Groin pain can happen to anyone, and it’s essential to understand its causes to seek proper treatment sooner. Imagine going for a run and suddenly feeling a very sharp pain or nagging pain in the groin area, making each step unbearable.
This blog post will explore the most common symptoms and uncommon causes of groin pain, the diagnostic process, treatment options, and prevention tips. By understanding the reasons behind groin pain, you can take control of your health and well-being.
Short Summary
- Common causes of groin pain include muscle strain, hernias, and hip-related issues.
- Uncommon causes such as nerve irritation, infections, or rare conditions require a proper diagnosis for effective treatment plans.
- Seek medical help if the groin pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by additional symptoms. Regular exercise and preventive checkups are essential to reduce the risk of injury.
Common Causes of Groin Pain
Groin pain can be caused by various factors, including a groin injury such as muscle strain, hernias, and hip-related issues. Understanding the cause is crucial for proper treatment, as each condition may require a different approach.
But what exactly are these common causes, and how can they be distinguished from one another? Let’s take a closer look.
Muscle Strain
Muscle strain in the groin area, also known as a pulled groin muscle or groin strain, is common, especially among athletes. It occurs when one of the groin muscles or tendons in the groin region is overstretched or torn because of a sudden, twisting movement or change in direction.
This injury can also be referred to as a pulled groin muscle. Groin pulls or groin strain may present with immediate pain, a popping sensation, and lingering discomfort for days or weeks.
Most cases of pain in the groin or muscle strains can be treated with:
- Rest
- Ice
- Compression
- Anti-inflammatory medications
However, more severe groin strains may require physical therapy to help rebuild the groin and abdominal muscles and prevent future injuries.
It’s crucial to give the pulled groin adequate rest, as a pulled groin muscle can take anywhere from four to eight weeks to heal, with chronic strains potentially taking up to six months for recovery.
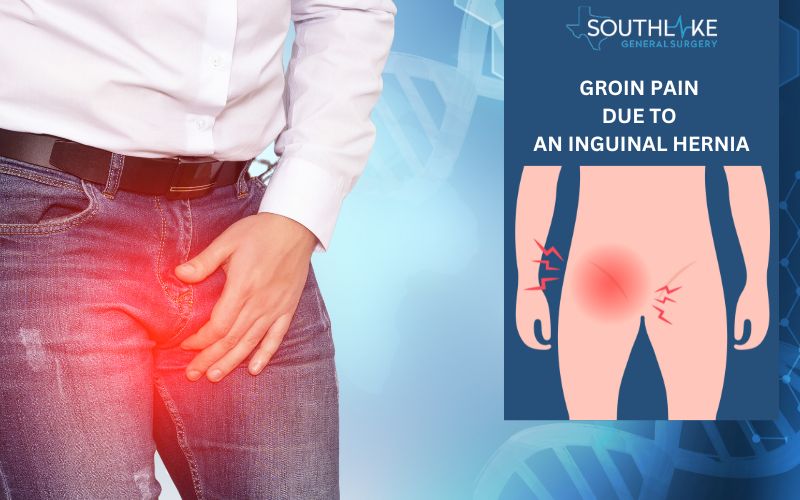
Inguinal Hernia
An inguinal hernia occurs when a part of the intestine or fatty tissue pushes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscle, causing a visible and palpable bulge in the lower abdomen, or groin area. Inguinal hernias experience pain and symptoms may include:
- A dull ache in the groin
- Burning pain
- A feeling of heaviness when standing
- In males, pain in the groin radiates toward the testicle or scrotum.
It is important to be aware of these and any additional inguinal hernia symptoms to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Inguinal hernias will not heal without treatment. In some cases, the inguinal hernias can cause a swollen or enlarged scrotum, which requires medical attention and possible surgical intervention.
Hernia repair surgery may be necessary to treat the condition, especially if there is a protrusion in the groin area or a noticeable lump.
Hip-Related Issues
Hip-related issues, such as arthritis or bursitis, can cause groin pain and may require a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and physical therapy. Pain can range from mild to severe, and a proper diagnosis is essential for determining the best course of treatment.
