit from non-surgical treatment, others necessitate surgical intervention, referred to as cholecystectomy – the removal of the gallbladder.
This procedure is frequently advised for large gallstones that induce ongoing discomfort or do not adequately respond to alternative treatments.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a minimally invasive surgical technique that comes with many benefits compared to traditional open surgery.
This technique involves creating a few small incisions, allowing for the insertion of a laparoscope, which is a thin tube equipped with a camera and surgical instruments. This allows the surgeon to gently take out the gallbladder.
Advantages of Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy:
- Reduced post-operative pain
- Faster healing and recovery
- Smaller scars
- Quicker return to regular activities (usually within a few weeks)
- Long-lasting relief from gallbladder issues
Conclusion
Gall bladder symptoms can definitely raise some concerns. These might indicate concerns that require medical evaluation. Recognizing the signs, causes, and treatment options for gallbladder issues is essential for keeping your health in check!
If you are facing symptoms associated with gallstones or gallbladder inflammation, it is crucial to obtain a prompt diagnosis and suitable treatment. Various methods exist for addressing gallbladder concerns. Multiple options exist that can be either non-surgical or may involve a laparoscopic cholecystectomy, based on the particular situation.
If you’re experiencing persistent pain in your upper right abdomen or noticing sudden weight loss, it’s important to seek medical attention right away. Getting help early and making some lifestyle changes can really make a difference in how gallbladder disease turns out.
Paying attention to your body and your feelings is really important. If you’re noticing any gallbladder symptoms, it’s a great idea to reach out to a healthcare provider. They can offer personalized guidance to assist you in effectively managing your symptoms.
Make an Appointment
If you are noticing signs of gallbladder problems, it is important to seek professional evaluation without delay.
At Southlake General Surgery in Texas, USA, renowned specialist Dr. Valeria Simone, MD, delivers exceptional care for gallbladder issues. To schedule a consultation, call +1 (817) 748-0200.
Timely intervention and tailored support are essential for successful management. Feel free to get in touch – prioritize your well-being and schedule your appointment today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the initial indicators of gallbladder problems?
One of the initial signs of gallstones frequently manifests as severe pain in the upper right region of the abdomen. The discomfort could also be felt in the back or the right shoulder area. It frequently occurs after enjoying fatty foods or having a substantial meal.
Can lifestyle changes improve gallbladder health?
Absolutely! Making some adjustments to your lifestyle can really support your gallbladder in functioning more effectively. Maintaining a healthy weight, enjoying balanced meals, and staying active are all essential for overall well-being. Implementing these changes may lower the possibility of forming gallstones.
What can one expect during the recovery process following gallbladder surgery?
After laparoscopic surgery, recovery tends to be quicker. Usually, the recovery period spans from a few days to about a week. Following surgery, adhering to your surgeon’s postoperative care instructions is essential for optimal recovery. This entails adhering to prescribed activity limitations and attending your scheduled follow-up appointments.
Medically Reviewed By: Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Board-certified General Surgeon at Southlake General Surgery, Texas, USA.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
References:
- Ahmed A, Cheung RC, Keeffe EB. Management of gallstones and their complications. Am Fam Physician. 2000 Mar 15;61(6):1673-80, 1687-8. PMID: 10750875.
- Corazziari E, Shaffer EA, Hogan WJ, Sherman S, Toouli J. Functional disorders of the biliary tract and pancreas. Gut. 1999 Sep;45 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):II48-54. doi: 10.1136/gut.45.2008.ii48. PMID: 10457045; PMCID: PMC1766688.
- Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015 Aug 22;386(9995):743-800. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60692-4. Epub 2015 Jun 7. PMID: 26063472; PMCID: PMC4561509.
- Gouma DJ, Obertop H. Acute calculous cholecystitis. What is new in diagnosis and therapy? HPB Surg. 1992;6(2):69-78. doi: 10.1155/1992/46529. PMID: 1292590; PMCID: PMC2443024.
- Thijs C, Knipschild P. Oral contraceptives and the risk of gallbladder disease: a meta-analysis. Am J Public Health. 1993 Aug;83(8):1113-20. doi: 10.2105/ajph.83.8.1113. PMID: 8342719; PMCID: PMC1695167.
- Knab LM, Boller AM, Mahvi DM. Cholecystitis. Surg Clin North Am. 2014 Apr;94(2):455-70. doi: 10.1016/j.suc.2014.01.005. Epub 2014 Feb 18. PMID: 24679431.
- Makino I, Yamaguchi T, Sato N, Yasui T, Kita I. Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis mimicking gallbladder carcinoma with a false-positive result on fluorodeoxyglucose PET. World J Gastroenterol. 2009 Aug 7;15(29):3691-3. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.3691. PMID: 19653352; PMCID: PMC2721248.
- Luo X, Li W, Bird N, Chin SB, Hill NA, Johnson AG. On the mechanical behavior of the human biliary system. World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Mar 7;13(9):1384-92. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i9.1384. PMID: 17457970; PMCID: PMC4146923.