By addressing the underlying cause of the hip issue, the associated groin pain can be effectively managed, and the patient may not require surgery.
Uncommon Causes of Groin Pain
While muscle strains, hernias, and hip issues are common causes of groin pain, there are also less frequent causes that should not be ignored. In some cases, nerve irritation, infections, and rare conditions like tumors or ankylosing spondylitis may be the source of pain or sore pain in the groin.
In these instances, proper diagnosis is essential to ensure that the most effective treatment plan is put in place.
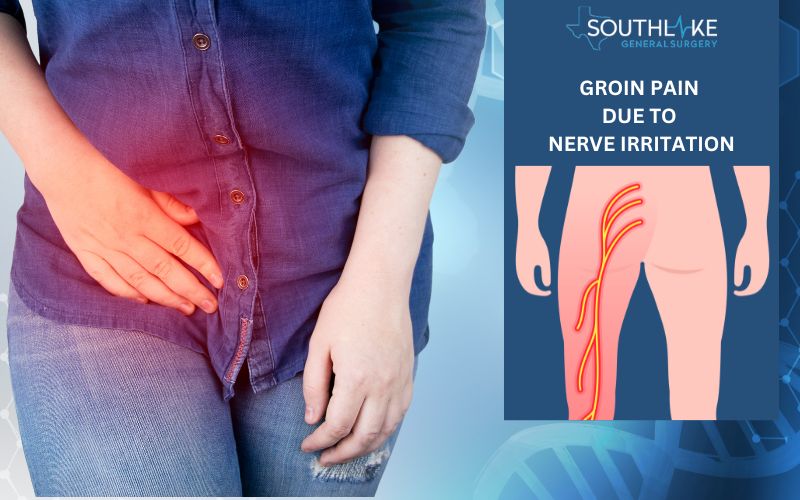
Nerve Irritation
Nerve irritation in the groin area, such as a pinched nerve, can cause pain or numbness, affecting one’s quality of life. This type of pain may be caused by certain abdominal conditions or a herniated disk compressing the nerve root.
Treatment for nerve irritation may include a local anesthetic injection to alleviate pain and discomfort.
Infections
Infections, such as abscesses or sexually transmitted diseases, can cause groin pain and may require antibiotics or other treatments as advised by a physician. Signs of an infection causing this medical condition may include:
- Swelling
- Redness
- Warmth
- Tenderness in the groin area
Prompt and accurate diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and alleviate pain.
Rare Conditions
Rare conditions like tumors or ankylosing spondylitis can cause this problem and require specialized care and treatment. These conditions may present with atypical symptoms and often necessitate a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate course of action.
Early diagnosis and intervention can improve outcomes and help manage pain effectively.
Diagnosing Groin Pain

Diagnosing groin pain involves a physical examination, imaging tests, and diagnostic injections to determine the cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Accurate diagnosis is critical for ensuring that the most effective treatment is prescribed and that any underlying conditions are addressed.
Let’s explore how each diagnostic method contributes to understanding and treating this condition.
Physical Examination
A healthcare provider will perform a physical examination to assess the groin area and identify any abnormalities or potential causes of pain. This examination includes:
- Observation
- Palpation
- Percussion
- Auscultation
These techniques help the provider detect any tenderness, swelling, or other irregularities in the groin area.
The findings of a physical examination can provide valuable insight into potential sources of pain and guide further diagnostic testing and treatment.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests, such as:
- X-rays
- ultrasounds
- CT scans
- MRIs
Can help identify the cause of groin pain and guide treatment decisions. For example, X-rays can assess the severity of cartilage damage in hip osteoarthritis, while CT scans can diagnose conditions like kidney stones.
Ultrasounds can be utilized to identify groin pain associated with testicles or an inguinal hernia. These imaging tests provide valuable information to healthcare providers, allowing them to make informed treatment decisions.
Diagnostic Injections
Diagnostic injections, like lidocaine, can help pinpoint the source of pain and determine the most effective treatment approach. By administering an anesthetic agent to the affected area, healthcare providers can identify the precise source of pain and devise a customized treatment plan.
If the pain subsides temporarily after a diagnostic injection, it is likely that the source of the pain is in the area where the anesthetic was injected.
Treatment Options for Groin Pain

Treatment options for groin pain vary depending on the cause and may include:
- Lifestyle changes
- Medications
- Physical therapy
- Surgery
Both a muscle strain and a hernia can cause pain and soreness in the groin area. Understanding the underlying cause of the pain is essential for choosing the most effective treatment.
Let’s explore the various treatment options available and how they can help alleviate groin pain and improve overall health.
Lifestyle and Self-Care
Self-care measures, such as rest, ice, and compression, can help alleviate certain types of groin pain, like muscle strains and minor injuries. However, more severe cases may require medical intervention, such as physical therapy or surgical treatment.
It’s important to listen to your body and consult a healthcare provider if self-care measures do not provide the desired relief or if the pain is particularly severe. A sore groin should not be ignored.
Medications
Medications, including over-the-counter pain relievers like Tylenol (acetaminophen) and Advil (ibuprofen), can help manage pain and inflammation associated with groin pain.
In more severe cases, prescription medications or stronger pain medications, such as opioids, may be necessary to control the pain.
Corticosteroids and anesthetic injections can also be used to alleviate pain and inflammation in certain cases.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can help strengthen groin muscles further, improve range of motion, and address underlying issues contributing to groin pain.
Working with a physical therapist, patients can engage in exercises, stretches, lifting weights, and other therapeutic modalities to improve their condition and prevent future injuries.
In cases where surgery is necessary, physical therapy can also play a crucial role in postoperative recovery, helping patients regain strength and function.
Surgery (Laparoscopic surgery or Open Surgery)
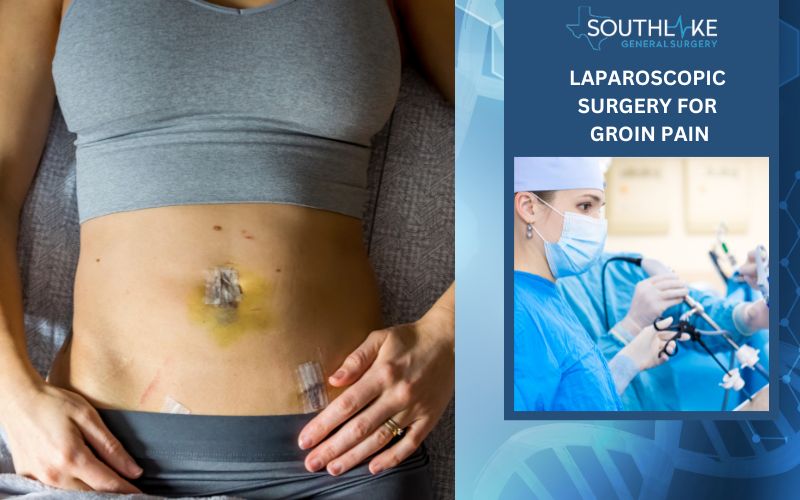
Surgery may be necessary for conditions like hernias or severe hip problems, requiring either laparoscopic or open surgery, such as hernia surgery.
Laparoscopic surgery is the most common surgical procedure, also known as a minimally invasive surgical technique that utilizes small incisions and a laparoscope to perform procedures within the abdominal and pelvic regions. This type of hernia surgery is less invasive than open hernia repair surgery, necessitating smaller incisions and a shorter recovery period.
On the other hand, open hernia repair surgery necessitates larger incisions and a longer recovery period. Both laparoscopic and open surgery may be used to address conditions such as hernias, endometriosis, and severe hip issues, depending on the specific case and the surgeon’s expertise.
It’s important to discuss your options with your healthcare provider and choose the best surgical approach for your condition.
Board-Certified General Surgeon Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Dr. Valeria Simone MD, a board-certified general surgeon, specializes in diagnosing and treating groin pain, hernia repair and offers customized treatment plans. With her expertise in laparoscopic and open hernia repair surgery, Dr. Simone can help you identify the cause of your groin pain and develop a personalized approach to treatment.
By working with an experienced surgeon like Dr. Simone, you can ensure that you receive the highest quality care and achieve the best possible outcome.
Preventing Groin Pain

Preventing groin pain involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, exercising regularly, and seeking routine medical check-ups. By making healthy choices and engaging in moderate physical activity, you can reduce the risk of groin pain and promote overall well-being.
In addition, regular medical check-ups can help detect and address any potential medical issues before they become more serious complications.
Tips from Dr. Valeria Simone MD
Dr. Valeria Simone MD offers tips for preventing groin pain, including proper stretching, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding heavy lifting. To reduce the risk of injury, it is important to warm up adequately before physical activity, practice stretching exercises regularly, and wear shoes with adequate support that fit properly.
Strengthening core muscles and maintaining a healthy weight can also help prevent groin pain and support overall health.
When to Seek Medical Help for Groin Pain
Seek medical help for groin pain if:
- It is severe, persistent, or accompanied by additional symptoms such as testicular pain, swelling, or potential hernia complications.
- Self-care measures do not provide relief.
- The pain is particularly severe.
Don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and treatment.
Early diagnosis and intervention can improve outcomes and help manage pain effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, groin pain can be caused by various factors, both common and uncommon. Understanding the cause is essential for proper diagnosis and effective treatment.
By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, exercising regularly, and seeking medical help when needed, you can take control of your health and prevent or manage this condition. Don’t let this condition hold you back – take the necessary steps to ensure a pain-free and active life.
Appointment
Schedule an appointment with a healthcare provider to discuss your groin pain, receive a proper diagnosis, and develop a personalized treatment plan.
By working with a professional, you can ensure that the most effective treatment is prescribed and that any underlying conditions are addressed.
Don’t wait – take control of your health and well-being by scheduling an appointment today at. Please contact our healthcare expert today at +1(817) 748-0200.
Follow us on Facebook and YouTube.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. When should I worry about groin pain?
If you have severe groin pain, swelling, or a lump around your testicle, or mild testicle pain lasting longer than a few days, it is important to schedule an appointment with your doctor.
Even if the pain improves with home treatment, if it does not get better within a few days, you should seek medical attention.
2. How do you relieve groin pain?
To relieve groin pain, rest the area and apply ice for 15-30 minutes, 2-4 times a day. Use an elastic wrap to support the area and take anti-inflammatory painkillers as needed.
Avoid any activity causing pain, and temporarily stop participation in any physical activity.
3. What causes pain in the inner thigh near the groin?
Pain in the inner thigh muscles and groin can be caused by a pulled muscle, hernia, kidney stone, or osteoarthritis. Treatments can include resting, applying warm or cool compresses, and home remedies.
In some cases, medical treatment may also be required.
4. What does an inflamed groin feel like?
An inflamed groin may cause a feeling of pressure or fullness in the lower abdomen, tenderness experiencing pain when squeezing the legs together, a lump on one side of the groin (or both), and possibly swelling or bruising in the area.
You may also experience pain when raising the knee of the injured side, and if it is a bad strain, you may walk with a limp while it heals.
5. What can cause groin pain in males?
Groin pain in males can often be caused by hernias, a pulled muscle, ligaments, or tendons, or an injury or disease affecting the hip joint. Trauma from direct or indirect contact can also be a source of pain.
6. Is groin pain caused by a hernia?
Yes, groin pain can indeed be caused by a hernia. A hernia occurs when an organ or fatty tissue pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue.
In the case of an inguinal hernia, it’s the intestines pushing through the abdominal wall, leading to a lump in the groin area. This can result in groin pain caused by the protruding tissue, especially when coughing, bending over, or lifting heavy objects. This indicates a hernia rather than a pulled groin.